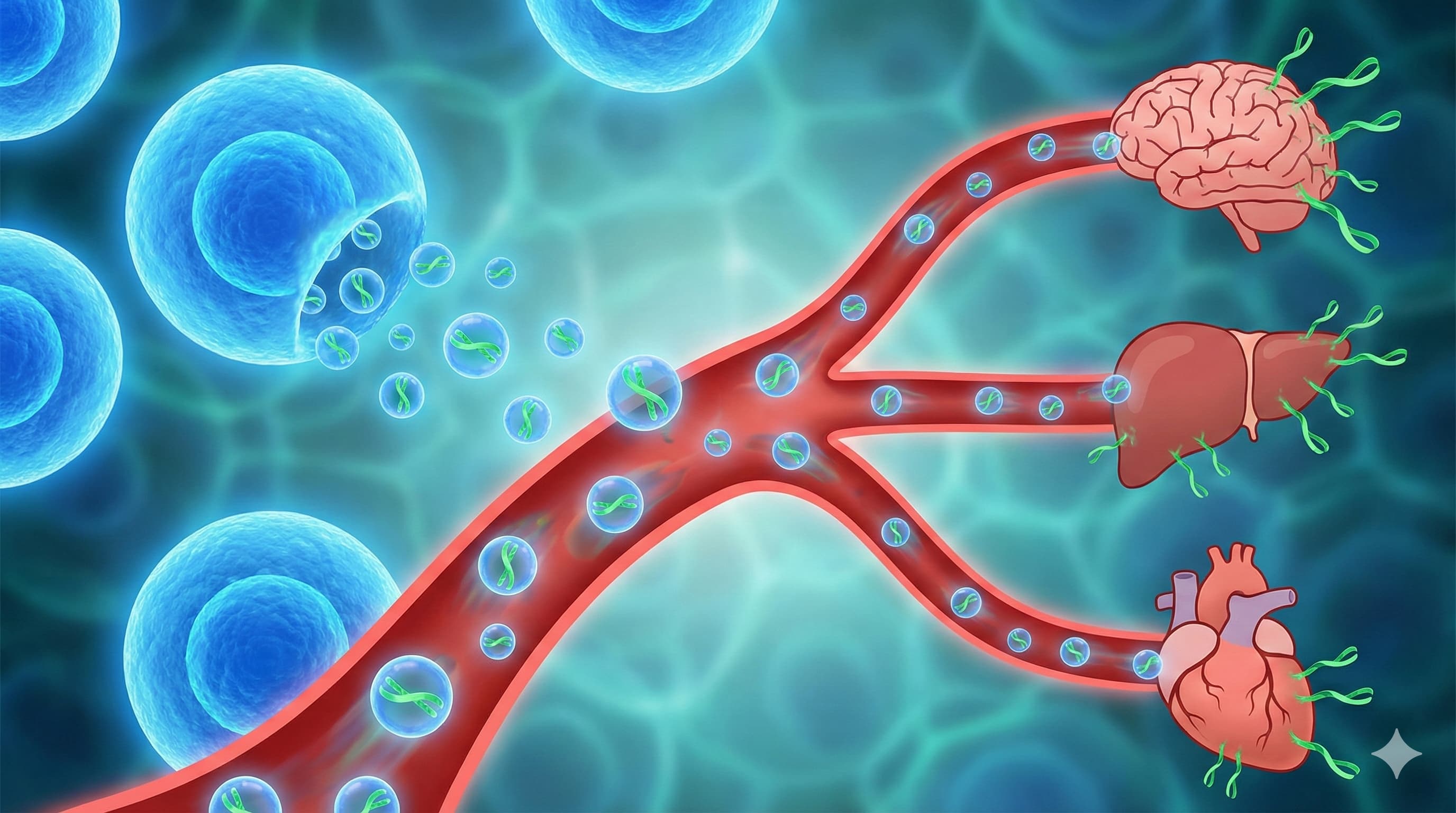
A research team led by Prof. Alessio Lanna (CEO of Sentcell) has released a provocative manuscript describing a new “fluid” organ of the immune system: “Telomere Rivers.” Building on their previous discovery that antigen-presenting cells (APCs) donate telomeres to T cells, this study claims that specific CD4+ T cells subsequently release these telomeres into the bloodstream as extracellular vesicles. These “Rivers” reportedly travel systemically, acting as a “quorum-sensing” youth signal that elongates telomeres in distant tissues (brain, liver, heart) and reverses senescence markers.
