- A team of researchers from IRB Barcelona and CNAG identifies the IL-17 protein as a determining factor in skin ageing. Local IL-17 orchestrates skin aging.
- Blocking the function of IL-17 reduces the pro-inflammatory state and delays the appearance of age-related features in the skin, including hair follicle growth.
- Published in the journal Nature Aging, the work opens up new perspectives in the development of therapies to improve skin ageing health.
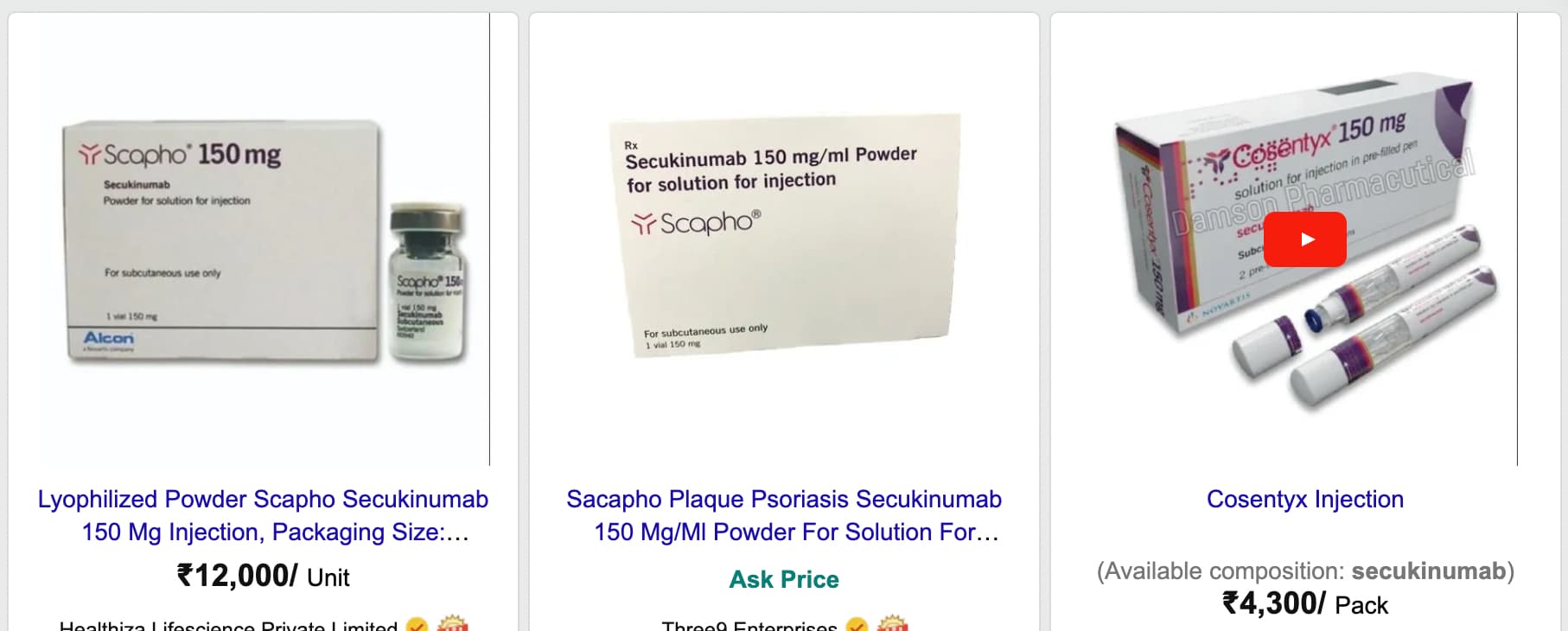
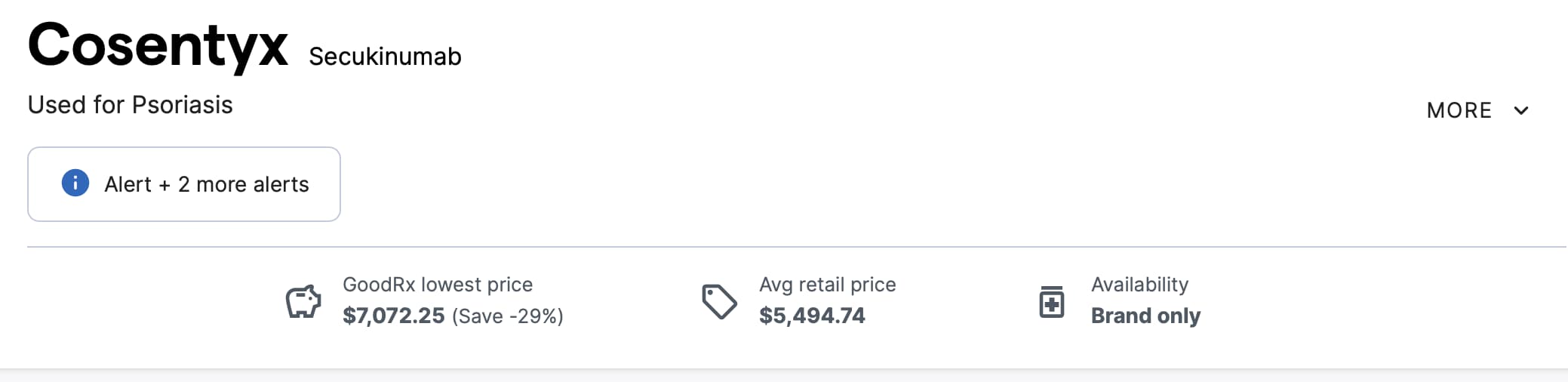
- There are numerous FDA-approved drugs already on the market that inhibit IL-17 (they are used for treatment of psoriasis).
