Alan Greene was the one that got me on Gly Nac. His site probably has the study of elderly people that took it and got much better, I’ve forgotten where it came from but was well done. I used the formula from the study and he used it too. I think it was 9 grams of each/day. I did this for quite a while and did think it made me much stronger. I tapered right down after the afib. Nothing like a visit to the ER.
It looks like you’re unfairly blaming NAC for your afib. Even intravenous NAC not only doesn’t increase afib risk but actually decreases it:
I’m taking glycine anyway, so I’ll add back a gram and see what happens. Thanks for checking.
I’m not sure if this holds any weight but I’m using NAC specifically to lower my histamine. Although I’ve never been tested, I seem to have histamine intolerance/MCAS. My histamine spikes fairly regularly and NAC has been a lifesaver. It’s quick and effective.
This is extremely interesting.
I’va had severe insomnia recently on several occasions, often accompanied by itching. It’s finally chatGPT that suggested the culprit was histamine, and indeed, on the worst insomnia nights, I ate a lot of high-histamine foods, and cutting them out stopped the insomnia. Later, my doctor prescribed me an anti-histamine, and while I don’t want to take that long term (it’s more of an experiment), it definitively helps me sleep.
How much Nac do you take to help with histamine?
I find the same thing for myself. When my histamine is up I tend to have hot flashes which makes it difficult to sleep. I have 600 mg capsules and I take one at a time. If my histamine is just starting to go up, only 1 capsule will nip it. For a severe attack I keep taking capsules until I get relief. There have been a few times that I needed at least 6 capsules over the course of a few hours. That’s rather rare though.
Since we’re talking about difficult sleeping… that’s been an ongoing issue over the past decade for me. I started using sermorelin and at the very beginning it helped. Then the honeymoon was over. After about 2 months of sermorelin I added VIP. I find that I fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer.
I want to say high gram glycine has a special relationship with tea in the morning…
I used to take it with coffee, where it just acted as a slightly off putting sugar, but man does glycine accentuate a tea bag… brings all the flavor out and sweetens it without any offput
I guess it prevents me from overdoing the coffee, as tea is more measured in the caffeine for maximal health
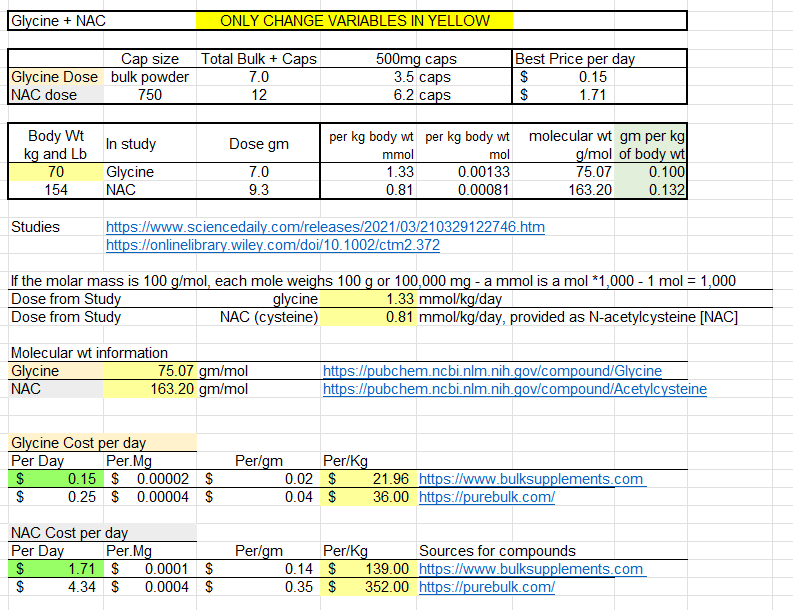
This spread sheet is based on some older studies on GlyNAC the name that the Nestle supplement division gave to this combo and trademarked.
Glycine_NAC_dosing_costing_v1.xlsx (31.9 KB)
You may want to find a cheaper source of NAC. I typically pay $.09 per 600 mg cap or less. I use Bulk Supplements and Nutricost.
