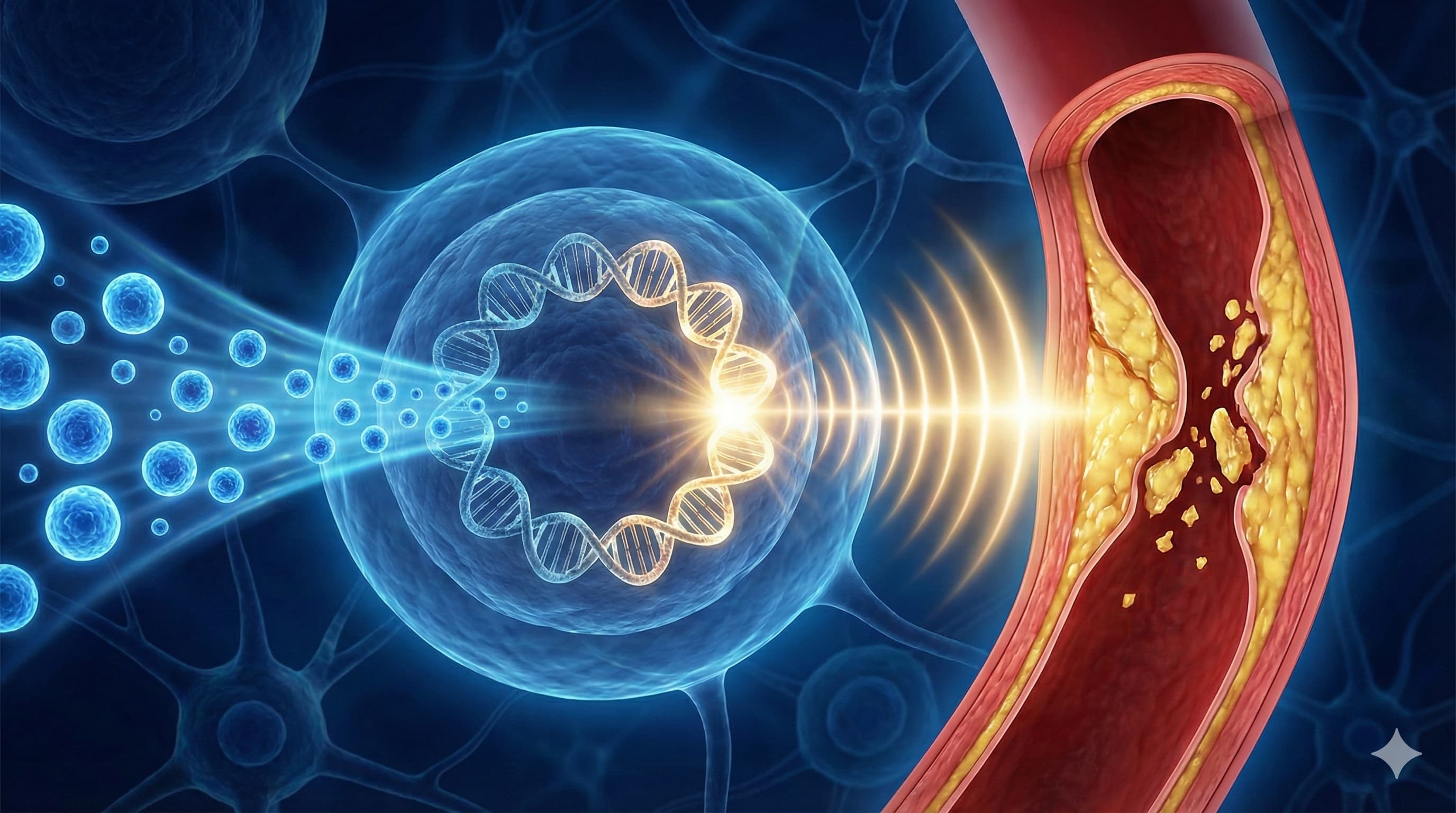
In a significant study from Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University (China), published in the journal Redox Biology, researchers have uncovered a potent anti-aging mechanism of melatonin that goes far beyond sleep. We have long known that atherosclerotic plaques—the fatty deposits that cause heart attacks—become deadly when they become “unstable” and rupture. This instability is largely driven by the cellular senescence (aging) of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMCs) which normally form a protective cap over the plaque.
The “Big Idea” here is that melatonin acts as a specific molecular key that unlocks SIRT6, a member of the sirtuin family often dubbed the “longevity gene.” By binding to membrane receptors on the surface of blood vessel cells, melatonin triggers a signaling cascade that upregulates SIRT6. This, in turn, activates Nrf2, the body’s master antioxidant defense system. The result? Senescent cells are rejuvenated, oxidative stress is crushed, and the fibrous caps of atherosclerotic plaques thicken and stabilize, drastically reducing the risk of rupture. This study moves melatonin from the “sleep aid” drawer to the “cardiovascular longevity” shelf, albeit at doses that challenge standard protocols.
