Actually I found a couple of studies with canagliflozin in beagles, but there’s nothing as of yet with any others.
If you have both Medicare and commercial insurance, you can usually get Costco Pharmacy to take the coupon for Jardiance, provided you tell them to avoid Medicare for Jardiance. Technically the prohibition only applies if you use Medicare insurance, but many pharmacies (and also the manufacturers that issue the coupon) apply the prohibition if you HAVE Medicare insurance, regardless of whether you use Medicare or not.
Very interesting, comparing SGLT2 (dapagliflozin) vs GLP-1 (liraglutide) vs acarbose: Dapagliflozin restores odour-induced functional integration of primary olfactory cortex circuit but not olfactory-related regional brain activation in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 16-week randomised comparative study 2025
Results: After 16 weeks, dapagliflozin restored odour-induced functional integration of the POC-sensorimotor cortex-middle temporal cortex circuit (Gaussian random field correction applied), whereas liraglutide and acarbose did not. Dapagliflozin also tended to improve attention (p = 0.071). In contrast, liraglutide enhanced odour-induced activation in the left hippocampus, which was not observed with dapagliflozin and acarbose. The decreased odour-induced directed FC was associated with changes in lipid levels, olfactory threshold, executive function and memory performance (all p < 0.05).
The associations between FC and metabolism, cognitive scores and olfactory behaviour provide additional insights into the neuroprotective effects of dapagliflozin. The decreased FC was positively associated with improvements in lipid levels (LDL-C and TC), which indicates that reductions of high cholesterol induced by dapagliflozin may have protective effects. Because LDL-C is a modifiable risk factor for dementia.46 The decreased FC was correlated with changes in olfactory threshold, executive function, and immediate and delayed memory. This suggests that modulation of the POC circuit may not only reflect changes in brain connectivity but also serve as a biomarker for cognitive and olfactory improvements in patients with T2D. Furthermore, the observed relationship between improved odour threshold and delayed memory suggested that olfactory function could be linked to memory performance, highlighting the potential of olfactory tests as early markers for cognitive decline in patients with T2D.
That is an amazing paper, Antoine! It’s Chinese, so I would love to see it replicated elsewhere, but assuming everything is legit, it’s a very rich paper.
From my point of view, it heavily underlines something I think about all the time, and we all frequently speculate about: to what degree do these drugs have benefits for healthy users, i.e. people who don’t have the indication for which these drugs have been developed. We know that as pathologies develop (such as diabetes), the body attempts to ameliorate some negative effects through compensatory mechanisms, and therefore those bodies are different from healthy bodies not just because of the original defect and the subsequent pathology, but also because of compensatory mechanisms ameliorating aspects of the pathology. Therefore drugs addressing the pathology might act very differently in healthy bodies without that pathology, or compensatory mechanisms. This has similarities to situations where some physiological changes associated with aging can be adaptive mechanisms.
In any case, this is another cautionary note, to not assume that just because a drug has benefit X (like e.g. neuroprotection, dementia, etc.) in, say, diabetics, it will have the same effect in non-diabetics, perhaps be even harmful. A ton of studies showing neurological benefits and dementia risk reduction of SGLT2i and GLP-1RA is in diabetics - more interesting for those of us without T2DM is what the effect is in our cohort.
Here we see this illustrated (my bold and italics) - from the paper:
“After 16 weeks of dapagliflozin treatment, the FC in the POC-sensorimotor cortex-middle temporal cortex circuit was restored under odour stimulation, but liraglutide or acarbose did not. More specifically, odour-induced directed FC from bPOC to left PreCG/PostCG and IFG, and FC from left PreCG/PostCG to right middle temporal gyrus decreased compared to baseline of diabetes, but no difference from normal control. The reduction towards normative levels may reflect normalisation of compensatory signalling. These results suggest that in the absence of structural or functional abnormalities of POC, odour-induced functional integration of the POC circuit in patients with T2D is compensatory, and this functional integration can be restored by dapagliflozin treatment. This POC circuit involves the integration of multisensory input, motor function and memory processes.32-35”
For those of us without T2DM, we need more studies in a healthy cohort, such as those where SGLT2i are used in HF (or other CVD) without concomitant T2DM: impact on risk of dementia and NDD.
A separate interest would be whether the variegated and differential benefits of dapa vs lira seen in this paper would stack or interfere with each other if taken together, perhaps dose or sequence dependent, plus again also in non-diabetics.
I tried to commission researchers to look at that HF and CKD cohorts but these indications were approved more recently so we don’t have enough data yet to get some signal.
However we have Mendelian randomization. And life extension in mice. So I’m more confident with SGLT2i than GLP-1RAs.
