Thanks for working this out.
I think I’ll just try fatty15 for once. Maybe this is the thing that could significantly help.
And berberine. There’s a LITTLE bit of research on it and LDL tho it probably isnt the high quality studies
https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/jmf.2019.0088
there are berberine gummies on amazon i just ordered (EDIT OH THEY MIGHT BE COUNTERFEIT) damnit I have to just try the non tasty ones from known brands
Here are some pricing I’ve recently gotten in a quote from India:
Ezetimibe 10mg, 300 Tablets total
• Zydus or,
• Sun Pharmaceutical Ezentia
10 tablet price is 180 (approx. $2.20 US per strip of 10 tablets)
total 180*30=5400 rupees
Bempedoic Acid Tablets, 180 mg - 300 tablets
• Zydus Bemdac 180mg
10 tablet price 250 (approx. $3.00 for 10 tablets strip)
totl 250*30=7500 rupees
Zydus Colchicindon 0.5 mg Tablets - 100 tablets
colchicine
10 tablet price 27 (Approx. $0.32 for 10 tablets)
total 27*10=270 rupees
Ive been taking blue brillo for 1.5 weeks now, the blueness feels a bit sketch
Statins are associated with decrease rates of low mood. I didn’t find any such side effect on the bempedoic acid trial.
People like the one in the first video make me so angry. They are not only spreading, in my view, false but also extremely dangerous information. I don’t think they care about anyone.
Got a lipids test on Monday, the day after 2nd day of foresight vision weekend (which meant LOADS of cauliflower that day). haven’t taken rapamycin in 3-4 weeks…
ApoB was 89. Which is an ok value. Less scary than earlier this year.
I was taking a lot of nexlizet up to one week ago (imported) so I need to do a retest when my break period from it is longer… still waiting for the particle sizes test. This will be really important for determining if that imported nexlizet actually works…
[
Apolipoprotein B and Non-HDL Cholesterol Better Reflect …
[image]
ScienceDirect.com
https://www.sciencedirect.com › science › article › pii
](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0735109721001911)
by CDL Johannesen · 2021 · Cited by 236 — The median values for apoB, non-HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol were 92 mg/dl, 3.1 mmol/l (120 mg/dl), and 2.3 mmol/l (89 mg/dl), …
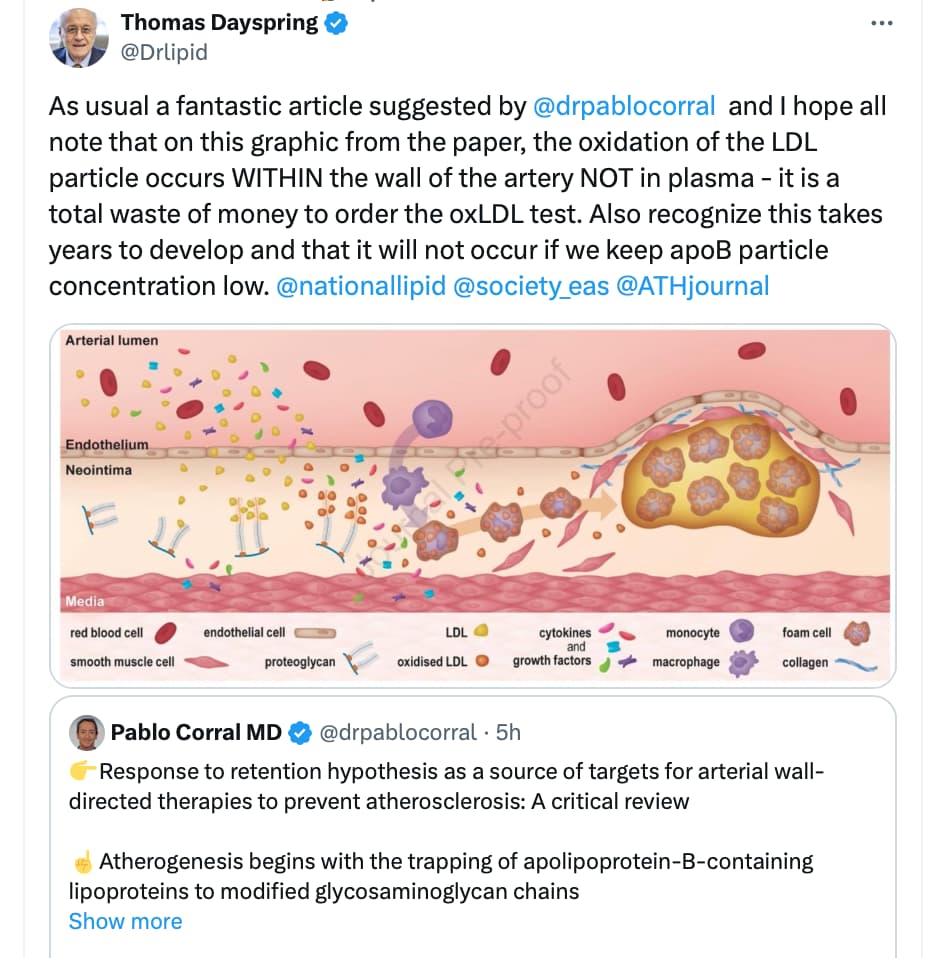
You’re building permanent atherosclerotic plaque in your arteries at that level still.
I know, it’s not ideal, but it’s better than the scary values earlier this year. B/c I’m taking off-label nexlizet I need to figure out if it actually is nexlizet… [and it has so much blue that the blue alone makes me averse, though REAL nexlizet in the states also has blue food coloring that’s sketch…]
