In a surprising pivot from neuroscience to muscle physiology, researchers have discovered that Donepezil—the gold-standard drug prescribed for Alzheimer’s disease—may double as a potent performance enhancer for skeletal muscle. A new study from the University of Kansas Medical Center (USA), published in the Journal of Applied Physiology, reveals that this acetylcholinesterase inhibitor does far more than just boost brain chemicals; it appears to directly rev up the energy engines (mitochondria) within muscle cells.
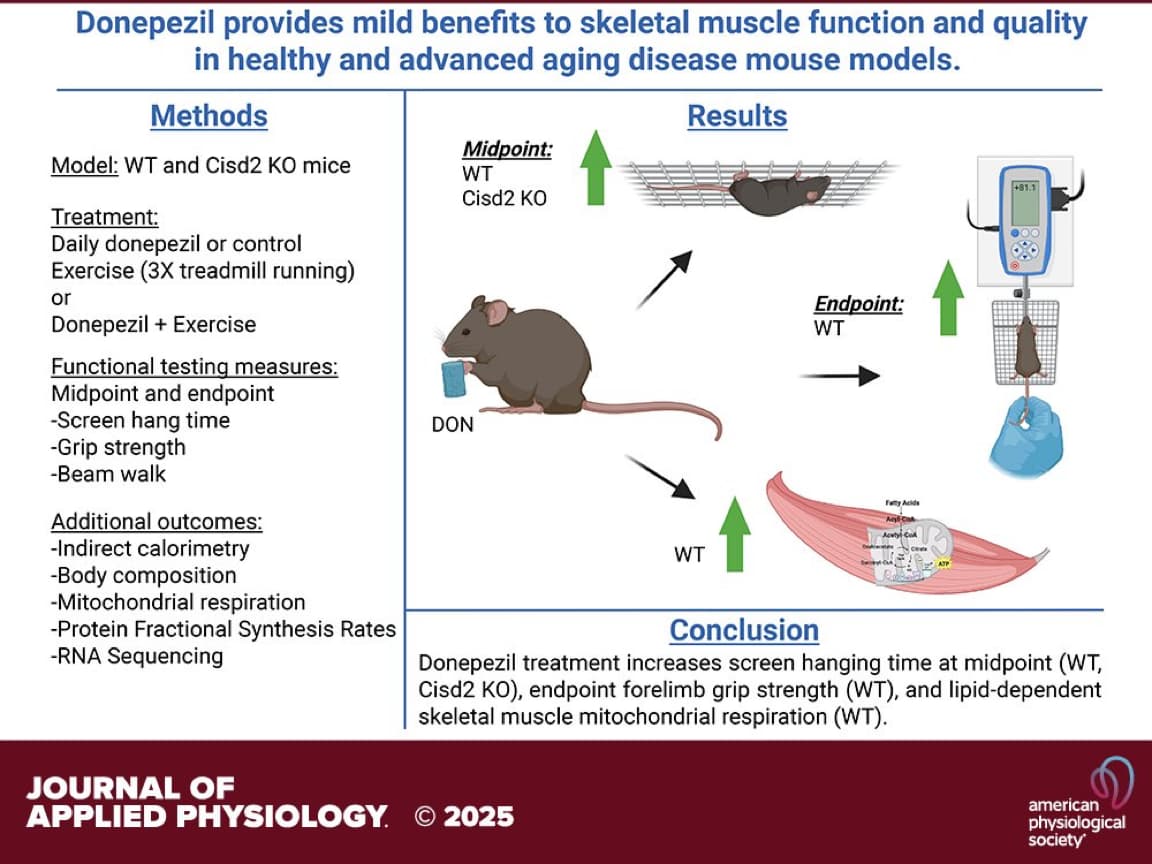
The “Big Idea” here is the repurposing of a generic, FDA-approved compound to combat physical frailty. While usually tasked with preventing cognitive decline, Donepezil was shown to significantly improve grip strength, coordination, and energy expenditure in mice. Crucially, it worked not only in healthy young animals but also in a genetic model of premature aging (Cisd2 knockout mice). The drug enhanced “lipid-driven” mitochondrial respiration—essentially helping muscle tissue burn fat more efficiently for fuel.
