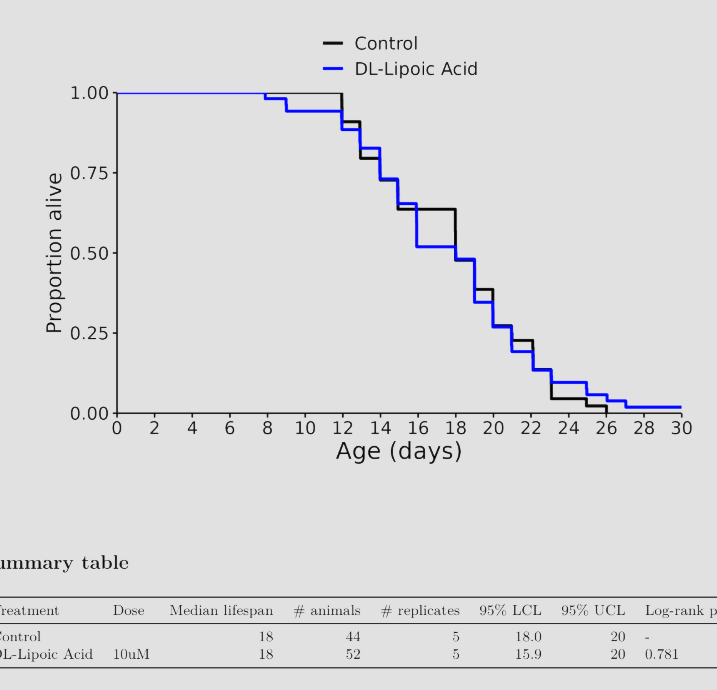
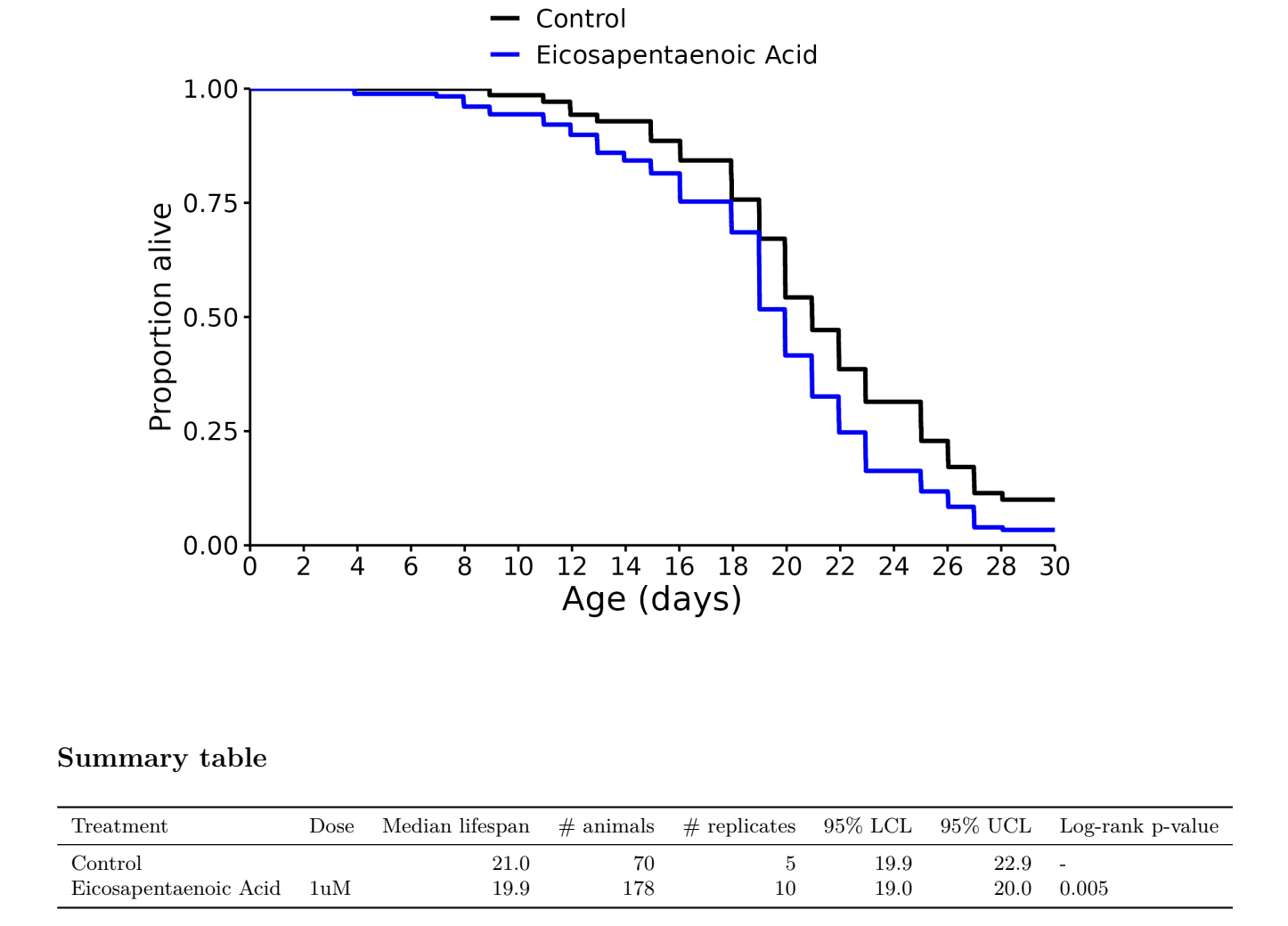
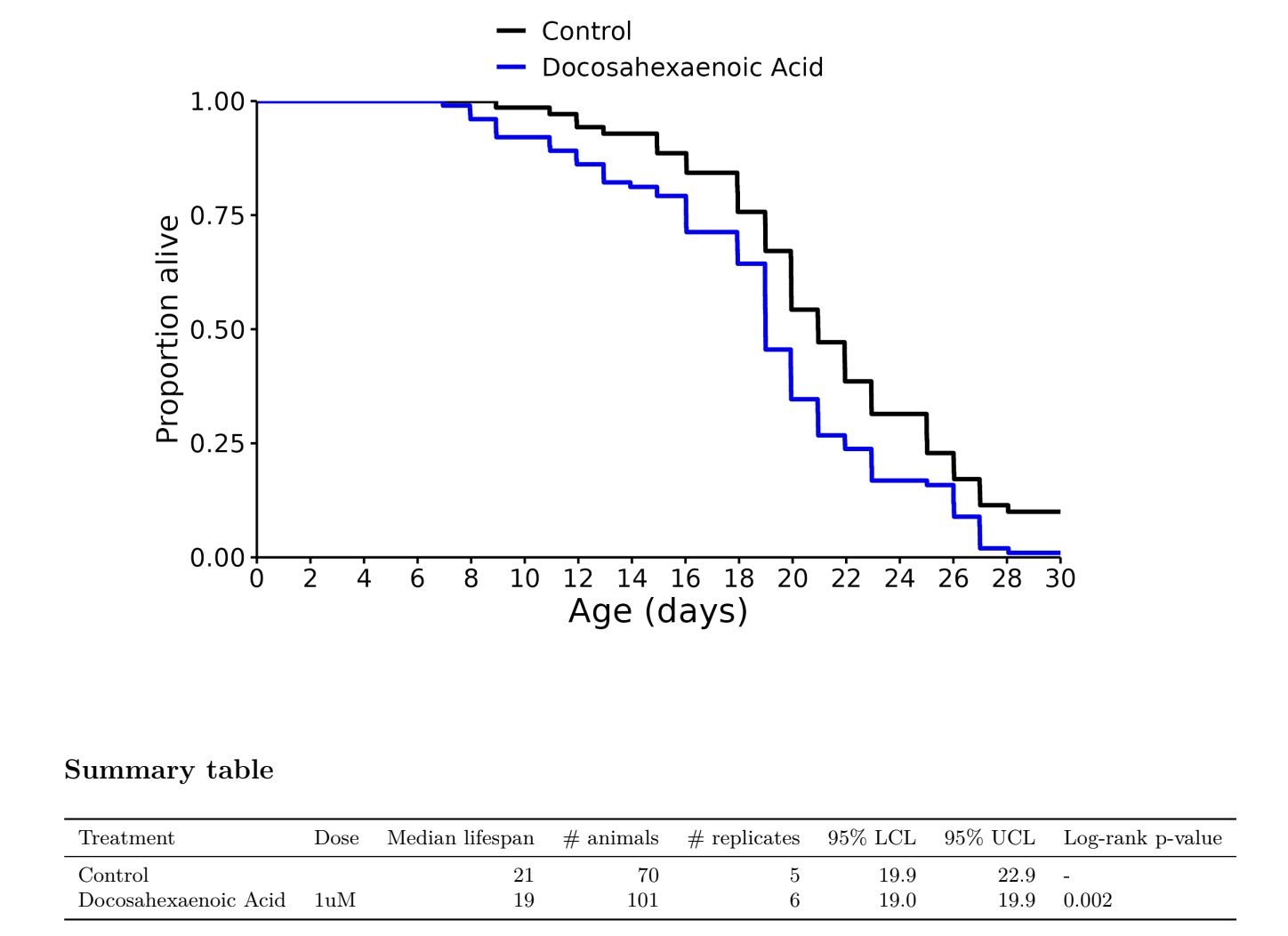
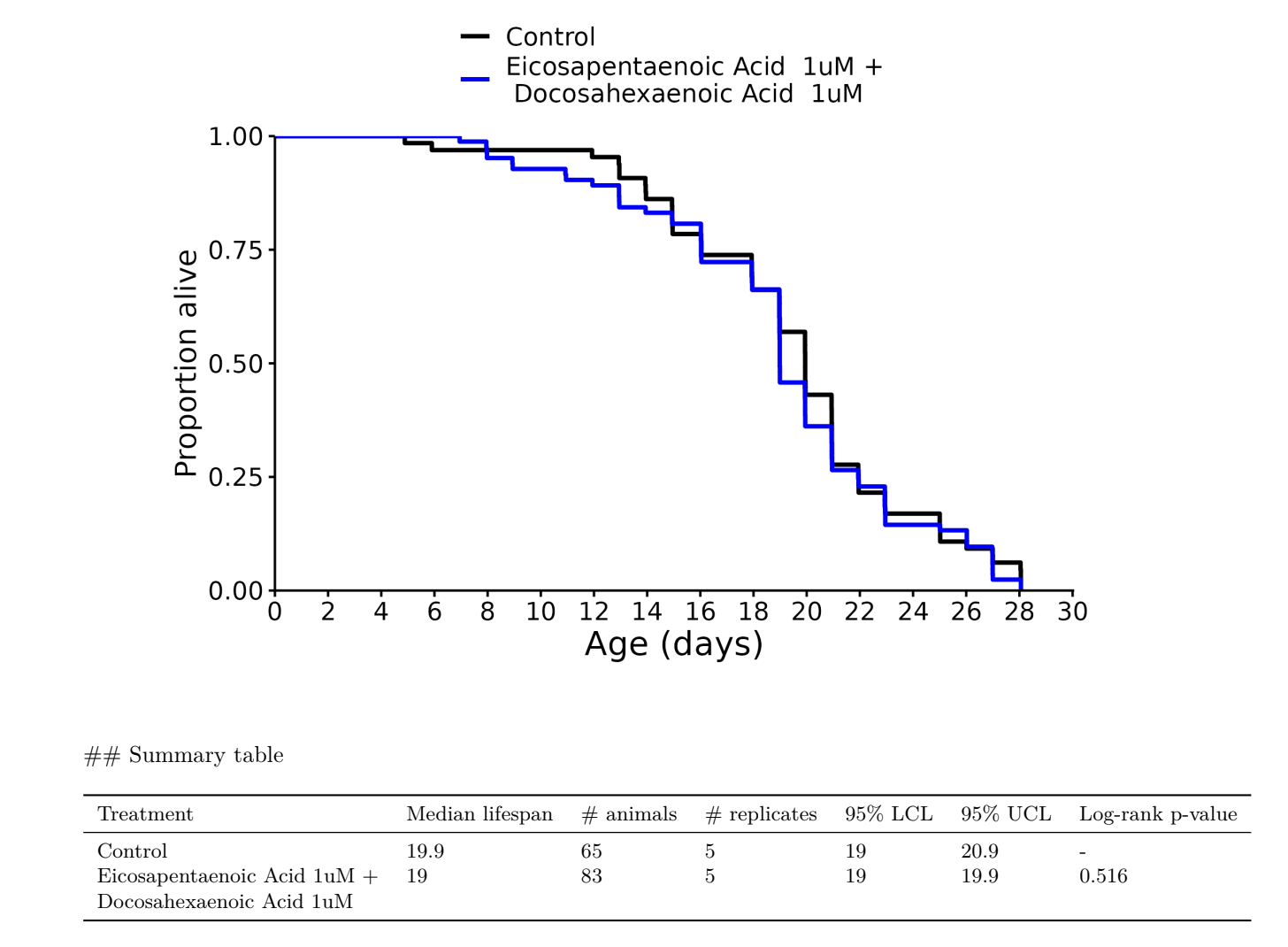
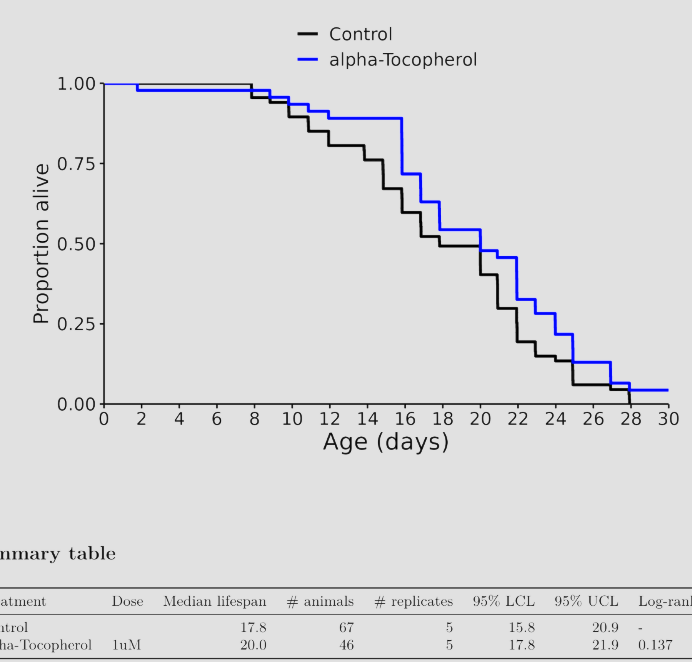
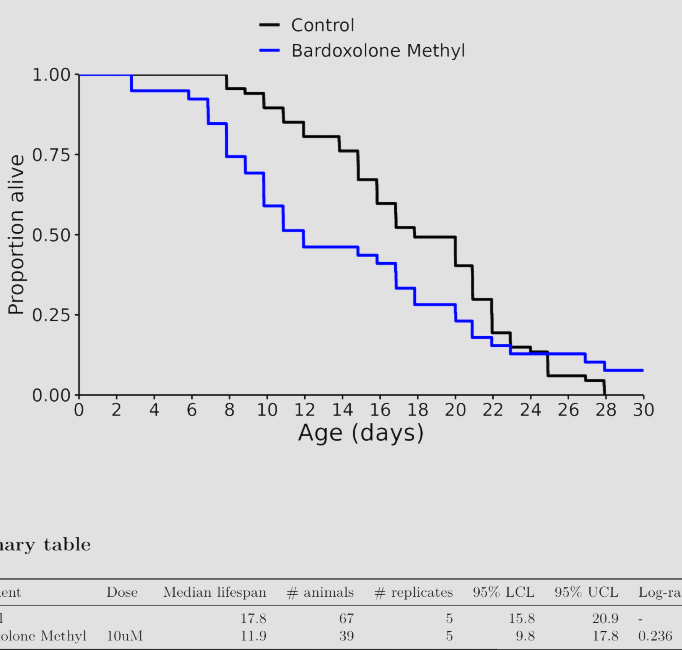
