Answer:
Bre1 encodes an E3 ubiquitin ligase, with the discovery of Bre1’s role in repairing mitochondrial damage, further investigation into its implications for PD is warranted.
Bre1 encodes an E3 ubiquitin ligase, which mediates the ubiquitination machinery that plays a broad range of biological roles in various aspects of DNA replication and repair
Recent studies have indicated that Bre1 is implicated in regulating Rad51 to participate in mitochondrial mtDNA repair, thereby mitigating mitochondrial damage resulting from the accumulation of ROS
Bre1 overexpression
Bre1 OE improves glycolysis and the key TCA cycle regulating enzyme OGDH
The TCA cycle and the respiratory chain are two pivotal components of intracellular energy metabolism that function synergistically to convert nutrients into ATP. Oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH) is a key regulatory point in the TCA cycle [65]. Responsible for catalyzing the dehydrogenation and decarboxylation of α-ketovalerate into succinyl-coenzyme A [66] . Studies have shown that a toxic metabolite of MPTP inhibits alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activities in mitochondria [67]. Our findings indicate that Bre1 OE significantly enhanced the transcriptional activity of OGDH. Besides, in the context of antioxidant stress, Bre1 reinstates the functionality of SOD and diminishes the level of ROS. These findings are consistent with the transcriptome sequencing data and validate the role of Bre1 in augmenting the glycolytic pathway, TCA cycle and antioxidant.
In conclusion, Bre1 is involved in repairing mitochondrial morphology, attenuating the damage induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS), restoring mitochondrial functionality, promoting energy metabolism, enhancing ATP levels, and thereby preventing neurodegeneration in PD and improving motor function. It also indicates that overexpressed Bre1 may present a potential therapeutic strategy for the PINK1 mutant form of PD. Further investigation will be conducted to elucidate the molecular mechanism through which Bre1 impacts mitochondria in future studies.
@John_Hemming: Interesting therapeutic avenue to improve mtDNA repair?
ChatGPT and other LLMs only suggest resveratrol for up-regulating the Bre1 homolog (RNF20). Hypoxia/HIF-1 can recruit RNF20/40 to hypoxia-induced genes (rather than expression upregulation).
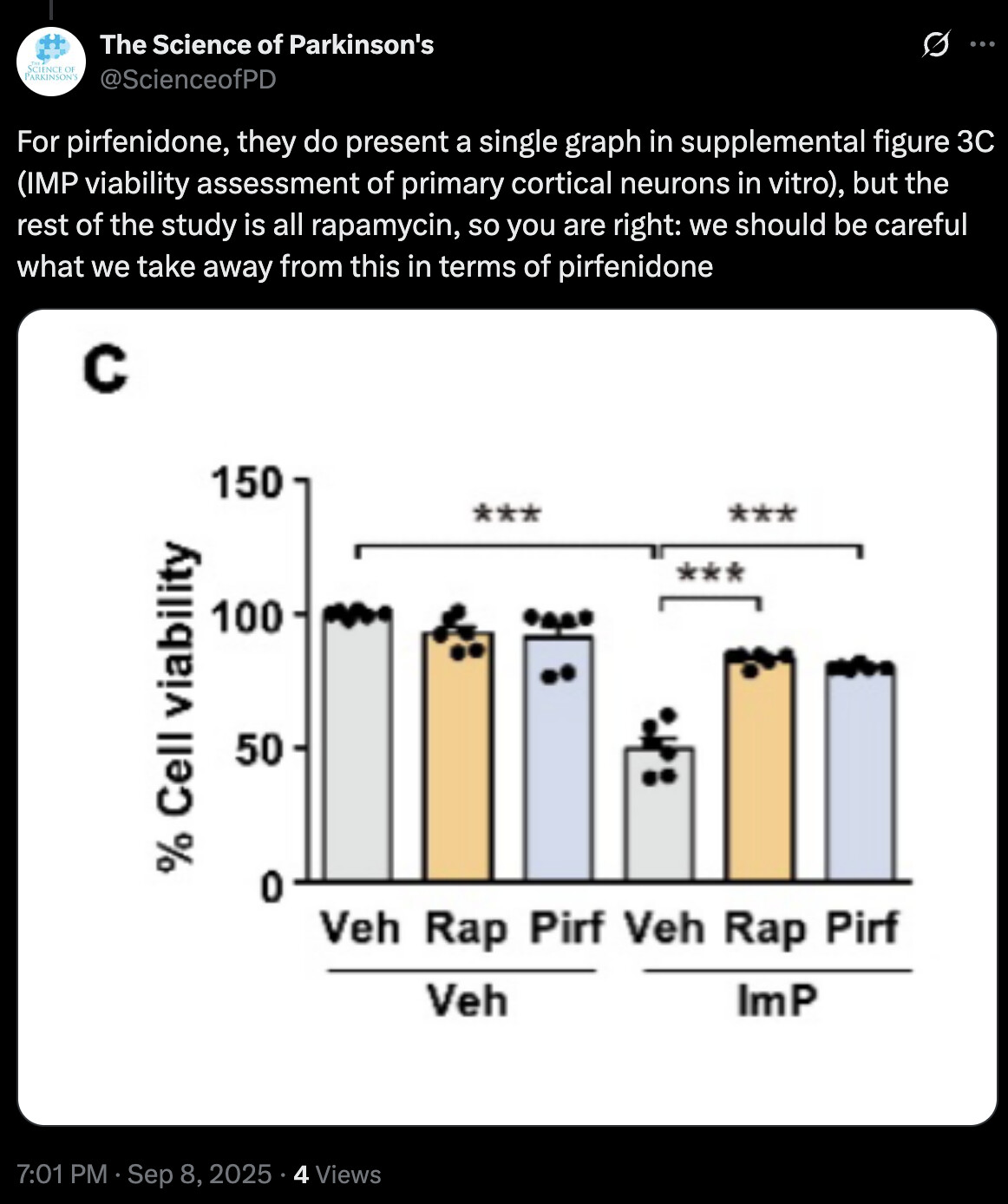
Turkish paper + rat model so low quality: Autophagy activation ameliorates cognitive deficits and alpha-synuclein pathology in an adeno-associated viral vector mediated rat model of Lewy body disorders 2025
