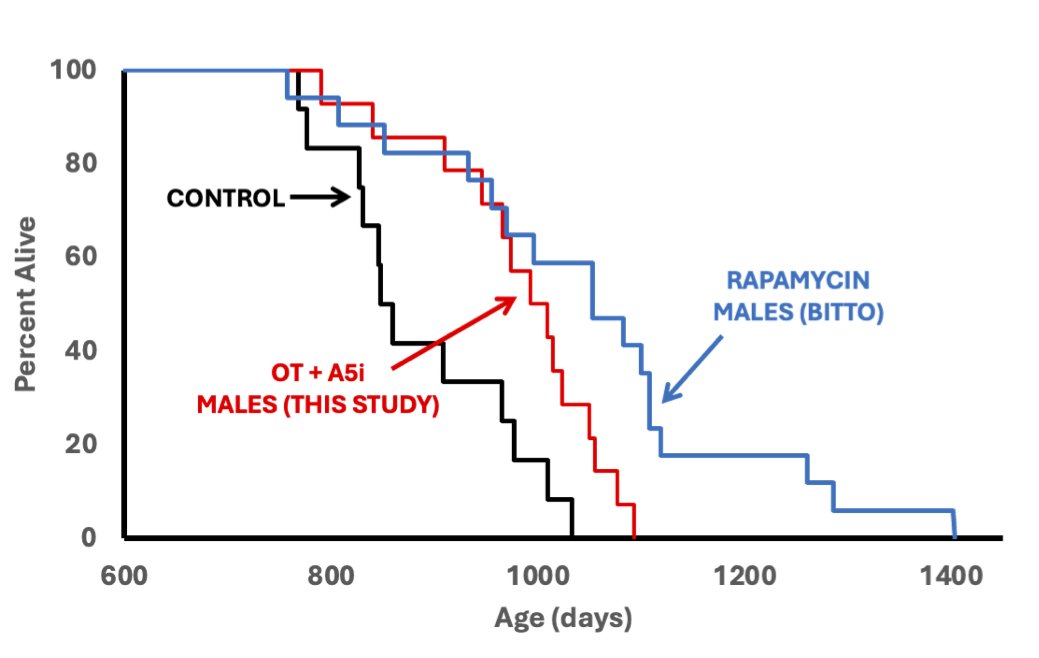
Be aware that in the study below they are using the unusual approach to lifespan increase calculated on “remaining lifespan”, which is very different from the typical ITP approach of calculating it on total lifespan.
Male mice receiving a combination of OT + A5i experienced:
- A 73% life extension from the point of treatment.
- A 14% boost in overall median lifespan.
From: Irina M Conboy
Sent: Wednesday, August 27, 2025 2:30 PM
Subject: Living longer and in a healthier state even when starting as old and frailHello everybody,
Our very recent paper on life-span and health-span extension by defined pharmacology is linked for your perusal Sex-specific longitudinal reversal of aging in old frail mice | Aging
One of the most intriguing findings, in my view, is that it works excellently for males (better than anything published thus far) and not at all for females.
Cheers,
Irina Conboy, PhD
Sex-specific longitudinal reversal of aging in old frail mice
Important studies report acute rejuvenation of mammalian cells and tissues by blood heterochronicity, old plasma dilution, defined factors, and partial reprogramming. And extension of rodent lifespan via single-prong methods was tried in recent years. Here, we examined whether simultaneous calibration of pathways that change with aging in opposite directions would be more effective in increasing healthspan and lifespan. Moreover, we started with the challenging age group - frail 25-months-old mice that are equivalent to ~75-year-old people. We used an Alk5 inhibitor (A5i) of the age-elevated, pro-fibrotic transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) pathway that regulates inflammatory factors, including IL-11, and oxytocin (OT) that is diminished with age and controls tissue homeostasis via G-protein-coupled receptor and ERK signaling. Treatment of old frail male mice with OT+A5i resulted in a remarkable 73% life extension from that time, and a 14% increase in the overall median lifespan. Further, these animals had significantly increased healthspan, with improved physical performance, endurance, short term memory, and resilience to mortality. Intriguingly, these benefits manifested only in the male and not in the female mice, yet OT+A5i had positive effects on fertility of middle-aged female mice. Mechanistically, the bio-orthogonal metabolic proteomics on the blood serum demonstrated that the acute, 7-day, treatment of the old mice with OT+A5i youthfully restored systemic signaling determinants and reduced protein noise in old mice of both sexes. However, after 4 months of OT+A5i, only old male, but not female, mice remained responsive, showing the youthful normalization of systemic proteome. These findings establish the significant health-span extension capacity of OT+A5i and emphasize the differences in aging and in response to longevity therapeutics between the sexes.