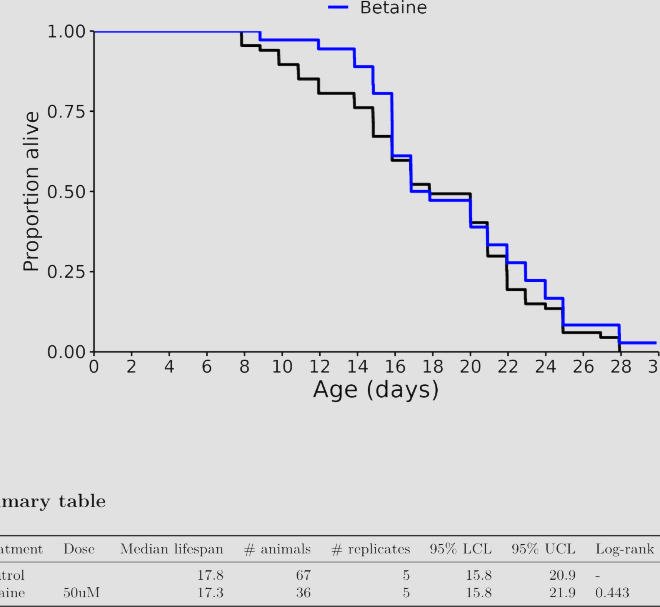
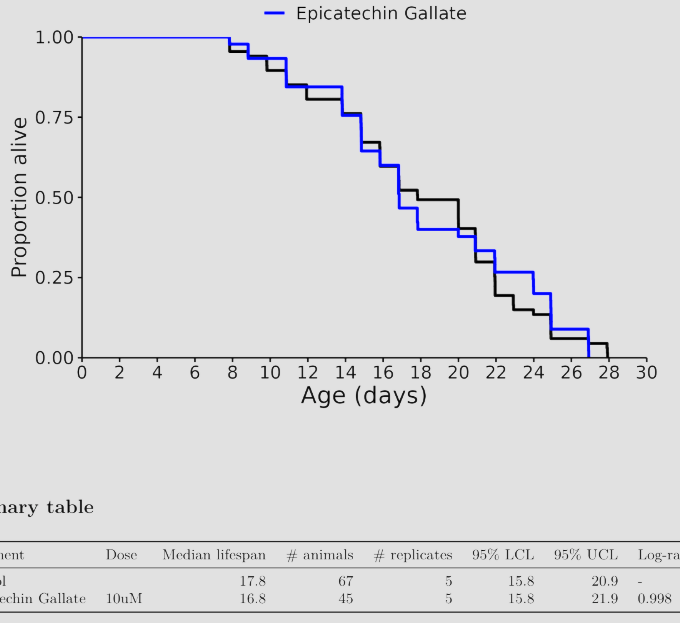
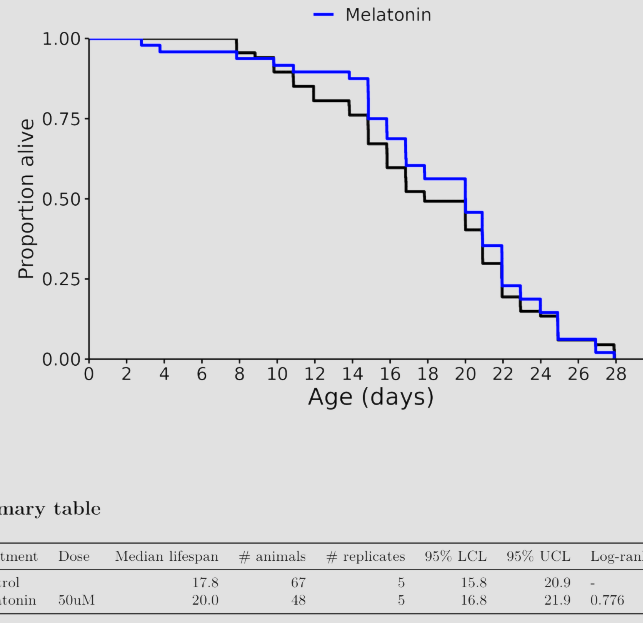
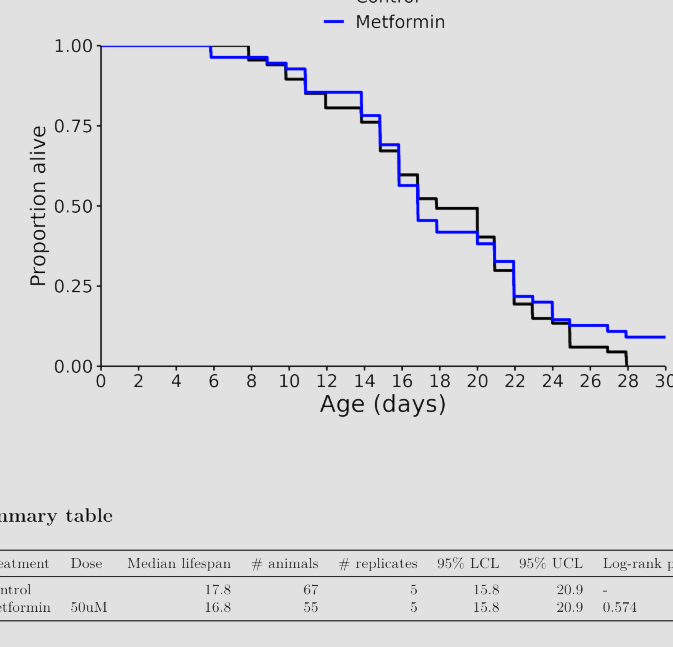
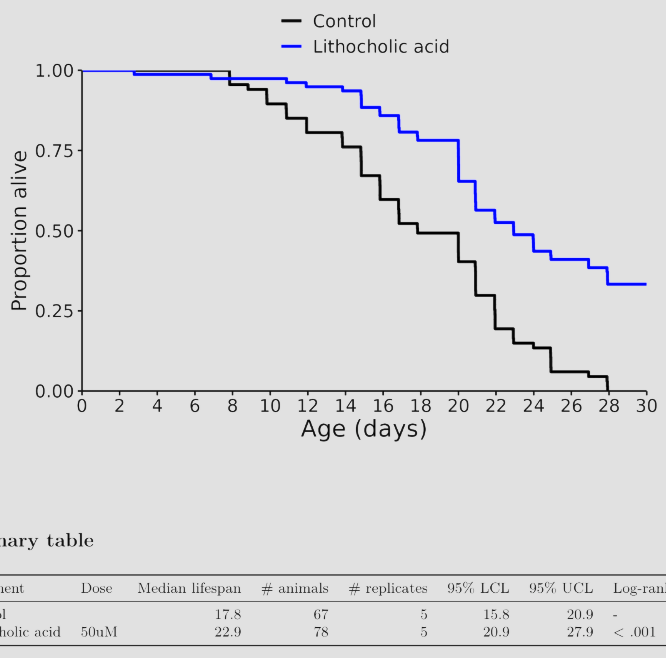
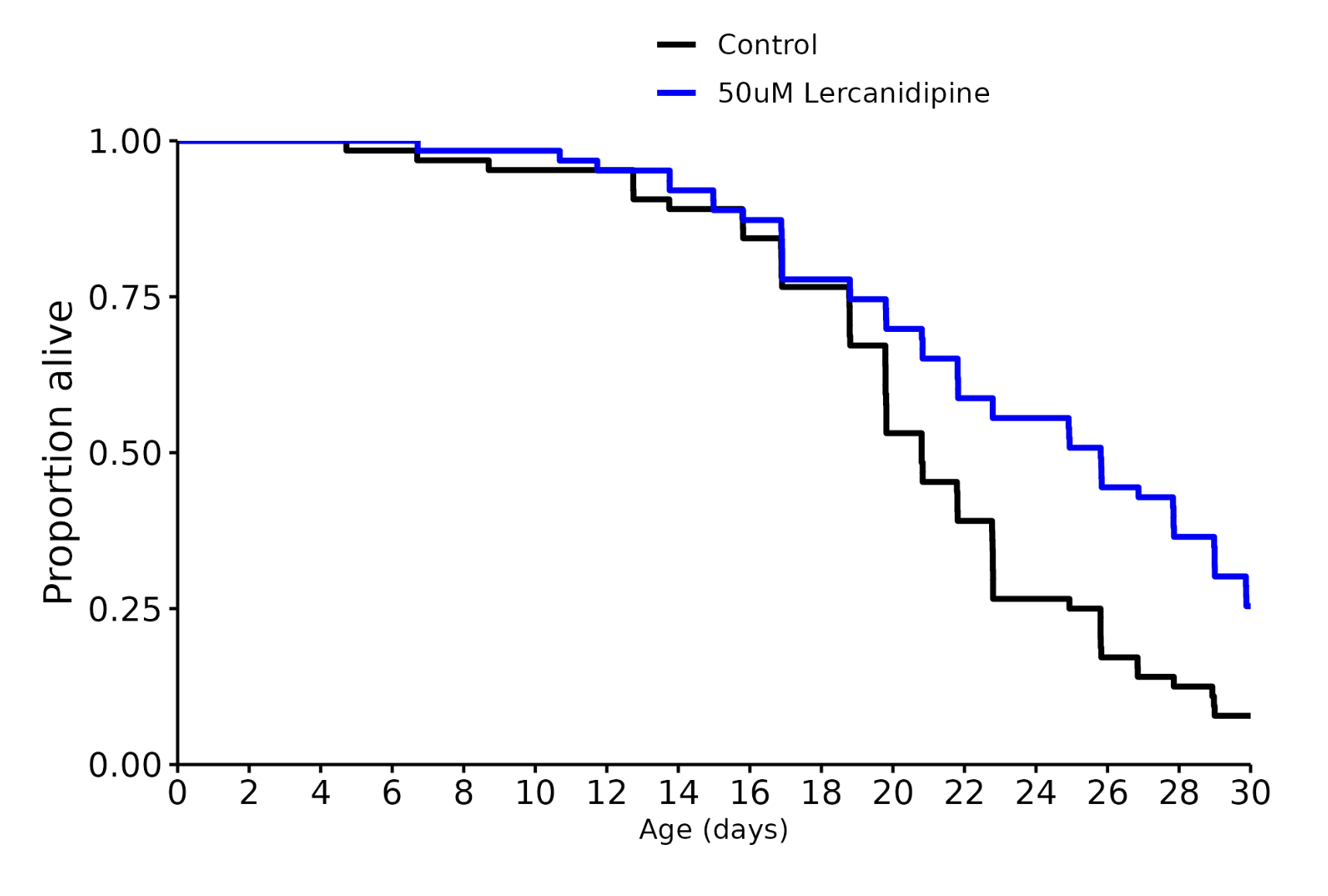