The dual-site AAV injection model offers advantage to study cognitive deficits in LBD.
Rapamycin reversed spatial learning deficits induced by a-syn overexpression.
Rapamycin preserved synaptic integrity in both hippocampus and striatum.
Rapamycin reduced a-syn pathology in all layers of CA2 and partially in CA3.
Autophagy was differentially regulated within the striatum and hippocampus.
Another -tinib for LBD: Safety, tolerability and potential biomarkers of vodobatinib in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies 2025
Abl kinase inhibitor vodobatinib was investigated in dementia with Lewy bodies and was safe.
The number of falls was reduced and CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 was significantly altered in the vodobatinib compared to placebo groups.
Larger trials and longer treatment periods are warranted
![]() Also by Charbel Moussa of Georgetown University…
Also by Charbel Moussa of Georgetown University… ![]()
Worth listening to, touches upon PD, but NDD more generally.
Not PD but a related disease: Patient-Derived Neurons Exhibit α-Synuclein Pathology and Previously Unrecognized Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Elevation in Mitochondrial Membrane Protein–Associated Neurodegeneration 2025
Mitochondrial membrane protein–associated neurodegeneration (MPAN) from the neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) family is a rare neurodegenerative disease marked by α-synuclein aggregation, brain iron accumulation, and midbrain dopaminergic neuron degeneration.
They found that Tanganil and Aqneursa helped:
Next, we used the modified amino acid AL, specifically the racemate acetyl-DL-leucine (ADLL) and the bioactive enantiomer acetyl-L-leucine (ALL), to modulate this pathological feature. Both ADLL and ALL reduced MHC-I levels in patient mDA neuronal cultures (Fig. 2E), offering a strategy for reducing pathological triggers of disease.
New type of PD model: A human striatal-midbrain assembloid model of alpha-synuclein propagation 2025
Animal models of the pathology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) have provided most of the treatments to date, but the disease is restricted to human patients. In vitro models using human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs)-derived neural organoids have provided improved access to study PD etiology. This study established a method to generate human striatal-midbrain assembloids (hSMAs) from hPSCs for modeling alpha-synuclein (α-syn) propagation and recapitulating basal ganglia circuits, including nigrostriatal and striatonigral pathways.
