But hard plaque is preferable to soft plaque. Both statins and exercise increase hard plaque.
If it was as simple as the guy from Harvard said, a simple rct where one group gets vitamin B complex + TMG (and omega 3 EPA?) while the other gets placebo should show significant differences in plaque development, calcification score and stroke/heart attack rates.
2.5mg MF, 1g TMG, 1Tbsp sunflower lecithin dropped mine from 11 to 7 in 4 weeks. I’m a compound heterozygote at MTHFR
Does that help with homocysteine?
Powerful
What is MF?
Is there a lot of support for sunflower lecithin in this context?
No, but some arguments I’ve heard say that omega 3 is only useful in combination with vitamin B and TMG.
Methylfolate. The lecithin is a source of phosphatidylcholine. I get standard doses of the other B vitamins in my multi as they play a role as well but I was on those at baseline before I added the 3 supplements above and got my HMCY to drop. I suspect majority of the effect is from TMG and to a lesser degree the folate.
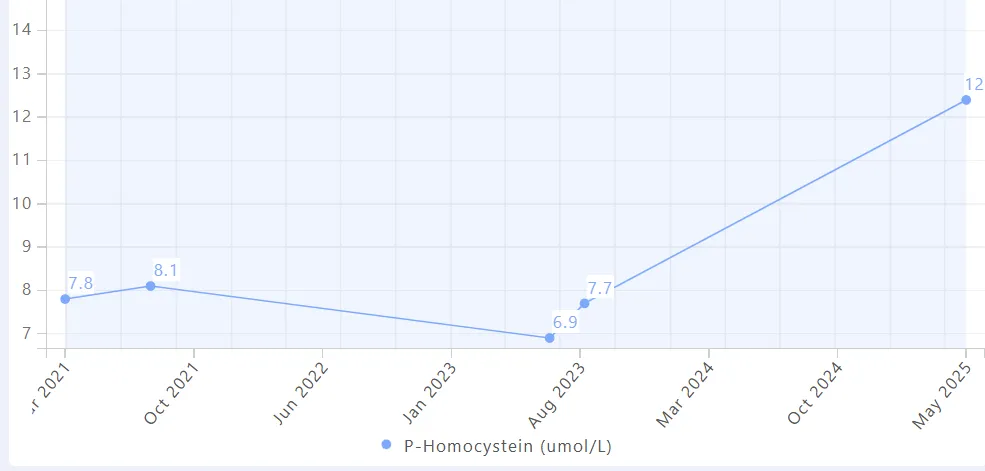
My homocysteine jumped from 7 → 12 µmol/L without any changes in diet or supplements. I’m fairly certain it’s tied to a persistent, low-grade gut issue I’ve been experiencing for the last 10 weeks.
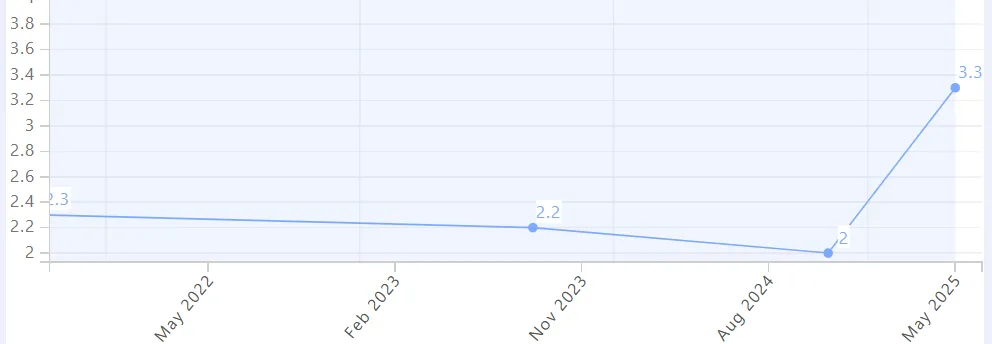
LDL-C also rose ~50% (2.0 → 3.1 mmol/L), and I suspect impaired bile production or recycling is part of the mechanism.
Other labs:
![]() B12, folate, and holoTC (active B12) all high-normal
B12, folate, and holoTC (active B12) all high-normal
![]() hsCRP moved from 0.1 → 0.2 mg/L
hsCRP moved from 0.1 → 0.2 mg/L
![]() WBC up from 3 → 4 x10⁹/L (mostly neutrophils—I normally run very low)
WBC up from 3 → 4 x10⁹/L (mostly neutrophils—I normally run very low)
![]() Haven’t tested B6, but unlikely the cause
Haven’t tested B6, but unlikely the cause
All stool tests have been negative—calprotectin, fecal hemoglobin, and PCR panels for:
![]() Bacteria: C. diff, Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, E. coli, Yersinia
Bacteria: C. diff, Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, E. coli, Yersinia
![]() Viruses: Norovirus, Rotavirus, Adenovirus, Sapovirus, Astrovirus
Viruses: Norovirus, Rotavirus, Adenovirus, Sapovirus, Astrovirus
![]() Parasites: Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Entamoeba
Parasites: Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Entamoeba
➤ Has anyone seen something similar—gut-driven shifts in both homocysteine and LDL-C?