met with one of the ppl from reason’s startup at foresight, he mentioned a lot about intracellular “free cholesterol” plaque and cholesterl transport to the bile.
oh, and drinking crazy high amounts of green tea might help reduce oxidation though i don’t know how much is actually needed.
Why not statins as well? Can’t you check your desmosterol levels with EmpowerDX (to not get too low desmosterol… 0.8 mg/dl for E4, 1 mg/dl for the rest).
Hm good idea I should, though do intracellular hepatic levels of it correlate with levels in the bloodstream?
Statins have many other problematic effects (as I pointed out in the GG/Cooenzyme Q thread)…
Statins inhibit HMGCR in all tissues, but the brain is most important in the scenario of brain transplants into brainless clones. So making sure synthesis in brain isn’t inhibited too much could be important (why we can measure serum desmosterol, highly correlated with CSF levels, and desmosterol is used primarily in the brain). Lower desmosterol assosciated with MCI and AD.
Any other possible side effects (muscle pains, liver inflammation (elevated LFT’s), insulin resistance) are most important. Anything else don’t matter as they improve all-cause mortality from their potent apoB lowering effect and a little bit from decreasing CRP. Don’t matter in the sense there is a net benefit. At least in high risk patients, but you determine what the lowering in apoB is worth to you.
Overall anti-aging via prevention of apoB causing disease in brain and heart, plaque, reduction inflammation. If you get no side effects which is the case for the vast majority of people.
Ok this is good advice! I was precisely worried about the brain cholesterol synthesis which is why I stopped taking statins.
Yeah I’m aware most people don’t feel terribly from statins, but I already am not the most energetic person and I don’t want to risk it further.
Cardiovascular Health
The circulatory system, also known as the cardiovascular system (CVS), is a vast network of organs and vessels that are responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients, oxygen, other gases, and hormones to and from cells. Without the circulatory system, the body would not be able to fight disease or maintain a stable internal environment like a proper temperature and pH, referred to as homeostasis. The cardiovascular system is made up of three independent systems that work together: the heart (cardiovascular), lungs (pulmonary) and arteries, veins, coronary and portal vessels (systemic).