Human striatal organoids and midbrain organoids were generated using a stepwise differentiation protocol from hPSCs, and both regionalized neural organoids were assembled to form hSMAs, mimicking some basal ganglia circuits. Both the nigrostriatal and striatonigral pathways were present and the neurons such as dopaminergic (DA) neurons and GABAergic neurons were electrophysiologically active in the hSMAs. hSMA development in the presence of increased α-syn from SNCA overexpression, induced nigrostriatal system damage, which is typical of the disease. Using the α-syn-linker-mKO2 reporter and a bimolecular fluorescence complementation system, we demonstrated that fluorescent α-syn was retrogradely transported from the striatal area to DA neurons of the midbrain area and exhibited α-syn aggregates and Lewy body-like inclusions. Furthermore, phosphorylated and detergent-resistant α-syn aggregates, similar to pathological form in human patients, was accumulated in midbrain area of hSMAs. Treatment with protein aggregation inhibitor (Anle138b) and autophagy inducer (Rapamycin) reduced α-syn aggregation, indicating potential of hSMAs for drug testing.
This study established hSMAs as a novel platform for modeling PD, demonstrating α-syn propagation and associated neural pathologies. These assembloids offer significant potential for developing therapeutic strategies and understanding the mechanisms of PD progression.
The electrical field across the membrane is really strong.
**Skin intraneural phosphorylated α-synuclein is a highly specific biomarker for early Parkinson’s disease **
“In contrast, olfactory function, although more impaired in PD than in non-PD patients, only seems to have a more limited diagnostic accuracy.”
Certainly in my case. I have a highly reduced sense of smell, and I don’t have PD.
Tried this? I’ve heard good things about this
Have not tried this.
I’ve tried several other nootropics but none of them did enough to justify the cost/benefit ratio.
Forgot to cross post here, SGLT2i seem like a no-brainer for people at risk of PD: Canagliflozin - Another Top Longevity Drug - #1847 by adssx
Turkish preprint: Personalized Metabolite Biomarker Predictions Reveal Heterogeneous Characteristics of Parkinson’s Disease 2025
Furthermore, certain metabolites such as melatonin, sphingosine, and biliverdin, though not identified by the general approach, showed distinct secretion patterns across patient clusters. For instance, an undersecretion pattern of melatonin, possibly associated with the sleep disturbance symptom of PD, was detected exclusively in one subgroup.
While certain metabolites like melatonin, prostaglandins, sphingosine, biliverdin, tyramine, and betaine etc., which are associated with PD or neurodegeneration, were not predicted as potential biomarkers in the classical approach, they demonstrated group-specific patterns in the cluster-based approach.
For instance, melatonin, 6-hydroxymelatonin, and L-iduronic acid exhibit an undersecretion pattern in cluster C3, while no clear trend is observed in clusters C1 and C2.
@John_Hemming: they looked at serum and not CSF I guess, still, there might be people with PD who benefit more from melatonin supplementation than others.
I think the nub of the issue is neurodegeneration which results from damage to the mitochondria. That could have many causes and the symptoms will still be the same. Once things get beyond a certain limit the mitophagy fails.
Cure PD UK update: Ibuprofen, methylcobalamin, benfotiamine, probucol and chlorogenic acid failed in PD models (fwiw):
Ouch. I’m taking benfotiamine partially because it was supposed to be neuroprotective. This sucks. I wonder if chlorogenic acid levels likely to be obtained from coffee are clinically relevant, I always found it unsatisfying in association studies with coffee that given everything that is actually present in coffee, we’re not measuring amounts, makes it very noisy.
I don’t understand much but I thought people smarter than me here could interpret it. ChatGPT says that this paper “Suggests that some individuals might have altered baseline HMGCR activity (due to variants), which could interact with statin therapy in ways that differ by genotype. Flags that genetic variation in HMGCR might modulate susceptibility or phenotypic expression of PD — which is relevant for personalized medicine hypotheses involving statins. Thus, while it doesn’t provide evidence for or against statin use in PD, it offers mechanistic/biological plausibility that modulation of that pathway might affect disease in some patients.”
Might explain the discrepancy in results regarding statin and PD risk.