For the longevity community, this suggests that the cholinergic system (which Donepezil modulates) might be an overlooked lever for maintaining physical robustness. If these findings translate to humans, the “anti-frailty” pill of the future might already be sitting in millions of medicine cabinets, offering a dual-shield against both neural and physical decay.
Source:
- Open Access Paper: Donepezil treatment, alone or combined with exercise, enhances skeletal muscle function in healthy and advanced aging disease mouse models
- Institution: University of Kansas Medical Center, USA.
- Journal: Journal of Applied Physiology.
- Impact Evaluation: The impact score of this journal is 3.3 (JIF) / 6.0 (CiteScore), evaluated against a typical high-end range of 0–60+ for top general science, therefore this is a Medium impact journal. (It is a respected, specialized physiology journal, though not a broad-reach “glamour” journal).
Part 2: The Biohacker Analysis
Study Design Specifications
- Type: In vivo (Murine model).
-
Subjects:
- Species: Mouse (Mus musculus).
- Strains: C57BL/6J (Wild Type - WT) and Cisd2 knockout (Cisd2KO - a model of premature aging/mitochondrial dysfunction).
- Sex: Male and Female.
- N-number: 10–12 mice per group (Total ~44–48).
- Duration: 11 weeks (Treatment ran from age 4 weeks to 15 weeks).
- Lifespan Data: None reported. The study endpoint was 15 weeks of age (young adult). This was a functional healthspan study, not a mortality study.
Mechanistic Deep Dive
The authors hypothesized that increasing acetylcholine availability via Donepezil (DON) would improve neuromuscular junction (NMJ) stability and mitochondrial quality.
- Mitochondrial Respiration: DON treatment significantly increased State 3 respiration (ADP-stimulated) using palmitoylcarnitine (lipid substrate). This indicates an enhanced capacity for Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in the gastrocnemius muscle.
- Neuromuscular Junction (NMJ): RNA-seq analysis revealed DON altered gene expression specifically related to NMJ integrity and synaptic transmission, potentially countering the “dying back” of motor neurons seen in sarcopenia.
- Systemic Metabolism: DON increased non-resting energy expenditure in WT mice, suggesting a systemic metabolic upregulation, likely driven by the increased mitochondrial demand.
- Dystrophin Modulation: The study noted alterations in dystrophin expression, a structural protein critical for muscle fiber integrity, though the directionality (reduced in WT, distinct in KO) suggests a remodeling process rather than simple upregulation.
Novelty
- Peripheral vs. Central: We know DON works in the brain. This paper provides rare in vivo evidence that DON acts peripherally on skeletal muscle mitochondria, independent of exercise.
- Mitochondrial “Unlocking”: The finding that an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor specifically rescues lipid-based respiration is novel. It suggests the cholinergic system is a gatekeeper for metabolic flexibility in muscle tissue.
- Cisd2 Rescue: Efficacy in the Cisd2KO model (which mimics mitochondrial-driven aging) validates the drug’s potential in treating mitochondrial frailty, not just generic weakness.
Critical Limitations
- Age of Subjects: This is the most glaring weakness. The mice were treated from 4 to 15 weeks old. These are developing/young adult mice. The “aging” model was genetic (Cisd2KO), not chronological. We have zero data from this paper on whether DON reverses sarcopenia in naturally aged (e.g., 24-month-old) mice.
- Supratherapeutic Dosing: The dose (~5 mg/kg) translates to a very high human dose (see Part 3). The effects seen might be pharmacological artifacts of high dosing rather than physiological restoration.
- Thermal Stress Confounder: The authors admit behavioral testing was done at room temperature (22°C), which is cold stress for mice (thermoneutrality is ~30°C). Cholinergic drugs affect thermoregulation; the “increased energy expenditure” could partially be an enhanced shivering/thermogenic response to cold.