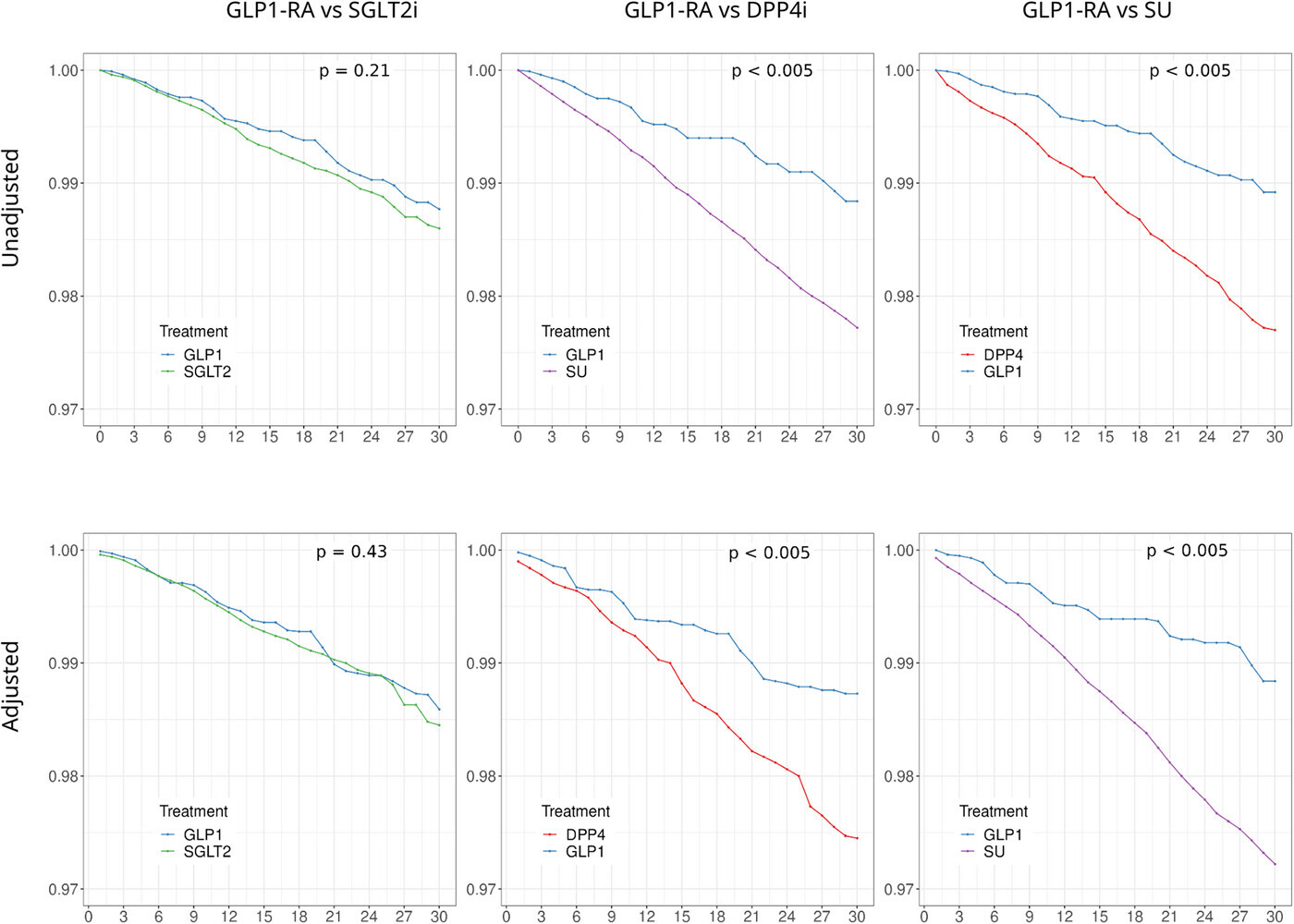
In total, 93,872, 110,366, and 95,838 patients were included in the SGLT2i vs. DPP4i, GLP-1RA vs. DPP4i, and SGLT2i vs. GLP-1RA comparisons, respectively. SGLT2i users had a significantly lower risk of PD compared with both DPP4i users (HR = 0.80, 95 % CI: 0.69–0.93, p = 0.003) and GLP-1RA users (HR = 0.80, 95 % CI: 0.69–0.93, p = 0.003). No significant difference was observed between GLP-1RA and DPP4i users (HR = 0.97, 95 % CI: 0.85–1.10, p = 0.656). The meta-analysis further supported the reduced PD risk associated with SGLT2i use.
It seems in Fig. 2b, GLP-1RA vs DPP4i the under 65 subgroup had a HR of 0.70 with reasonable CI in favor of GLP-1RA?
They excluded the under 50 due to low number of events. How low? Disappointing.
