SGLT2 Inhibitors, but Not GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, Reduce Incidence of Gout in People Living With Type 2 Diabetes Across the Therapeutic Spectrum 2024
SGLT2i with metformin demonstrated a statistically significant decreased incidence of gout at 5 years compared to the metformin control cohort (HR 0.75 [95% CI 0.69-0.82], P < 0.0001). Similarly, SGLT2i with insulin demonstrated a statistically significant decreased incidence of gout at 5 years compared to the insulin control cohort (HR 0.83 [95% CI 0.74–0.92], P < 0.0001). Conversely, no significant disparity in gout incidence was observed between the use of GLP-1Ra and matched controls. Subgroup analysis showed an associated reduced incidence of gout with SGLT2i use compared to GLP-1Ra, in groups using metformin (HR 0.77 [95% CI 0.70-0.86], P < 0.0001) or insulin (HR 0.82 [95% CI 0.73-0.91)], P < 0.0001).
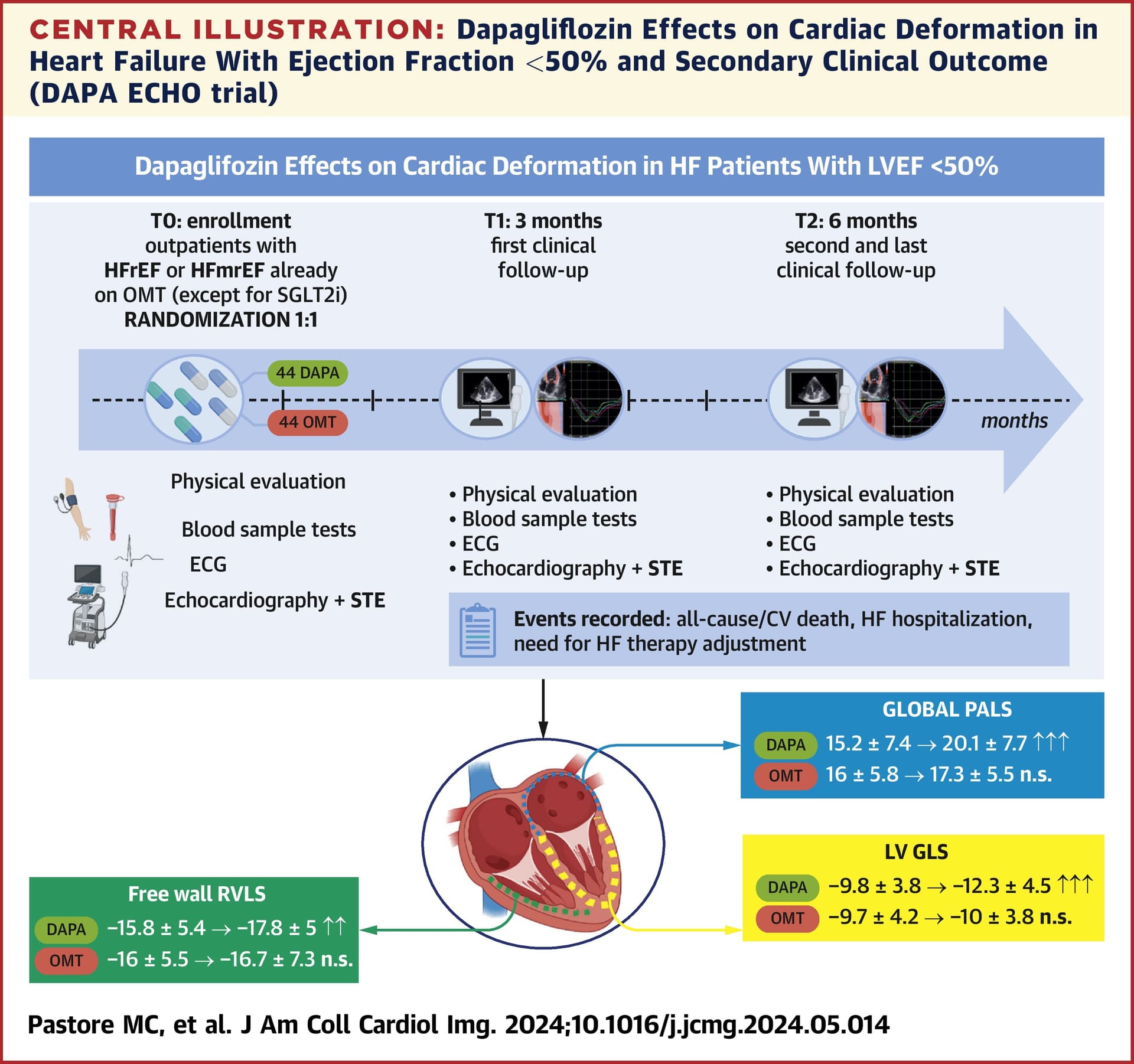
Impact of SGLT2 inhibition on markers of reverse cardiac remodelling in heart failure: Systematic review and meta-analysis 2024 (poke @59vw @LukeMV)
Pooled data demonstrated SGLT2 inhibition, compared with placebo control, resulted in significant improvements in mean difference of LVEDV [-11.62 ml (95% confidence interval, CI -17.90 to -5.25; z = 3.67, P = 0.0004)], LVEDVi [-6.08 ml (95% CI -9.96 to -2.20; z = 3.07; P = 0.002)], LVESV [-12.47 ml (95% CI -19.12 