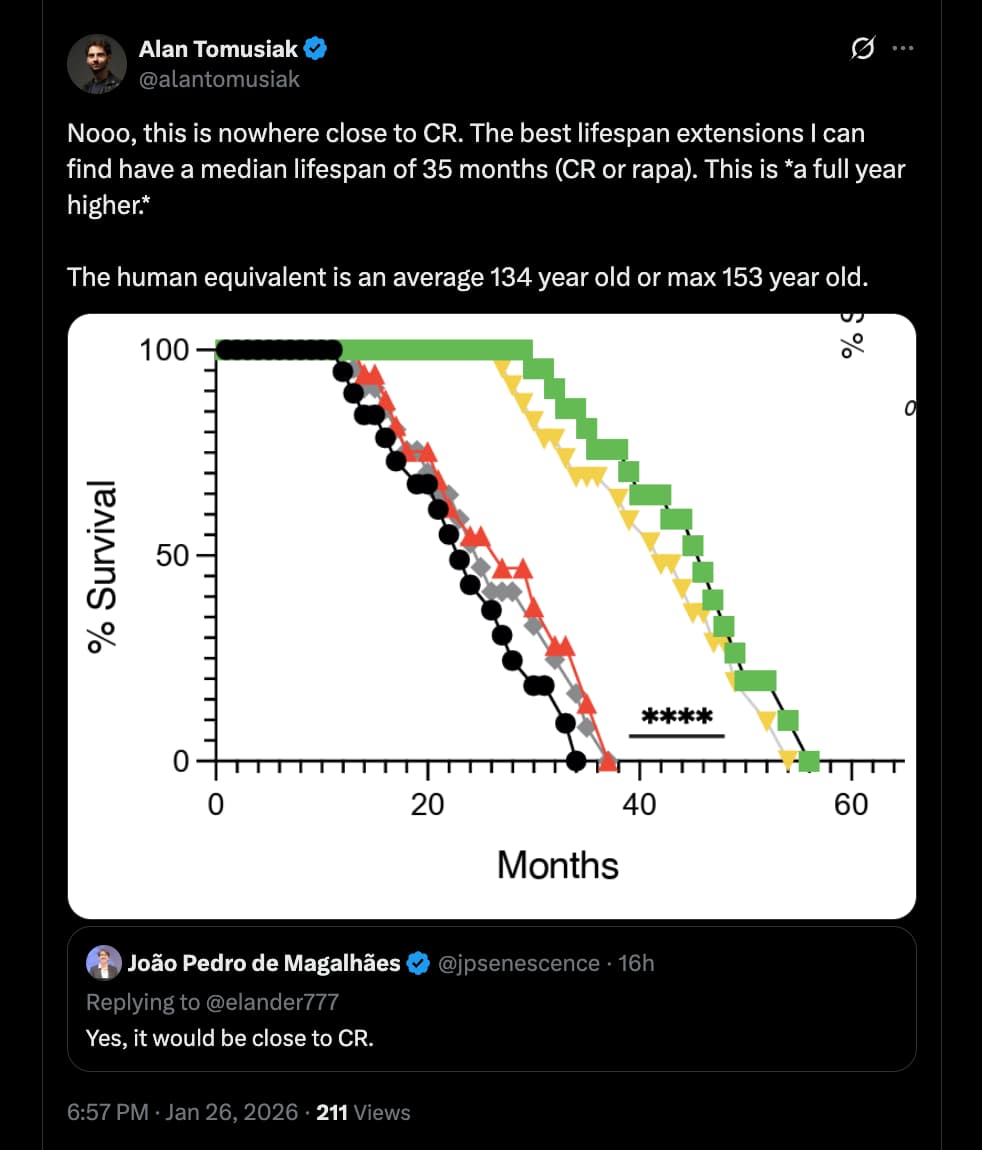
The most explosive claim is the lifespan data: 20-month-old mice treated with these telomeric vesicles allegedly survived to a median of ~47 months, with some reaching nearly 5 years (~60 months). If replicated, this would vastly outperform current gold standards like Rapamycin (which typically offers ~15–25% extension). The mechanism hinges on a metabolic switch: the process requires Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) and the exclusion of the glycolytic enzyme GAPDH from the vesicles. The authors suggest that “Artificial Rivers”—bioengineered vesicles lacking GAPDH—can replicate this rejuvenation, effectively creating a transplantable “program of youth” that functions independently of the donor’s T cells.