NAC can indirectly calm mast cells, but the quick sleep effect is more likely from its anxiolytic/glutamate action than histamine lowering. For histamine issues, DAO enzyme or quercetin (unless you’ve slow MAOA) would be more on point.
New study about cysteine (and maybe NAC?):
Dietary cysteine enhances intestinal stemness via CD8+ T cell-derived IL-22
I did that spread sheet 5 years ago and have not undated it since then ![]()
Back on high gram glycine for a few months and my body fat composition not the same…
It’s the only thing in my stack I feel that has this effect. Rapa? Jardiance? Telmisartan 80? The rest of the stack? If I stop the glycine, I gain fat, IMO.
I’m taking a lot of stuff, but I feel its taking the high gram glycine that cuts the fat…
And why? Apparently among its many qualities it may stimulate glp-1 and possibly act as an agonist… How does it compare in this role with the other glp-1 meds?
I maxx dosed glycine but did not expect this…
AI summary
Introduction to Glycine
- The speaker introduces glycine, a non-essential amino acid, and shares their personal experience of increasing their dosage over the past 90 days.
- They express a desire to discuss the benefits, side effects, and the suitability of glycine for different individuals.
- Glycine plays a significant role in building proteins, creating important compounds, and maintaining cellular function.
Functions of Glycine
- Glycine acts as a neurotransmitter, calming the nervous system and promoting better sleep and reduced stress.
- It is involved in motor control, aiding in smoother muscle function.
- Glycine is essential for collagen production, which supports skin, joints, and connective tissue health.
Benefits of Taking Glycine
- Glycine has anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce bloating and discomfort.
- It aids in mental clarity and muscle recovery by contributing to creatine production.
- Studies suggest glycine can improve insulin sensitivity, benefiting those with blood sugar regulation issues.
- It is linked to lower blood pressure and a reduced risk of heart attacks.
- Glycine protects the liver from damage and promotes better sleep quality when taken before bed.
Possible Side Effects of Glycine
- Generally, glycine is well-tolerated, with most individuals able to handle doses up to 6 grams without significant issues.
- Mild side effects may include stomach rumbling, nausea, or soft stools, particularly when taken on an empty stomach.
- Higher doses, such as 30 grams or more, have not shown serious adverse effects in studies, but caution is advised.
- Excessive intake may lead to gastrointestinal issues or tremors.
Who Should Consider Glycine
- Athletes may benefit from glycine for faster recovery and muscle support.
- Individuals with insulin resistance may find glycine helpful in managing blood sugar levels.
- Those with heart issues may consider glycine for its potential to lower blood pressure.
- People experiencing sleep deprivation may want to explore glycine for improved sleep quality.
Who Should Avoid Glycine
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid glycine due to insufficient research on its effects in these populations.
- Individuals taking medications such as clozapine should consult a doctor, as glycine may interfere with these drugs.
- Those with liver conditions or on specific medications should also seek medical advice before using glycine.
Personal Experience with Glycine
- The speaker shares their experience of taking higher doses of glycine, noting significant improvements in sleep quality.
- They tracked their sleep using an Aura Ring, observing faster transitions to REM sleep, which is a key indicator of sleep quality.
- The speaker also notes enhanced recovery, feeling as if they were recovering faster than in their 20s and 30s.
- They report being able to increase their workout frequency and experience less muscle soreness.
- The speaker mentions improvements in skin appearance, attributing this to glycine’s role in collagen synthesis and its effects on hydration and skin barrier function.
Conclusion on Glycine Supplementation
- The speaker emphasizes the importance of personal experimentation with supplements, encouraging viewers to assess their own responses.
- They clarify that their experience is not a recommendation for others to take high doses of glycine without consideration.
- The speaker invites viewers to engage in their own scientific exploration of supplements and fitness regimens.
I MEGADOSED Glycine for 2 Years - My Results Overview
AI Summary
Introduction to Glycine
- The speaker has been taking 10 to 15 grams of glycine daily for two years and considers it one of the safest and most effective health supplements.
- Glycine supports various health benefits including collagen turnover, antioxidant synthesis, reduction of visceral fat, blood sugar regulation, skin protection against glycation, sleep improvement, and reduction of mental anxiety.