to -5.82; z = 3.68; P = 0.0002)], LVESVi [-6.02 ml (95% CI -10.34 to -1.70; z = 2.73; P = 0.006)], LVM [-9.77 g (95% CI -17.65 to -1.89; z = 2.43; P = 0.02)], LVMi (-3.52 g [95% CI -7.04 to 0.01; z = 1.96; P = 0.05)] and LVEF [+2.54 mL (95% CI 1.10 to 3.98; z = 3.62; P = 0.0005)]. No significant difference in GLS (n = 327) [+0.42% (95%CI -0.19 to 1.02; P = 0.18)] or LAVi [-3.25 ml (95% CI -8.20 to 1.69; z = 1.29; P = 0.20)] was noted.
This meta-analysis provides additional data and insight into the effects of SGLT2 inhibition on reverse cardiac remodelling in patients with HF. Compared with placebo control, we found that treatment with a SGLT2 inhibitor produced significant improvements in several markers of reverse cardiac remodelling.
SGLT2 inhibition, blood lipids, and cardiovascular disease: A Mendelian randomization study 2024
SGLT2 inhibition was associated with reduced risk of heart failure (HF) (OR 0.44 [95% CI 0.32-0.61]; P = 6.0 × 10-7), atrial fibrillation (AF) (0.47 [0.37-0.61]; P = 1.81 × 10-8), coronary artery disease (CAD) (0.47 [0.30-0.73]; P = 7.46 × 10-4), myocardial infarction (MI) (0.30 [0.15-0.61]; P = 7.44 × 10-4), any stroke (AS) (0.28 [0.18-0.42]; P = 1.14 × 10-9), and ischaemic stroke (IS) (0.27 [0.17-0.44]; P = 1.97 × 10-7).
Our study showed the association of SGLT2 inhibition with the reduced risk of CVDs and blood lipids might mediate this association.