Source:
- BioRxiv Paper: CD4⁺ T cells confer transplantable rejuvenation via Rivers of telomeres
- Context: Sentcell UK Laboratories & University of Oxford (UK) |
- Impact Evaluation: Preprint (No JIF). Note: This manuscript has not yet undergone peer review. Its findings, while built on a 2022 Nature Cell Biology precursor, represent extraordinary claims that require independent validation.
Related reading: New World record lifespan achieved in mice by Rejuvenating T Cells - #2 by EnrQay
Biohacker Analysis: Technical Breakdown
Study Design Specifications
- Type: Pre-clinical In vivo (Murine) & In vitro (Human/Mouse cells).
-
Subjects: C57BL/6J mice.
- Recipients: Aged 20-month-old males (equivalent to ~60-year-old humans).
- Donors: Young (3-month) or “rejuvenated” old T cells.
-
N-numbers:
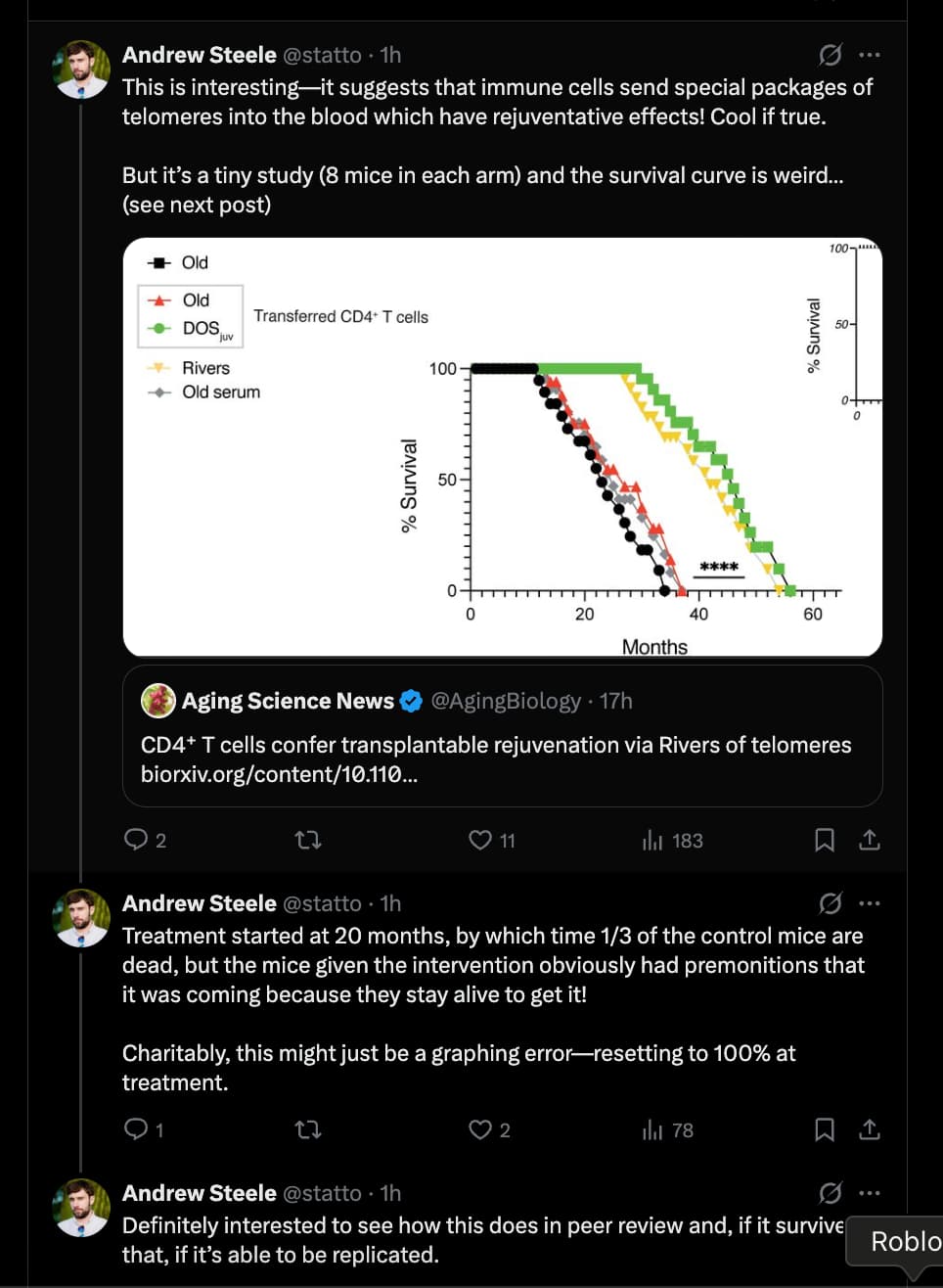
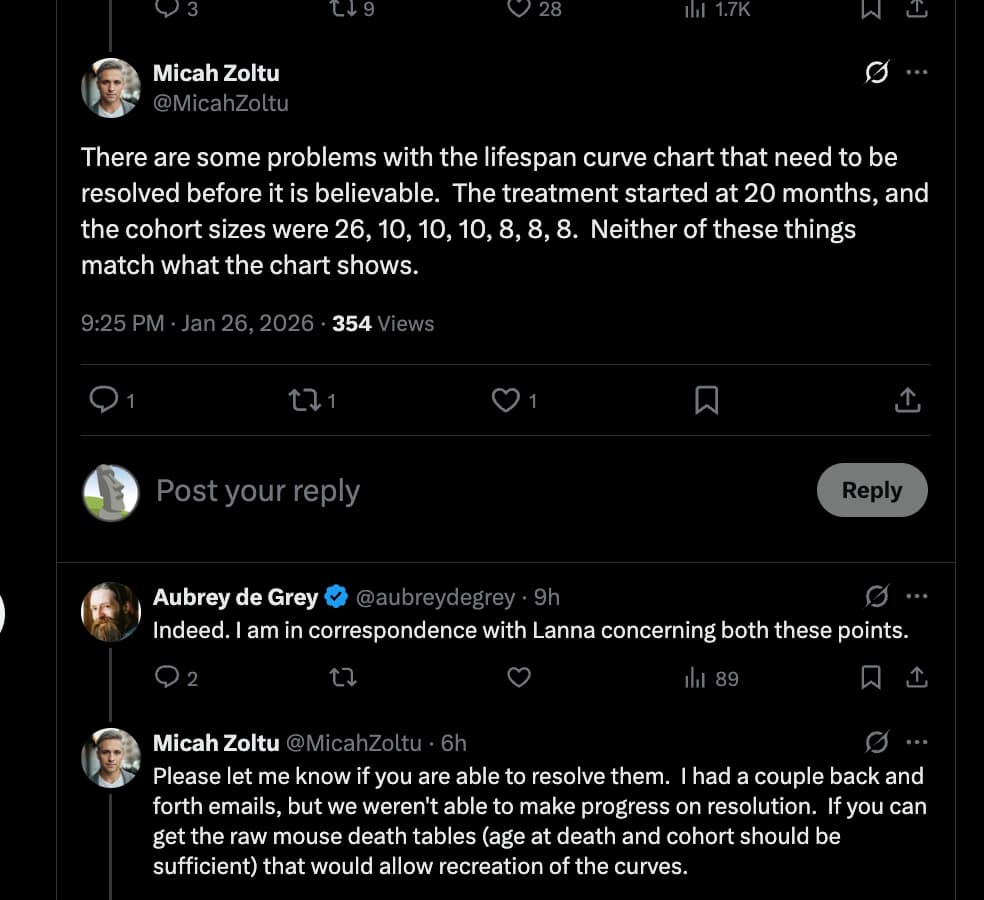
- Lifespan Cohorts: n=10 for River transplant; n=10 for Artificial Rivers; n=10 for Control vesicles; n=8 for DOS-rejuvenated T cells; n=8 for Old T cells; n=8 for Untreated Old Serum.