Also, risk of PD onset is one thing, but pathology or symptom alleviation is another. Could it be that SGLT2i might be better at prevention, but once you got it GLP-1RA could be better for amelioration? They mentioned the trial with Lixisenatide, but what happens wrt. PD when you give Lixisenatide to non-diabetics, especially younger onset PD?
Again let’s keep in mind: results in diabetics. Considerable number with co-morbidities, especially hypertension. Might there not be some interaction with BP medications in the context of PD? I wonder if they did a subgroup analysis depending on the BP med combination.
Your weekly SGLT2 article review ![]()
Overall, our results are consistent with prior observational analyses comparing GLP-1RA to DPP4i or SU in diabetic populations and reinforce previous findings that GLP-1RA may be protective against dementia, but not to a greater extent than SGLT2i.
Compared to metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors are associated with significantly lower risks of ocular hypertension (hazard ratio [HR], 0.73; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.60–0.89), POAG (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.51–0.81), and the need for glaucoma medications (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.69–0.84) in 5 years.
The primary outcome of baseline-adjusted ISSI-2 at 48 weeks was not different between the empagliflozin and placebo group (525 ± 30.4 vs. 560 ± 33.4, p = 0.43). Additional measures of beta-cell function, insulinogenic index/HOMA-IR, and ΔCpep0-120/Δgluc0-120 × Matsuda index also did not differ between the groups. While there was no difference in the secondary outcome of prevalence of dysglycemia at 48 weeks between the arms (empagliflozin 65.7% vs. 48.2% in placebo, p = 0.18), the glucose tolerance worsened in 9.4% of participants in the empagliflozin group as compared to 28% in the placebo group (p = 0.08).
Both SGLT2is significantly improved E-wave deceleration time, LAVI, LV-EDVI, LV-ESVI, LV-MI, and LVEF. Neither medication produced significant changes in RWT, and no significant differences were noted between groups regarding HF hospitalizations or all-cause mortality.
Empagliflozin demonstrated more pronounced effects on LV remodeling markers, including peak E-wave velocity, E/e’ ratio, and LV-SI, compared to dapagliflozin.
There is growing interest in expanding SGLT2i use to broader populations, with draft UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) 2025 guidelines proposing it as first-line therapy for all people with T2DM, in combination with metformin.
These findings provide critical real-world evidence supporting a universal SGLT2i strategy in T2DM management, which is of direct relevance to current guideline deliberations.
A total of 15 studies (16 trials) involving 101,430 patients were included. SGLT2 inhibitors did not significantly reduce genital cancer risk compared to placebo (RR 1.10; 95% CI 0.93–1.31; P = 0.28; moderate certainty of evidence), with consistent findings across subgroup analyses. No significant effects of SGLT2 inhibitors were observed for cervical, endometrial, ovarian, prostate, uterine, penile, or vulvar cancers. Dapagliflozin potentially increased the risk of male genital cancers (RR 1.31; 95% CI 0.99–1.74; P = 0.06). SGLT2 inhibition significantly reduced testicular [odds ratio (OR) 0.012; 95% CI 0.001–0.220; P = 0.003] and cervical (OR 0.013; 95% CI 0.001–0.122; P = 1.615 × 10 − 4) cancer risks. Pooled results from both discovery and replication cohorts demonstrated that SGLT2 inhibition reduced cervical cancer risk (OR 0.016; 95% CI 0.002–0.116; P < 0.0001).
SGLT2 inhibitors exhibited a neutral overall risk profile for genital cancers, while genetic evidence demonstrated beneficial effects specifically for cervical cancer.
To assess the effect of empagliflozin and dapagliflozin on SCD in patients with type 2 diabetes, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease.
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted on randomized controlled trials. A total of 58,569 participants from 8 trials were included, with 30,565 patients treated with SGLT2 inhibitors and 28,104 controls assigned to placebo. The median follow-up period was 29 months. We performed pooled analysis, meta-regression, and subgroup analyses to explore the impact on SCD risk across different populations and treatment regimens.
The pooled analysis showed a reduced risk of SCD with SGLT2 inhibitors (OR: 0.82; 95% CI: 0.72–0.94; p = 0.0104), with negligible heterogeneity (τ2 = 0.0000; I2 = 0.0%; Q = 3.17, p = 0.8687). Subgroup-specific estimates (age, follow-up duration, population, and SGLT2 inhibitor type) did not reach statistical significance. Meta-regression showed no significant moderation by mean age, study duration, or gender. No evidence of publication bias was detected.
Empagliflozin and dapagliflozin may reduce the relative risk of sudden cardiac death. These data expand the spectrum of cardiovascular benefits attributed to SGLT2 inhibition. Further trials specifically designed to address pre-adjudicated arrhythmic endpoints are warranted.