Source:
- Open Access Paper: Melatonin attenuates atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability through SIRT6-dependent regulation of vascular smooth muscle cells senescence
- Impact Evaluation: The impact score of Redox Biology is 11.9 (2024 JIF), evaluated against a typical high-end range of 0–10+ for specialized biology journals. Therefore, this is an Elite impact journal, ranking in the top quartile (Q1) of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology.
The Biohacker Analysis
Study Design Specifications
- Type: In vivo (Murine model) & In vitro (Primary VSMCs).
-
Subjects: Male ApoE-/- mice (standard atherosclerosis model).
- N-number: ~8 per group.
- Groups: Vehicle, Melatonin (Mel), Melatonin + Receptor Antagonist (Luzindole), SIRT6-Knockdown variations.
- Treatment Duration: 8 weeks.
- Lifespan Data: Not applicable (Study focused on plaque morphology, not organismal lifespan).
Mechanistic Deep Dive
The study establishes a clear, linear pathway for plaque stabilization:
- Trigger: Melatonin binds to MT1/MT2 membrane receptors (specifically MT2 is implicated via Luzindole blocking).
- Transducer: This binding upregulates SIRT6 transcription and protein expression.
- Effector: SIRT6 deacetylates or otherwise activates Nrf2 (Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2).
- Outcome: Nrf2 drives the expression of antioxidant enzymes, suppressing ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species).
- Phenotype: Reduction in p16/p21 (senescence markers) and SASP (Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype) factors like IL-1β and MMP-2. The fibrous cap thickens, preventing plaque rupture.
Organ-Specific Aging Priority: Vascular System (specifically Carotid Arteries).
Novelty
We knew melatonin was an antioxidant, and we knew SIRT6 was atheroprotective. The novelty is the direct causal link: Melatonin requires the MT Receptor → SIRT6 axis to stabilize plaques. Knocking down SIRT6 completely nullified melatonin’s benefits, proving SIRT6 is the indispensable middleman in this longevity pathway.
Critical Limitations
- Murine Biology: ApoE-/- mice are hyperlipidemic by design; their plaque dynamics differ slightly from human slow-progressing atherosclerosis.
- Short Duration: 8 weeks is insufficient to assess long-term desensitization of melatonin receptors or potential hormonal downregulation (e.g., endogenous testosterone/estrogen axes).
- Supraphysiological Dosing: The benefits were seen at massive relative doses (see Translational Protocol below). It is unclear if standard human supplementation (1–5 mg) achieves the tissue saturation needed to trigger this SIRT6 response in arteries.
Actionable Intelligence
The Translational Protocol
-
Human Equivalent Dose (HED):
- Animal Dose: 20 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal).
- Conversion Formula: Human HED (mg/kg) = Animal Dose (mg/kg) × (Animal Km / Human Km) = 20×(3/37)≈1.62 mg/kg.
- The Math: For a 75 kg (165 lb) adult, the dose is ~121 mg/day.
- Context: This is 24x the standard 5 mg sleep dose. This places the protocol in the “High-Dose Melatonin” (HDM) territory often used in oncology or ALS trials, not standard biohacking.
-
Pharmacokinetics (PK/PD):
- Bioavailability: Oral melatonin bioavailability is low (~3–15%) due to extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism. The study used injection (i.p.), which bypasses this. To mimic i.p. levels, an oral dose might need to be even higher (potentially 200–300 mg), or administered via transdermal/sublingual/rectal routes to bypass the liver.
- Half-life: Short (~20–45 minutes). Sustained Release (SR) formulations or split dosing (morning/night) may be required for continuous SIRT6 activation, though melatonin is typically strictly circadian.
Safety & Toxicity Check
- NOAEL/LD50: Melatonin has an incredibly high safety profile. Human studies have administered 1,000 mg/dayfor weeks with no acute toxicity. The LD50 in animals is often unreachable.
-
Adverse Effects:
- Drowsiness: The most obvious barrier to daytime dosing.
- Desensitization: Chronic supraphysiological dosing may desensitize receptors, though data is conflicting.
- Hormonal: Potential minor suppression of LH/FSH (gonadal axis) at extremely high doses, though rarely clinically significant in adults.
Biomarker Verification Panel
-
Efficacy Markers:
- hs-CRP: Expect reduction (anti-inflammatory).
- Oxidized LDL (OxLDL): Should decrease via Nrf2 activation.
- CIMT (Carotid Intima-Media Thickness): The direct clinical correlate to the mouse findings. Measurable via ultrasound.
-
Safety Monitoring:
- Liver Enzymes (ALT/AST): Rare toxicity, but necessary for high-dose protocols.
- Thyroid Panel: Melatonin interacts with thyroid function; monitor TSH.
Feasibility & ROI
- Cost: Very Low. Melatonin is a commodity supplement. Even 100 mg/day costs <$30/month.
- ROI: High. If it replicates 50% of the plaque stabilizing effect, it rivals statins/PCSK9 inhibitors for plaque morphology improvement at a fraction of the cost.
Population Applicability
-
Contraindications:
- Autoimmune Diseases: Melatonin stimulates Th1 immune responses (via IL-2, IL-12) and may exacerbate Rheumatoid Arthritis or Lupus.
- Pregnancy/Trying to Conceive: Potential interference with ovulation at high doses.