➤ Has anyone gone from really solid digestion to subtly “off” without diet changes or other changes in lifestyle? How did you go about troubleshooting it (aware of both colonoscopy and abdominal ultrasound to rule out anything anatomical & serious)?
Considering SIBO testing next—would any one have experience with that, or tips for uncovering root causes?
Thanks in advance for reading!
LDL-C (mmol/L)
This is very interesting - I observed the same thing you did, though my persistent LDL increase happened 2 years before my Hcy increase
There is indeed a correlation between bile acid obstruction, Hcy and LDL. Or maybe it’s just a coincidence!
Did you look at pancreatic enzymes, and was it accompanied by new digestive issues?
Are you high fat-ish?
What do you think is the more likely reason then?
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) lowers homocysteine (tHcy) for two biochemical reasons, both centred on choline metabolism.
1 Digestion → choline → betaine → BHMT reaction
- Hydrolysis in the gut. Pancreatic phospholipase A₂ and intestinal phospholipase D clip dietary PC, releasing free choline and lyso-PC that is quickly reacylated or absorbed.
- Hepatic oxidation of choline to betaine. In hepatocyte mitochondria, choline → betaine-aldehyde (choline dehydrogenase) → betaine (betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase).
- Betaine donates a methyl group to homocysteine. Betaine-homocysteine-methyltransferase (BHMT) uses betaine to remethylate homocysteine → methionine, producing dimethyl-glycine and lowering circulating tHcy (PubMed Central, PubMed).
A typical PC capsule (7.5 g) contains ≈ 1 g choline; complete oxidation yields ≈ 1 g betaine. That is in the same range as the 1.5 g betaine that produced a 12 % fall in fasting tHcy in classic trials. In a 2-week RCT, 2.6 g choline as PC/d cut fasting tHcy 18 % and blunted a methionine-load rise by 29 % (PubMed, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam).
2 Feedback on the PEMT pathway (SAM sparing)
The liver can make PC de novo by methylating phosphatidylethanolamine (PEMT pathway), consuming three S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM) molecules and generating three S-adenosyl-homocysteine (SAH) → homocysteine. Supplying PC in the diet down-regulates PEMT, so fewer SAM→SAH conversions occur and less homocysteine is produced in the first place (ScienceDirect). This “SAM-sparing” effect complements the BHMT route above.
3 Net effect & practical notes
Intake form Typical choline supplied Expected fall in fasting tHcy* Comments ½ lb beets (reference) 0.3–1.1 g betaine 0.2–0.9 µmol L⁻¹ Already covered 7.5 g PC capsule ≈ 1 g choline → 1 g betaine pot. ≈ 1–2 µmol L⁻¹ Single daily dose 2–3 PC caps (≈ 2–3 g choline) Matches RCT dose 2–4 µmol L⁻¹ (≈ 15–20 %) Seen within 2–6 wk *Interpolated from Olthof et al. and other PC/betaine trials; largest absolute drops occur in people starting >12 µmol L⁻¹.
4 How to leverage PC effectively
- Dose-responsive up to ~3 g choline/d. Larger doses show diminishing returns unless tHcy is very high.
- Split doses with meals improve absorption and cut fishy‐odor trimethylamine formation.
- Ensure folate & B-12 adequacy. The BHMT route bypasses folate, but the folate-dependent MTR pathway handles about half of daily homocysteine recycling; deficiencies blunt total effect.
- Genetics matter. BHMT activity is higher in people with the common MTHFR 677TT variant, so they often respond more to choline/betaine than to folate.
- Watch phospholipid load if you have NAFLD. PC is generally hepatoprotective, but very high PC or choline can raise fasting TMAO in some gut-microbiome profiles.
In short, phosphatidylcholine trims homocysteine both by supplying choline → betaine for the BHMT remethylation reaction and by sparing SAM through down-regulation of hepatic PEMT. A couple of grams of choline as PC daily is enough to reproduce the ~15–20 % homocysteine fall seen in controlled trials—several-fold more than beets alone, and without the pink urine.
A good review that concludes what we already know: homocysteine lowering is only useful to lower the risk of stroke, all other associations are not proven to be causal: Homocysteine and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Outcome-Wide Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses and Mendelian Randomization Studies 2025
All the 3 types of studies collectively support that Hcy is a key causal risk factor, and Hcy-lowering (specifically with folic acid) may serve as an effective intervention for stroke.
This decreased my homocysteine from 15 to 8, for what it’s worth, but I’m testing methylcobalamin now only.
I’ve gotten my levels down to 7.4 and am happy with that.
Eric Verdin commented in Attia’s podcast that NMN and NR raised his homocysteine from ~8 to ~ twice that. It quickly reversed when he quit.
Methylfolate, Methyl B12 and TMG are essential in longevity stacks IMO, for the remethylation of homocysteine.
These supplements might be beneficial by themselves but not for their homocysteine-lowering effect. See: Parkinson's disease - #914 by adssx