- Baseline Control: n=26 (Transfer-free old animals).
- Tissue Analysis: n=5 per group.
Lifespan Analysis & The “Control Problem”
- Control Group Performance: The control mice in this study (treated with saline or inactive vesicles) exhibited a median lifespan consistent with standard laboratory conditions, dying between 26–28 months of age.
-
Benchmarking against Pabis et al. (2023):
- Context: The preprint The impact of short-lived controls on the interpretation of lifespan experiments (2023)argues that many “successful” longevity interventions only appear effective because the control animals die prematurely (Median <900 days/30 months) due to stress or poor husbandry.
- Verdict: By Pabis’s strict “900-Day Rule,” the controls in the Lanna study are indeed “short-lived” (falling short of the ~30-month gold standard).
- The Anomaly: However, the magnitude of the effect in the treatment group renders the “weak control” argument moot. The treated mice did not just recover to the 900-day baseline; they shattered it, living to ~1,400–1,800 days. While short-lived controls typically inflate relative (%) gains, they cannot explain the absolute survival duration observed here, which exceeds the species’ known biological ceiling.
Lifespan Data
-
Median Lifespan Extension:
- Absolute: ~17 months extension beyond controls.
- Relative: ~65% increase (Treatment Median ~43–45 months vs. Control Median ~26–28 months).
-
Maximum Lifespan:
- Absolute: Several subjects survived to ~60 months (5 years).
- Relative: ~70–90% increase over historical maximums (typically ~34–36 months for C57BL/6J).
- Comparative Significance: For context, Rapamycin (the current gold standard) typically delivers a 15–25% median extension. This intervention claims an effect size roughly 300% greater than Rapamycin.
Mechanistic Deep Dive
- The “River” Payload: The vesicles are not just bags of telomeres; they are enriched with stemness factors (Wnt5a, Notch1, Runx2) and depleted of GAPDH.
- Metabolic Gating: The formation of these vesicles is gated by CPT1A (the rate-limiting enzyme of fatty acid oxidation). Senescent T cells fail to produce Rivers because they are stuck in glycolysis/ceramide synthesis.
- GAPDH as the “Aging Brake”: The study posits GAPDH as a competitive inhibitor of stemness factors within vesicles. Silencing GAPDH in APCs created “Artificial Rivers” that rejuvenated tissues even without T cells.
- Target Tissues: Rejuvenation was observed in the Brain, Liver, Kidney, Heart, and Lung, suggesting the vesicles cross the blood-brain barrier.
Novelty
- Extracellular Telomeres: Shifts the paradigm from telomeres being purely intracellular “clocks” to intercellular “signaling particles.”
- Transplantable Youth: Demonstrates that the product of the immune interaction (the vesicle) is sufficient for rejuvenation, bypassing the need for successful T-cell engraftment.
Critical Limitations & Red Flags
- The “Too Good to Be True” Problem: A ~70%+ increase in median lifespan from late-life intervention is virtually unheard of in mammal literature.
- Conflict of Interest: The lead author is the CEO of Sentcell, the biotech company holding the IP for the “DOS” compound and Artificial Rivers.
- Tumorigenesis Risk: Delivery of active Wnt/Notch stemness factors + telomeres to aged tissues is a textbook recipe for cancer. The paper claims extended healthspan, but rigorous cancer assays are missing.
- Dosing Obscurity: The treatment used ~5,000 particles. This is an incredibly low quantity for systemic EVs, raising questions about the signal amplification mechanism.