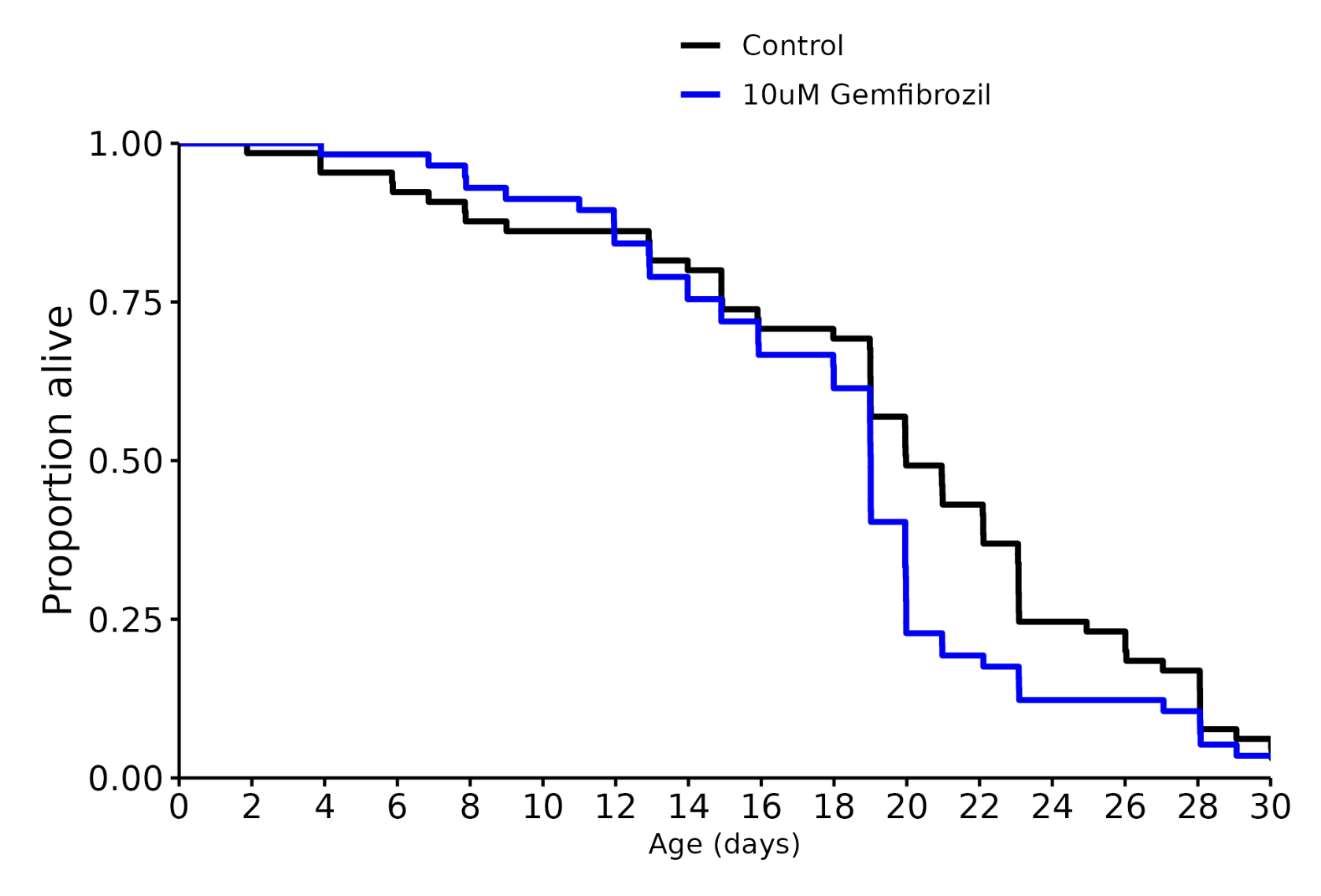
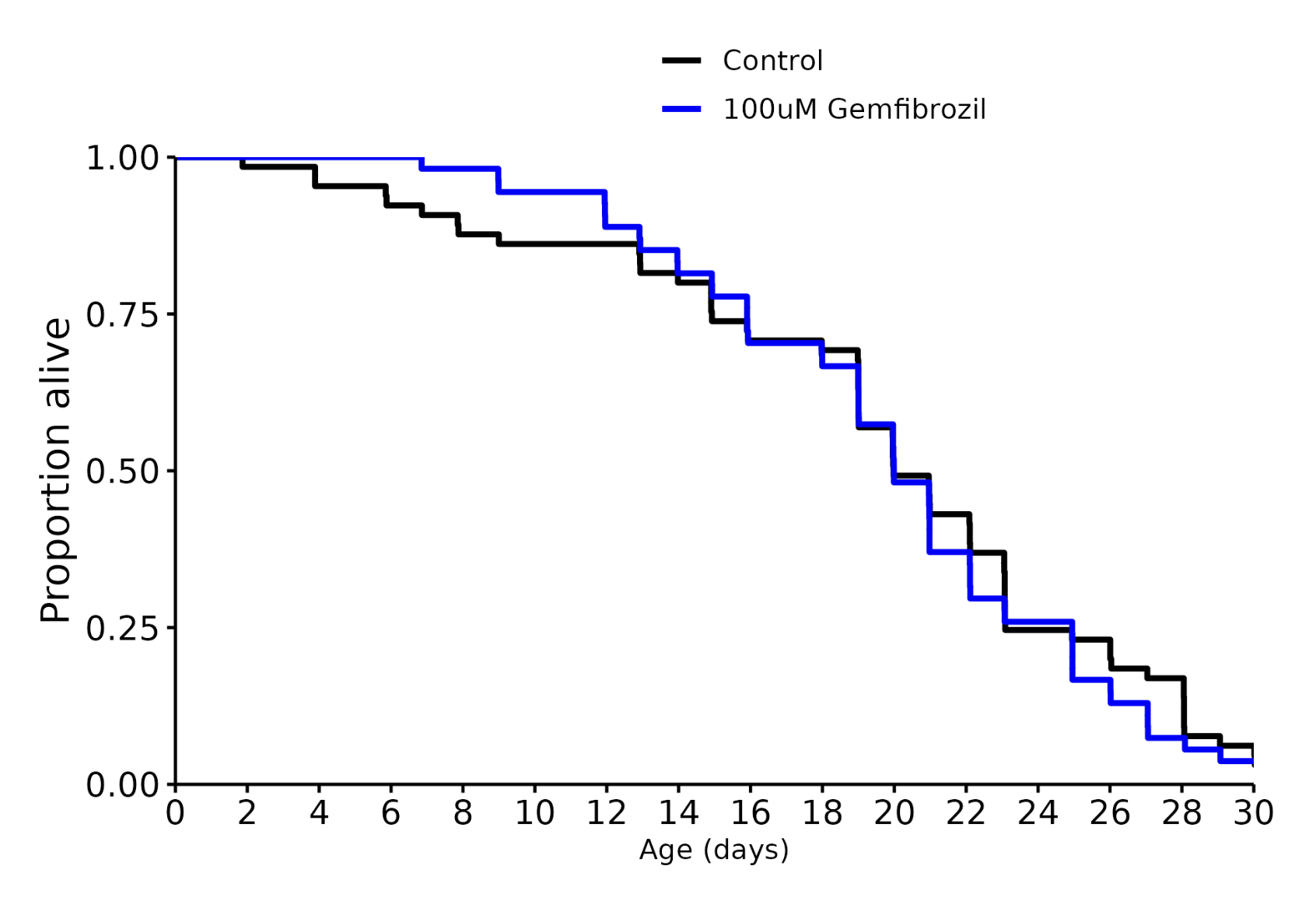
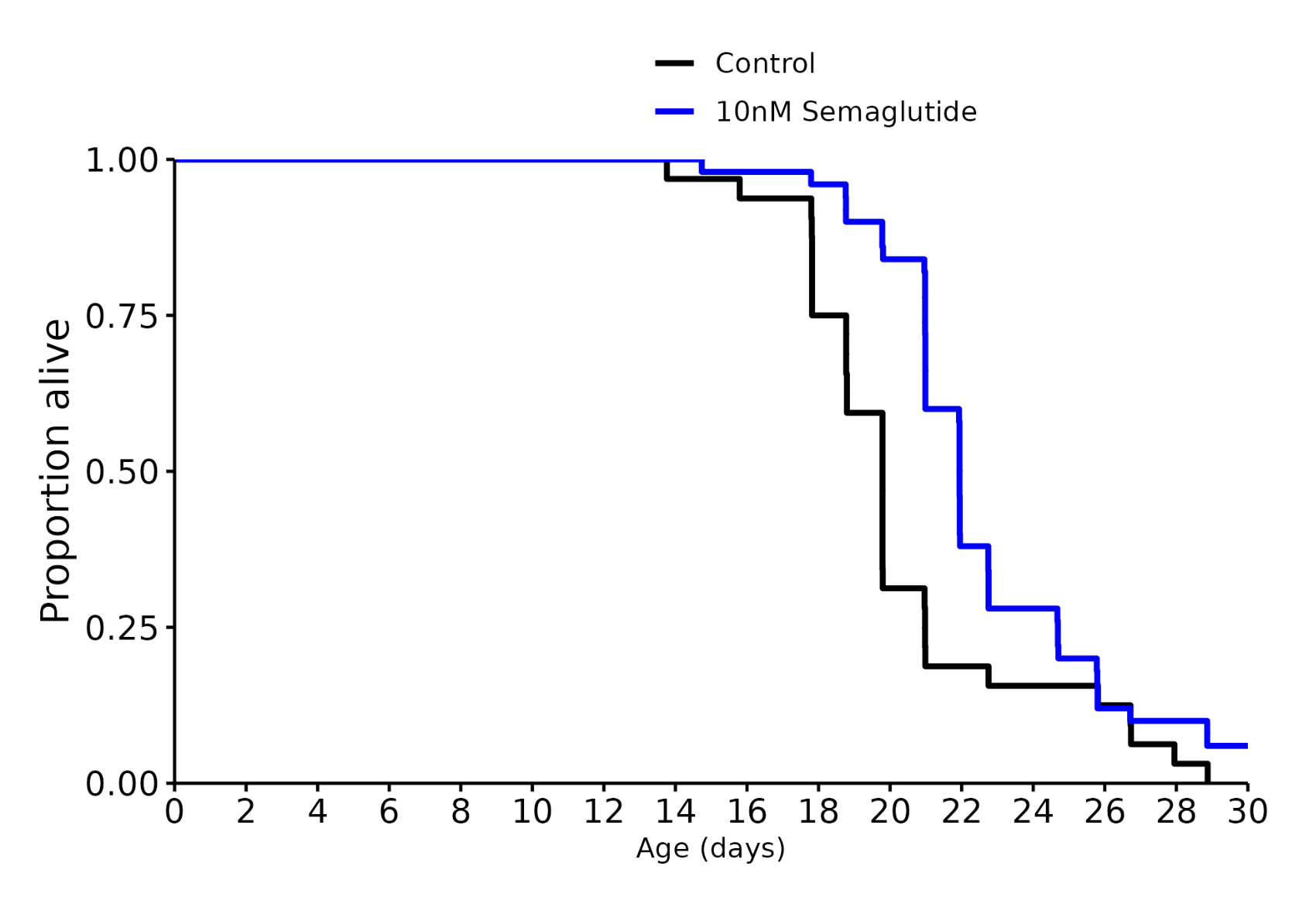
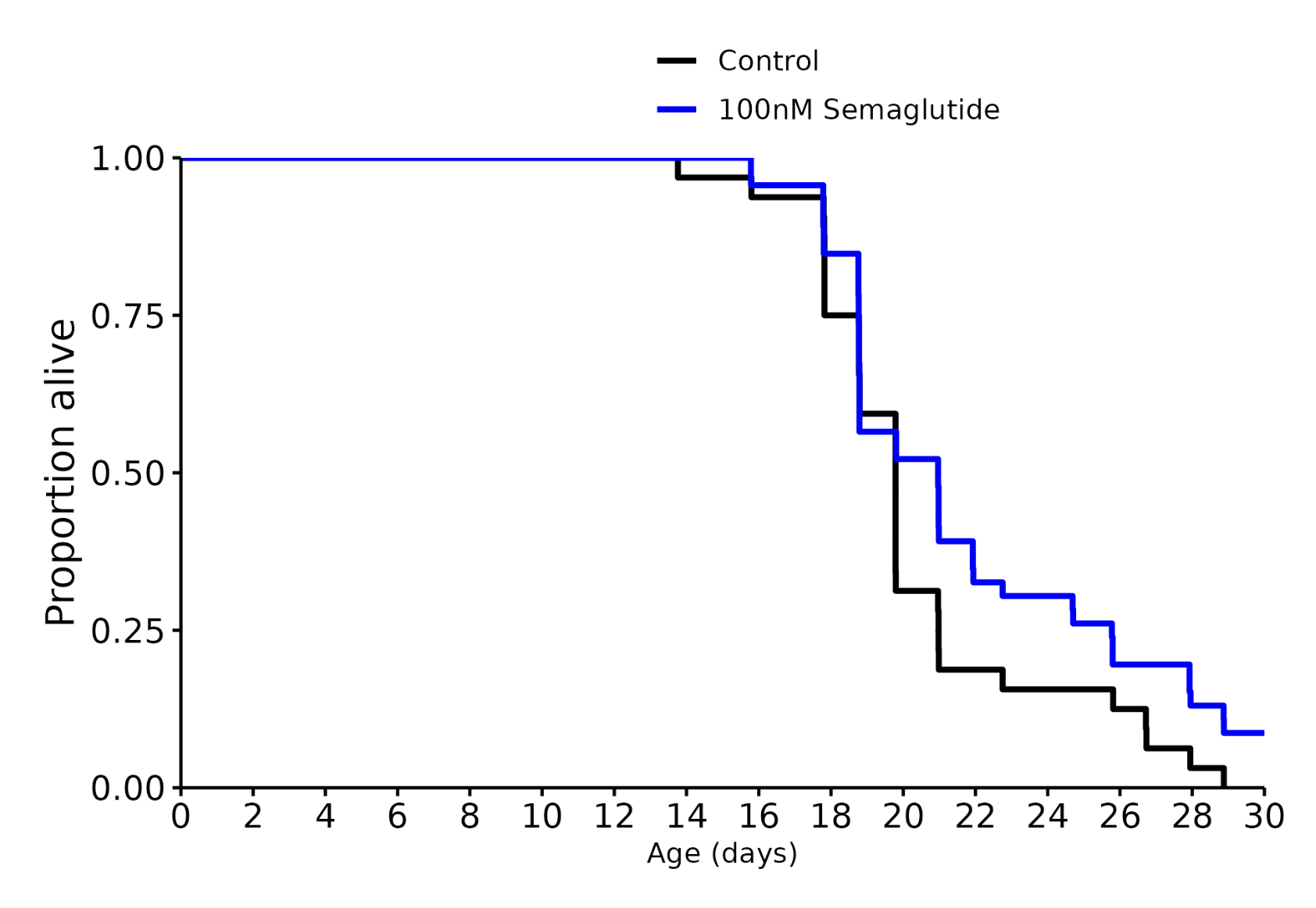
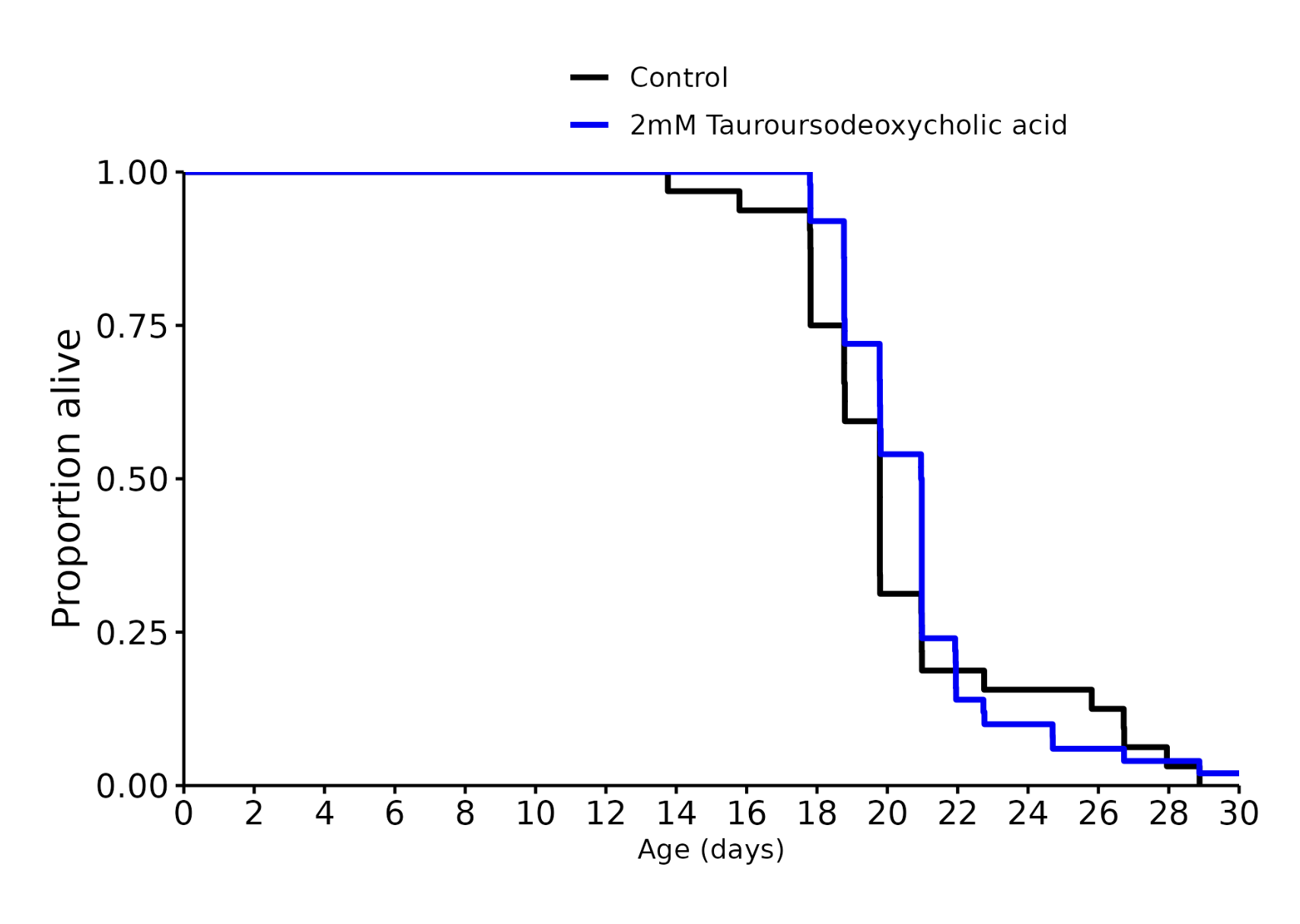
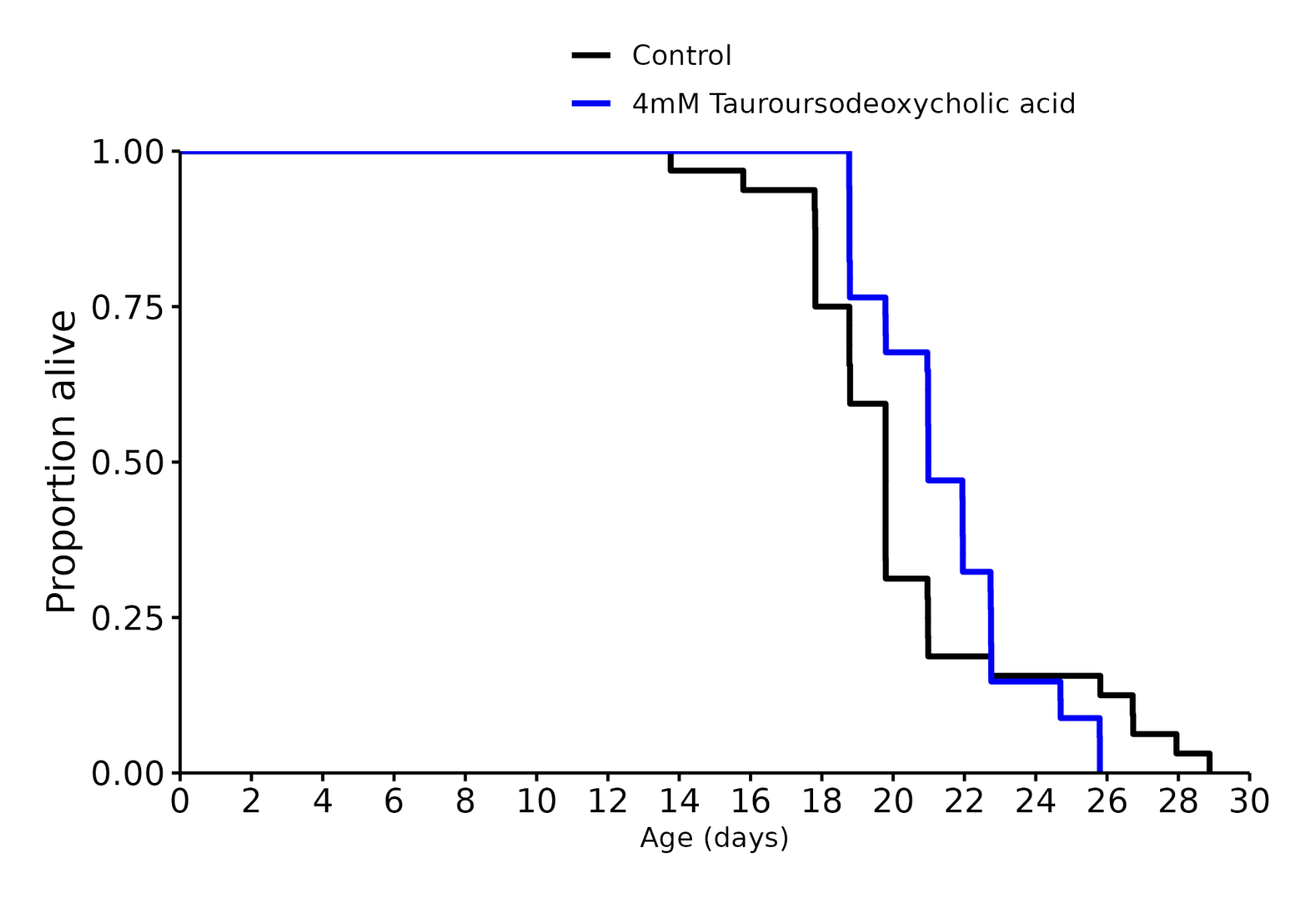
I don’t know, but I was referring to these charts in general across many different species involved in longevity studies. The median always seems to be more impressive than the life extension.
No, they don’t kill them off they end the experiment, so the curve can just not go to the bottom.
Of course. That makes more sense.
Shouldn’t effect the median either way unless the intervention was insanely effective, but you’re totally right about the graph. Thanks for pointing that out.
The lifespan equations I posted about a couple of weeks ago have a constant factor that is basically random entropic death. It may be that even if you have an unlimited lifespan, you will eventually be hit by a car.