Reversing the symptoms of ageing in skin
Previous studies had described that IL-17 is related to some autoimmune skin diseases, such as psoriasis, and there are existing treatments that block this protein. The team of researchers studied the response of various aspects to blocking IL-17 activity, including hair follicle growth, transepidermal water loss, wound healing, and genetic markers of ageing. These four parameters showed an improvement after treatment, as the acquisition of these ageing traits was significantly delayed.
“IL-17 protein is essential for vital body functions, such as defense against microbes and wound healing, so permanently blocking it would not be an option. What we have observed is that its temporary inhibition offers benefits that could be of interest at a therapeutic level,” says Dr. Guiomar Solanas, associate researcher at IRB Barcelona.
Future work by the researchers will focus on clarifying the ageing processes that are related to inflammatory states in the skin and how these are linked to IL-17. The team will also address whether IL-17 is involved in the ageing and deterioration of other tissues and organs.
Read the research Summary Press Release Here:
Full Research Paper (open access)
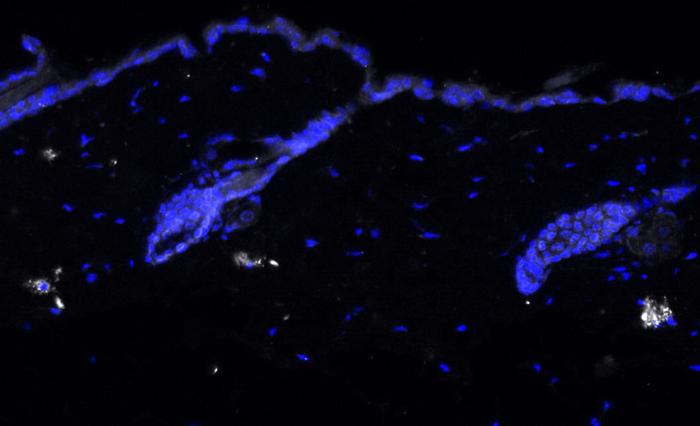
Targeting lymphoid-derived IL-17 signaling to delay skin aging
Skin aging is characterized by structural and functional changes that contribute to age-associated frailty. This probably depends on synergy between alterations in the local niche and stem cell-intrinsic changes, underscored by proinflammatory microenvironments that drive pleotropic changes. The nature of these age-associated inflammatory cues, or how they affect tissue aging, is unknown. Based on single-cell RNA sequencing of the dermal compartment of mouse skin, we show a skew towards an IL-17-expressing phenotype of T helper cells, γδ T cells and innate lymphoid cells in aged skin. Importantly, in vivo blockade of IL-17 signaling during aging reduces the proinflammatory state of the skin, delaying the appearance of age-related traits. Mechanistically, aberrant IL-17 signals through NF-κB in epidermal cells to impair homeostatic functions while promoting an inflammatory state. Our results indicate that aged skin shows signs of chronic inflammation and that increased IL-17 signaling could be targeted to prevent age-associated skin ailments.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-023-00431-z
See Full Discussion on this News topic here: IL-17 Protein Plays an Important Role in Skin Aging, FDA Approved Therapies Available