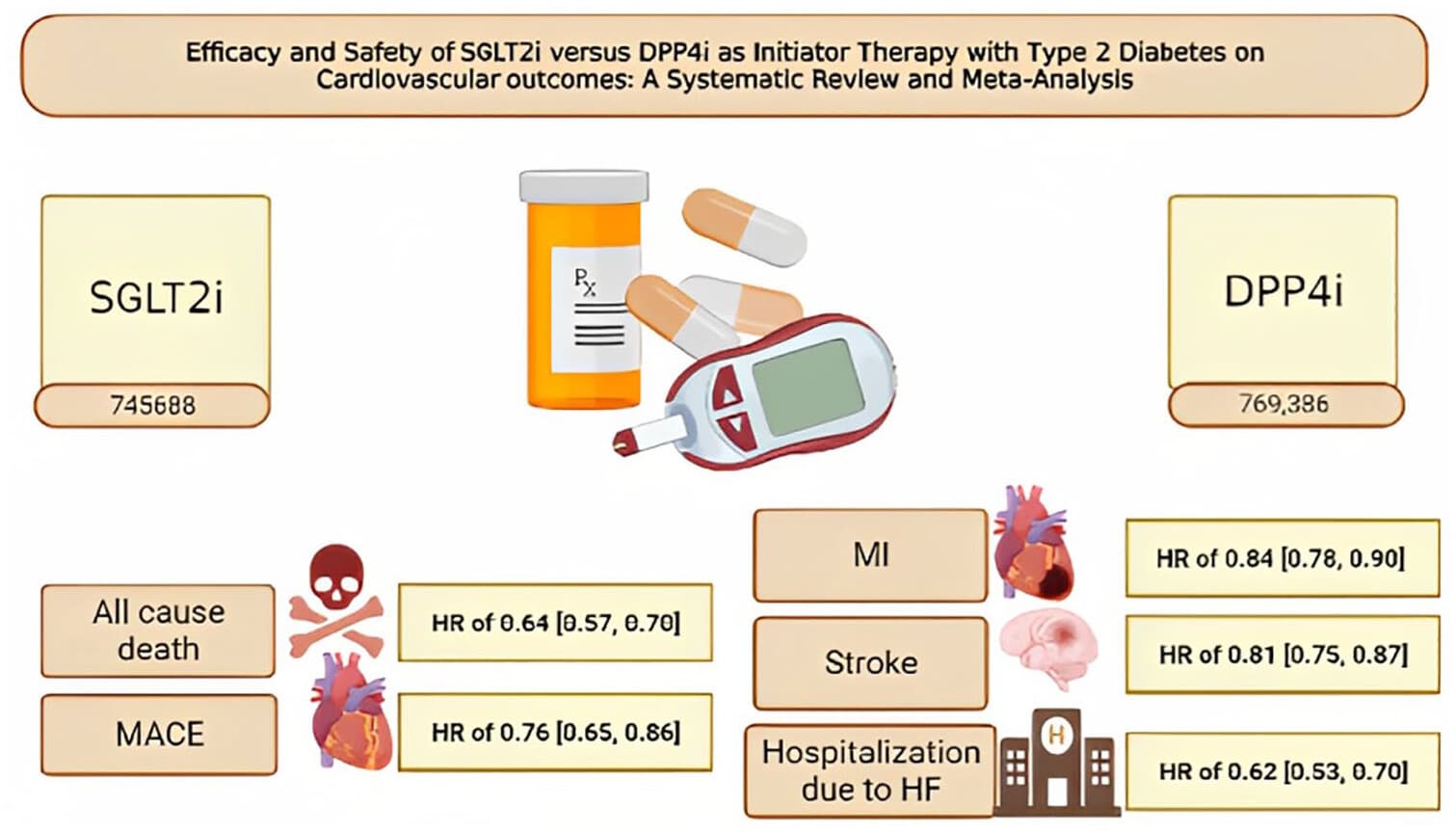
Cardioprotective effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor versus dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of comparative safety and efficacy 2024
Upon pooling the included articles with sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, the primary outcome of all-cause death demonstrated an hazard ratio of 0.64 (0.57, 0.70), I 2: 65.54%, p < 0.001, and major adverse cardiovascular events yielded an hazard ratio of 0.76 (0.65, 0.86), I 2: 87.83%, p < 0.001. The secondary outcomes included myocardial infarction with an hazard ratio of 0.84 (0.78, 0.90), I 2: 47.64%, p < 0.001, stroke with an hazard ratio of 0.81 (0.75, 0.87), I 2: 36.78%, p < 0.001, and hospitalization with an hazard ratio of 0.62 (0.53, 0.70), I 2: 83.32%, p < 0.001.
![]()