New results:
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA): -5%
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA): -10%
EPA + DHA: -5%
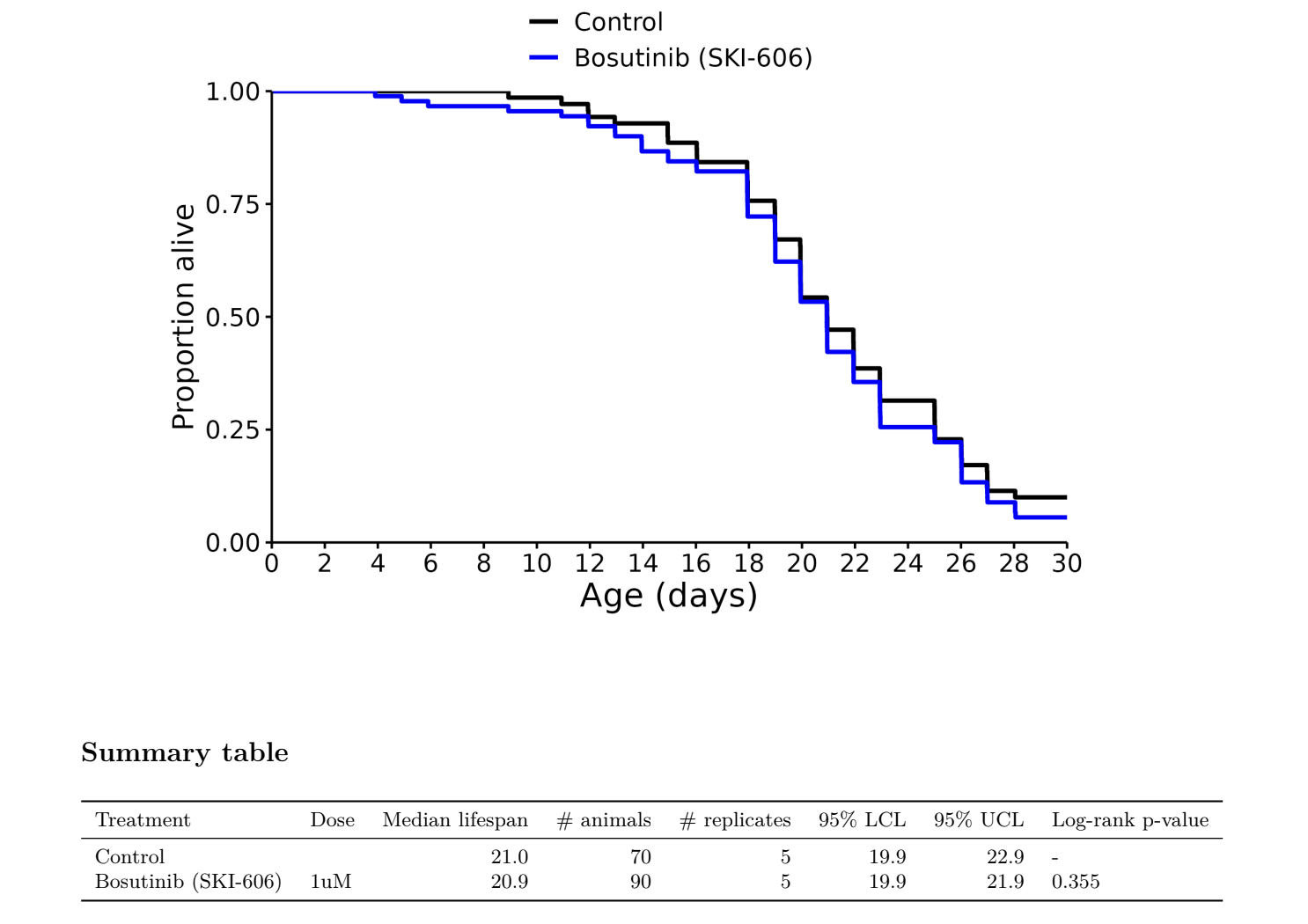
Bosutinib SKI-606: no effect
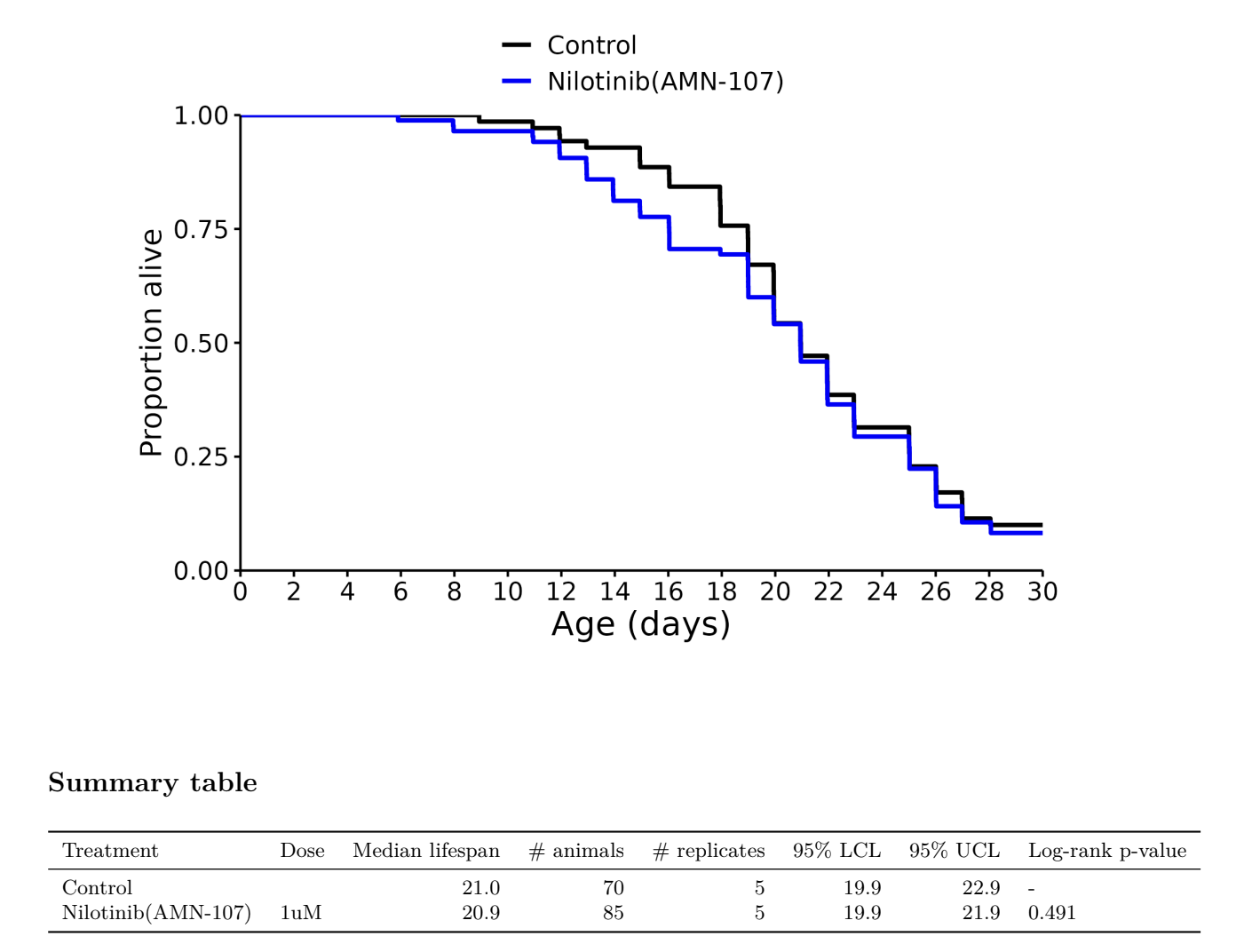
Nilotinib AMN-107: no effect
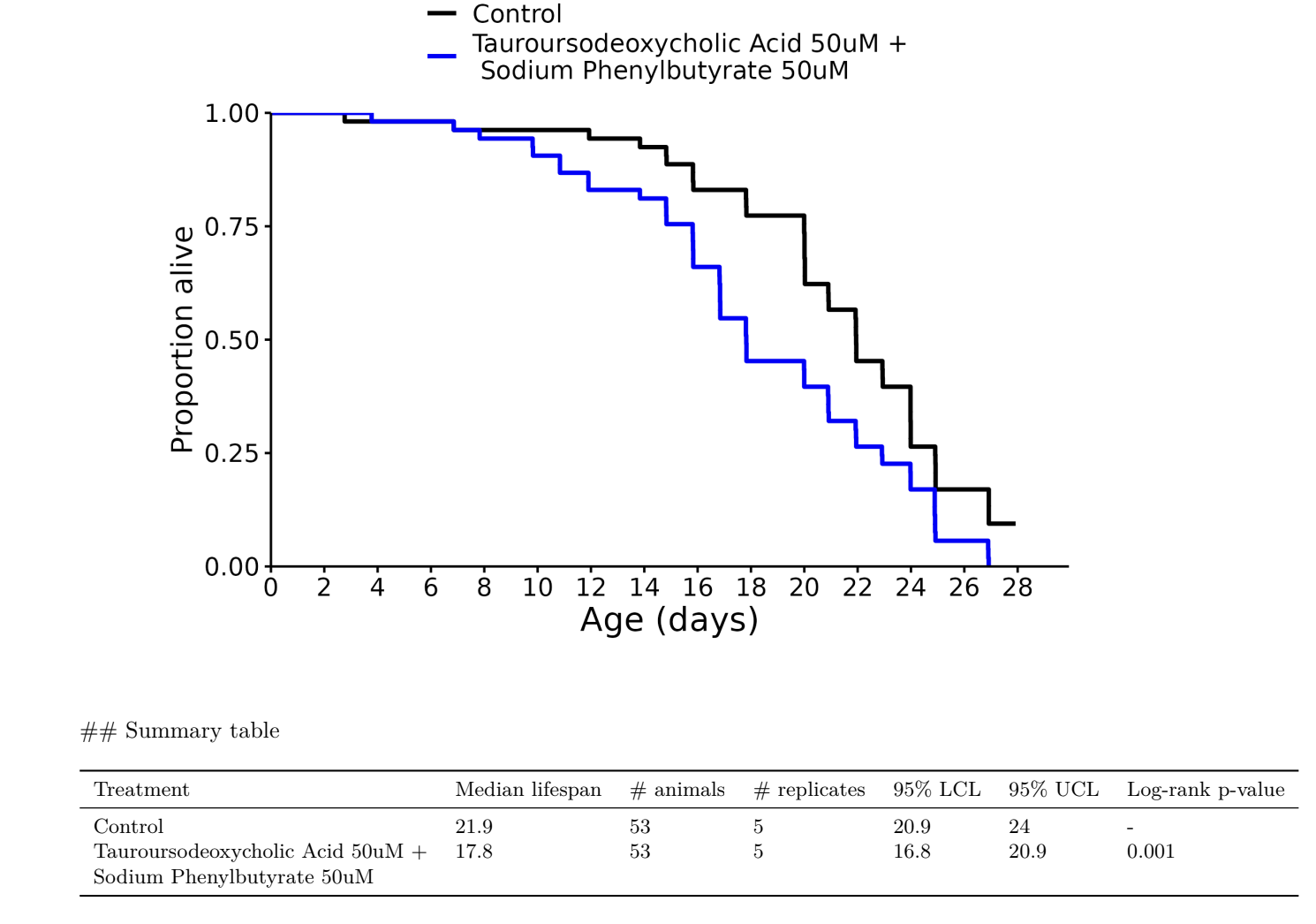
Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid (TUDCA) + Sodium Phenylbutyrate: -19%!