Cholesterol & Triglycerides
-
- CHOLESTEROL, TOTAL
(mg/dL)
-
- 162
Dec 2024
* <small>Range: <200</small>
-
- TRIGLYCERIDES
(mg/dL)
-
- 79
Dec 2024
* <small>Range: <150</small>
-
- CHOL/HDLC RATIO
(calc)
-
- 2.9
Dec 2024
* <small>Range: <5.0</small>
-
- NON HDL CHOLESTEROL
(mg/dL (calc))
-
- 107
Dec 2024
* <small>Range: <130</small>
HDL Particles
High density lipoprotein (HDL) particles are often referred to as good cholesterol, because they are associated with a decreased risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
-
- HDL LARGE
(nmol/L)
-
- 5387 L
Jun 2024
* <small>Range: >6729</small>
-
- HDL CHOLESTEROL
(mg/dL)
-
- 55
Dec 2024
* <small>Range: >39</small>
LDL Particles
Low-density lipoprotein particle (LDL-P) testing evaluates LDL particles according to their number, size, density, and/or electrical charge. Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) are particles that transport lipids throughout the body. Each particle contains a combination of protein, cholesterol, triglyceride, and phospholipid molecules. Their composition changes as they circulate in the blood. Some molecules are removed and others are added, resulting in lipoprotein particles whose properties vary from large and fluffy to small and dense. LDL particle testing determines the relative amounts of particles of differing properties. Traditional lipid testing measures the amount of LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) present in the blood, but it does not evaluate the number of particles of LDL (LDL-P). Some studies have shown that increased numbers of small dense LDL particles are more likely to cause atherosclerosis than fewer light, fluffy LDL particles. An increased number of small, dense LDL could be one of the reasons that some people have heart attacks even though their total and LDL cholesterol concentrations are not particularly high."
-
- LIPOPROTEIN (a)
(nmol/L)
-
- 16
Jun 2024
* <small>Range: <75</small>
-
- LDL PARTICLE NUMBER
(nmol/L)
-
- 1954 H
Jun 2024
* <small>Range: <1138</small>
-
- LDL SMALL
(nmol/L)
-
- 357 H
Jun 2024
* <small>Range: <142</small>
-
- LDL MEDIUM
(nmol/L)
-
- 343 H
Jun 2024
* <small>Range: <215</small>
-
- LDL PATTERN
(Pattern)
-
- B A
Jun 2024
* <small>Range: A</small>
-
- LDL PEAK SIZE
(Angstrom)
-
- 215.6 L
Jun 2024
* <small>Range: >222.9</small>
-
- LDL-CHOLESTEROL
(mg/dL (calc))
-
- 90
Dec 2024
* <small>Range: <100</small>
-
- APOLIPOPROTEIN B
(mg/dL)
-
- 89
Dec 2024
* <small>Range: See Comments</small>
Muscle side effects are temporary and stop after cessation, and the dose-response relationship is non-linear, so even the smallest dose of the lowest one available has very high efficacy, decreasing side effects.
If you monitor desmosterol you should be fine on the brain side. If you don’t want to try any of the half a dozen or so of statins, there is always PCSK9 inhibitors, or maybe next year obicetrapib which would be less expensive.
If you can monitor desmosterol, there is no reason to start with any other one… Peter Attia always uses statins first if tolerated. So much data with statins. Quite little with bempedoic acid, and ezetimibe in comparison.
In the meantime, I’m developing a better taste for large amounts of garlic+ginger - this will help
Several garlic-derived organosulfur compounds, including diallyl disulfide and trisulfide and 2-propenethiol, prevent cholesterol synthesis in cell cultures by inhibiting lanosterol 4α-methyl oxidase. Diallyl disulfide was active at a level of 15 μmol L−1, while the other compounds were somewhat less active. S -Allylcysteine was only active at much higher millimolar concentrations (Singh, 2006). Earlier studies implicated ajoene and allicin as inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis (Ferri, 2003; Gebhardt, 1996). Allicin has been suggested to affect atherosclerosis not only by acting as an antioxidant, but also by modifying lipoproteins and inhibiting LDL uptake and degradation by macrophages (Gonen, 2005).