- The speaker shares personal observations of significant health improvements attributed to glycine, including a decrease in visceral fat, improved skin health, better sleep quality, and optimal blood sugar levels despite a high carbohydrate intake.
Benefits of Glycine for Skin Health
- Glycine is the primary amino acid in collagen, constituting about 30 percent of its structure, and is essential for collagen turnover.
- The optimal daily intake of glycine is estimated to be around 15 grams, with 12 grams needed for collagen turnover and 3 grams for other vital functions such as creatine and heme synthesis.
- Glycine helps inhibit the formation of Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs), which can degrade collagen and are linked to various diseases including Alzheimer’s and heart disease.
- By lowering blood sugar and increasing glutathione production, glycine can prevent glycation and degradation of skin collagen.
- The speaker consumes glycine mixed with beverages or foods, noting its sweet taste and ease of incorporation into the diet.
Lifespan Extension Potential of Glycine
- Glycine has been associated with lifespan extension in studies conducted by the National Institute of Aging, where a diet consisting of 8 percent glycine extended the lifespan of male mice by 6 percent and female mice by 2 percent.
- The mechanism by which glycine may extend lifespan is thought to involve methionine restriction, which has been shown to increase lifespan across various species.
- Glycine supplementation can mimic the effects of methionine restriction without the need to reduce methionine intake from dietary sources.
- The speaker acknowledges that while they cannot definitively claim glycine extends their lifespan, they have observed health benefits that may be partially attributed to glycine intake.
Glycine’s Role in Fat Loss and Metabolism
- The speaker observed a significant reduction in visceral fat after adjusting their methionine and glycine intake, noting a drop from 350 grams to 54 grams.
- Increased glycine intake and reduced methionine intake have been linked to enhanced fat oxidation and reduced adiposity.
- Research indicates that lower glycine levels correlate with higher visceral fat levels, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy glycine-methionine ratio.
Glycine’s Impact on Sleep Quality
- Glycine has been shown to improve sleep quality by lowering body temperature and enhancing GABA signaling, which promotes calmness and relaxation.
- The speaker takes around 3 grams of glycine before bed to aid in sleep, aligning with studies that support this dosage for sleep benefits.
- Glycine is generally considered safe, with the speaker reporting no negative side effects even at high doses, including up to 30 grams per day.
Safety and Potential Side Effects of Glycine
- Although glycine is a natural amino acid found in collagen-rich foods, some individuals may experience adverse reactions such as nausea, anxiety, or headaches due to genetic factors affecting neurotransmitter profiles.
- Dr. Tyler Panner discusses how glycine acts as a co-agonist at the NMDA receptor, which is crucial for neurotransmission and can affect mood and behavior.
- Some individuals may have genetic mutations that make them more sensitive to glutamate, leading to symptoms when consuming glycine.
- For those experiencing negative symptoms, reducing the glycine dosage is recommended.
Summary of Glycine Benefits
- Glycine supports skin collagen turnover and counters AGEs, leading to healthier skin.
- It enhances antioxidant defenses, lowers body temperature, and promotes better sleep through increased calming neurotransmitters.
- Glycine also contributes to lowering blood sugar levels and has protective effects on the heart, brain, and liver.
- The speaker expresses a strong preference for glycine as a daily supplement and mentions the existence of at least 14 other evidence-based supplements with scientifically proven benefits.
he may just have high gluthathione levels naturally
1g nac is doable for me, but 3g is really hard. it has a very sulphuric taste and 3g is too sulphuric for me and i seem to get a stomach upset but taking it with food helps to avoid this.
3g glycine is easy for me, glycine tastes like sugar, so it is very easy to swallow.
I think these articles suggest to not overdo it on NAC. I just take 600 mg with 2 g Glycine. Taking grams of NAC seems risky IMO.
I’m not sure a low dose like that will yield the same glutathione restoration benefits as the very high doses in the studies
Use capsules. From iHerb you can get 100x 600mg capsules of NAC for $12.28USD when you use the autoship and save (just cancel the autoship afterwards).
I take 2.4g a day.
I’ve been taking 4gm NAC + 4gm Glycine for 5 years now.
I have not read of any risk related to high dose NAC or Glycine.
NAC effect on glutathione.pdf (573.1 KB)