@CronosTempi: interesting that they pooled T2D, HF and CKD and still found benefits.
Preprint: Comparative effectiveness of empagliflozin versus dapagliflozin in adults with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease 2025
In patients with MASLD, empagliflozin was associated with better clinical outcomes compared to dapagliflozin, particularly in reducing cardiovascular and renal events, hospitalizations, and mortality.
On the complexity of polypharmacy (in a rare disease + animal model but still interesting): Dapagliflozin with losartan but not olmesartan has an add-on protective effect in experimental Alport syndrome 2025
And now the less good news (in special subpopulations though):
Patients treated with SGLT2 inhibitors demonstrated significantly higher rates of atrial fibrillation (10.4% vs 7.8%, HR 1.552, 95% CI 1.303-1.848, p<0.001) and ventricular tachycardia (4.8% vs 2.2%, HR 2.467, 95% CI 1.825-3.334, p<0.001) compared to those receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists. Ventricular fibrillation was also more common in the SGLT2 inhibitor group (2.4% vs 0.8%, HR 3.451, 95% CI 2.131-5.590, p<0.001).
SGLT2i use was associated with a 30.5% reduction in all-cause mortality (CI -33%, -28%, P < 0.0001, OR 0.228), however, SGLT2i users noted to have higher rates of drive-line infection (CI 1.39%, 5.55%, P <0.001, OR 1.32), right heart failure (CI 11.69%, 17.00%, P<0.0001, OR 2) and cardiorenal syndrome (7.13%,12.94%, P<0.0001, OR 1.49). No significant difference was observed in atrial fibrillation incidence between the two cohorts.
Thank you, Antoine, for pulling these together. Is it possible to be in love with a drug? Because I think I’m in love with SGLT2i ![]()
![]()
![]() . Yes, I am a little sick in the head, why do you ask
. Yes, I am a little sick in the head, why do you ask ![]() ?
?
But on a more serious note, I think most people would benefit from a carefully selected SGLT2i, especially those who are not at 100% optimal diet and exercise. Of course there are things to watch (urogenitary infections), but on the whole, these strike me as very safe drugs (as long as not carelessly stacked with insulin and other glucose lowering meds). Many people routinely pop a multivitamin daily, I think SGLT2i have even better justification. Not everyone is going to be suitable, but it’s worth exploring, IMHO. Maybe one day it’ll be common to take drugs preventatively. YMMV.
I think I am too!
I agree with you. I don’t understand why there isn’t already an SGLT2 hype as there is/was for metformin or whatever BS supplement.
I, too, am married to my SGLT2. I’m glad I jumped on this train even before all this barrage of new information. Been on it three years and counting.
*raises hand
I have a related but unrelated question, please.
Unmedicated, I get huge glucose spikes (easily over 200 mg/dl)
I am on dapagliflozin and take acarbose with meals and I rarely go over 140 these days.
I had my dapa this morning, but I forgot to take my acarbose with my rare treat of white pasta… white pasta, yep, I’m living life on the razors edge over here!!
At some point after my meal, my cgm showed me my glucose was 180 and climbing.
Here is my question…. I know we are supposed to take acarbose right before we start eating. If one forgets, at what point does there cease to be a benefit?
I was left not knowing if that was too late to take any, or if it might help it come down faster.
Said another way, how long after your meal would it be a complete waste of time to take? Or is there always at least a little benefit if your glucose is still up?
I’ve forgotten acarbose before and then taken it after food. I didn’t look at the amount of impact on my cgm, I did still experience the typical side effects of acarbose which suggests to me that there must have been some benefits too.
The rule of thumb with Acarbose is to take it with the first bite of food, but I’ve also forgotten and then just taken it as soon as I remembered, even if it was right after the meal. I don’t have CGM data to show how effective it was taking it after though so I’d be curious to know.
I believe it is Ok to take acarbose at any point in the meal. Best at the beginning, but still effective at the end. Just don’t take it more than 15 minutes after finishing your meal.
I’m lowering my Dapagliflozin dose to 5 mg because my hematocrit has raised to 52.3%… possibly causing me low-grade headaches upon waking. Unfortunate!
Are you on testosterone replacement therapy as well, or did dapa raise it that high on its own?
Timely comment. After donating blood six times a year for the last few years, I stopped donating a few months ago when I started taking finasteride. My hematocrit has been creeping up. In the meantime, I have had headaches in the morning, and that is not typical for me. I am now wondering if the two are connected.
Were you donating because Hct was high from TRT?
No. I lost a friend to leukemia when I was fifteen, and I swore I would donate whenever I could. I don’t really know what my baseline would be, because this is the first time in years I have gone four months without a whole blood donation.