Open access paper:
AI Summary:
Here’s a detailed and structured summary and analysis of the paper “Sex-specific longitudinal reversal of aging in old frail mice” published online on August 21, 2025 in Aging (Albany NY) (Aging-US).
Summary
Scope & Rationale
- The study investigates whether combining interventions that move aging-related pathways in opposite directions yields superior results in promoting healthspan and lifespan, compared to single-pronged methods.
- It focuses on frail mice aged 25 months, roughly equivalent to 75-year-old humans (Aging-US)—a particularly challenging and clinically relevant demographic.
Interventions Employed
- Alk5 inhibitor (A5i): Targets the elevated TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor-beta) pathway, which is pro-fibrotic and linked to inflammation (e.g., IL-11 regulation).
- Oxytocin (OT): A hormone that declines with age, important for tissue homeostasis via G-protein-coupled receptor and ERK signaling pathways (Aging-US).
Key Findings
Lifespan & Healthspan (Males)
-
Male mice receiving a combination of OT + A5i experienced:
- A 73% life extension from the point of treatment.
- A 14% boost in overall median lifespan.
- Notable improvements in physical performance, endurance, short-term memory, and mortality resilience(Aging-US).
Sex-Specific Effects
- These pronounced benefits were absent in female mice.
- However, in middle-aged female mice, OT + A5i enhanced fertility (Aging-US).
Systemic Proteomic Effects
- A short, 7-day treatment in both sexes restored youthful systemic signaling and reduced “protein noise” in serum.
- At the 4-month mark, only males maintained youthful normalization of the serum proteome; in females, responsiveness waned (Aging-US).
Mechanistic Insight
- The combined treatment appears to recalibrate aging-related signaling pathways in the male systemic proteome, leading to functional rejuvenation.
- Short-term gains were seen across both sexes, but sustained long-term benefits were male-specific (Aging-US).
Analysis & Perspective
Strengths
- Clinically relevant model: Using frail, aged mice strengthens translational relevance.
- Multi-pronged strategy: Targeting pathways that diverge with age (i.e., restoring diminished signals while inhibiting elevated ones) is strategic and innovative.
- Measuring both lifespan and functional healthspan offers more holistic insight.
- Sex-specific evaluation highlights crucial differences in therapeutic response—a valuable insight often overlooked.
Limitations and Considerations
- Lack of long-term female benefit: The discrepancy between sexes raises questions about underlying biology and requires exploration.
- Translational challenges: Whether these results can be replicated in humans remains unknown.
- Safety: Long-term effects on other systems (e.g., cancer risk, fibrosis) need careful assessment.
Implications & Future Directions
- Evidences that combination therapies might have enhanced potency in reversing aging markers.
- Personalized gerotherapeutics may require sex-specific designs.
- Encourages deeper exploration into why female physiology responds differently, which might involve hormonal cycles, receptor expression, or immune function.
- Opens the door to testing similar combinatorial interventions in other aging models or possibly early phase human studies.
Contextual Integration
- This study complements research showing that epigenetic rejuvenation—for example, via Yamanaka factors or chemical cocktails—can reverse aging signatures at the cellular level (Aging-US).
- However, Kato et al. focus on systemic, organismal outcomes (lifespan, physical and cognitive performance), marking a significant leap toward translational aging therapeutics.
Conclusion
The paper presents compelling evidence that a dual-intervention with oxytocin and ALK5 inhibitor can substantially reverse aging and extend lifespan in frail aged male mice, with systemic rejuvenation confirmed via proteomic analysis. The sex-specific outcomes underscore the importance of tailoring anti-aging therapies to biological differences and signal a move toward more nuanced, effective geroscience treatments.
Let me know if you’d like to dive deeper into specific data—such as survival curves, behavioral assays, proteomic profiles—or explore comparisons with similar longevity interventions.
Citation for reference formatting:
Kato C, Zheng J, Quang C, Siopack S, Cruz J, Robinson ZR, Fong N, Zhang ZA, Young P, Conboy MJ, Conboy IM. Sex-specific longitudinal reversal of aging in old frail mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2025 Aug 21; [Epub ahead of print] (Aging-US).