The trial showed that there were no statistically significant effects of the three forms of garlic on LDL-C concentrations. The six-month mean changes in LDL-C concentrations for raw garlic, powdered supplement, aged extract supplement, and placebo were +0.4 mg dL−1, +3.2 mg dL−1, +0.2 mg dL−1 and −3.9 mg dL−1, respectively. There were no statistically significant short-term or longer-term effects on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglyceride levels or total-cholesterol : HDL-C ratio. It was concluded that none of the forms of garlic used in the study, including raw garlic, when given at an approximate dose of a 4 g clove per day, six days per week, for six months, had statistically or clinically significant effects on LDL-C or other plasma lipid concentrations in adults with moderate hypercholesterolemia. Based on the results of these and other recent trials, it was concluded that physicians can advise patients with moderately elevated LDL-C concentrations that garlic supplements or dietary garlic in reasonable doses are unlikely to produce lipid benefits (Gardner, 2007).
A review of garlic and CVD by European experts states: “The investigations within the [European] Garlic & Health project as well as the majority of independent studies provided compelling evidence against a beneficial influence of garlic powders or garlic constituents on risk factors and pathological aspects of cardiovascular disease in animals and humans” (Espirito Santo, 2007). Reviews of statin alternatives in cardiovascular therapies and a meta-analysis of garlic supplementation and serum cholesterol by authors from Asia reach similar conclusions. These reviews conclude: “The negative result from the Stanford study, together with the absence of any evidence of clinical event reduction, means that at present garlic treatment can not be recommended for hyperlipidemia or for patients at risk of cardiovascular events” (Ong, 2008) and “the available evidence from randomized controlled trials does not demonstate any beneficial effect of garlic on serum cholesterol” (Khoo, 2009).
The Stanford trial did not specifically test garlic preparations containing distilled garlic oil or ajoene from garlic macerates. Ajoene, given at a dosage of 100 mg kg−1 (“polar fraction of garlic oil”) to rats made hyperlipidemic by feeding them coconut oil and 2% cholesterol, was reported to counteract the effects of the dietary lipids (Augusti, 2005). However, this level of ajoene used with rats corresponds to 7.5 g of pure ajoene for a 75 kg human, substantially higher than the doses recommended by supplement manufacturers and the levels of garlic products (13–15 mg allicin) used in the Stanford trial. Indeed, using a typical concentration of 0.1 mg g−1 ajoene in oil-macerate, 75 kg of oil-macerate, equal to the weight of a human, would have to be consumed! The majority of earlier clinical trials employing steam-distilled garlic oil with both normolipidemic and hyperlipidemic subjects showed, at best, small effects on serum cholesterol levels after 12 weeks; the studies showing small effects can be faulted for lacking diet control (Barrie, 1987).
BUT
The researcher, using fresh garlic homogenates, found evidence of liver damage after use of garlic for periods up to 21 days at levels ≥0.5 g of garlic per kg of body weight. They concluded that, based on a rat model, only daily doses of garlic ≤0.25 g kg−1 body weight (≤19 g or ∼five cloves for an adult weighing 150 lbs or 75 kg) are without harmful effects on the liver. They also note that for doses as low as 0.1 g kg−1 body weight, given daily for 28 days, there was significant deterioration in liver function tests (Rana, 2006). With rats given 2 g kg−1 fresh garlic, 55% mortality was observed after 15 days (Banerjee, 2002a). It should be noted that the average consumption of garlic, from all sources, in the United States is 4.2 grams per day, or slightly more than one clove (Lucier, 2000).
==
hm yeah, garlic is also stronger than ginger
What are the benefits of supplementing with powdered garlic? And for any purported benefits, can those only be obtained by combining powdered garlic with something else?