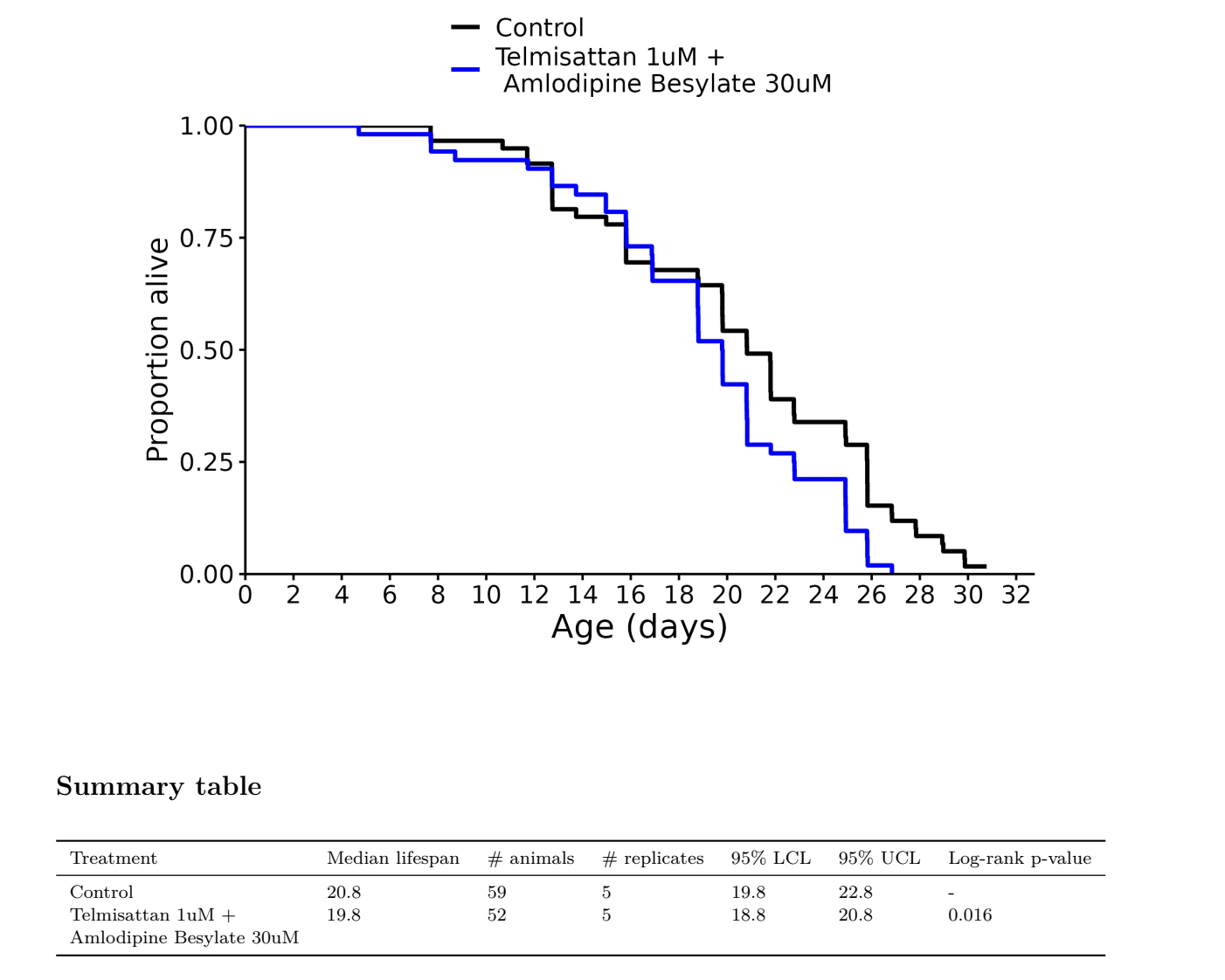
Telmisartan + Amlodipine: -5%
I presume these are all live food results.
Does either TUDCA or Phenylbutyrate have results on their own? It looks really bad…
Has the leaderboard been updated?
ChatGPT:
Lithocholic acid (LCA), a secondary bile acid produced by gut bacteria, has inhibitory effects on Escherichia coli (E. coli), particularly due to its detergent-like properties and ability to disrupt bacterial membranes.
Key Effects of LCA on E. coli:
- Membrane Disruption
- LCA is hydrophobic, and it can insert into lipid bilayers, causing membrane destabilization, leakage of cellular contents, and eventually cell death.
- Inhibition of Growth
- LCA inhibits the growth of many gram-negative bacteria, including E. coli, by interfering with nutrient transport, protein folding, and cell signaling.
- Resistance Mechanisms in E. coli
- Some E. coli strains express efflux pumps (like AcrAB-TolC) that expel bile acids to survive in bile-rich environments (e.g., the gut).
- These adaptations can modulate the bacterium’s sensitivity to LCA.
- Modulation of Gene Expression
- LCA can affect the expression of stress response genes, such as those involved in oxidative stress and membrane integrity.
- Potential Synergy with Antibiotics
- Some studies suggest that bile acids like LCA can sensitize E. coli to antibiotics by increasing membrane permeability.
Supporting Study:
- Begley et al., “The interaction between bacteria and bile” (FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2005): Reviews how bile acids, including LCA, affect gut bacteria and outlines E. coli’s defense strategies.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2005.04.002
Would you like more detailed molecular pathways or information on its use in antimicrobial strategies?
Well one writeup mentioned LCA may cause cancer and do liver damage. I’d suggest waiting a bit. This may be a machine error or a worm specific effect.
Yes. Great caution advised if we see an effect in just one species, as it may address a specific vulnerability in that species and not some broad slowing down of aging. Bacteria are food for these worms, so any molecule that weakens or makes the bacteria more available to the worm, might have outsize effects that are mostly irrelevant in more complex species. What’s nice about rapamycin, is that it appears that it works to a greater or lesser degree across many species up and down the evolutionary tree, so it seems it’s an evolutionarily preserved pathway, increasing the odds that it might work in humans, at least to some degree. It seems rapa works from worms up to monkeys - so we’re getting closer and closer to humans. Once you get to the great apes (that study is not happening!), we’ve pretty much tapped out what can be gleaned from animal models. And that means we need human studies.
The worms are just a start - a very, very, remote start. It needs a ton of validation from here. Mice and the ITP next. It’s a long road.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.910493/full
There is a lot here on LGA. This looks like, maybe, the start of drug discovery and not something you would want in a supplement. The problem here being that drug discovery takes so long you may need an anti-aging intervention to wait for it.
Follow up, this is a substance the worm cannot synthesize (but more advanced organisms can). The outsized effects on lifespan may be worm specific. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-08329-5
As you can see I think this is an E. Coli specific effect. Some of the best interventions on worms act through killing their food (which is E. Coli).
Similarly Melatonin has a range of effects on E. Coli which we cannot isolate from any effect on the worms.
Another reason I am not a fan of the WormBot is that worms don’t really have senescent cells.
From this alpha tocopherol seems to be good, but it has its own limits.
Vitamin E toxicity-induced coagulopathy has been described at high levels of serum alpha-tocopherol, but there is a case report of intracranial hemorrhage attributed to vitamin E toxicity occurring at serum alpha-tocopherol level of 23.3 mg/L
Personally I take a small amount of vitamin E twice a week as part of a multivitamin. However, I don’t think in the long term it is a “longevity” supplement. Whereas I do think melatonin is notwithstanding the results from WormBot.
An idea just came to mind: Lung cancer patients were given drugs in a trial and their gray hair turned dark. Gray hair reversal could be a sign of serious rejuvenation.
The drugs used were Nivolumab, Atezolizumab and Pembrolizumab.
They seem like a good candidate for the Ora Biomedical Million Molecule Challenge. Individually, grouped up in 2s, all 3 at once and each one of those paired with rapamycin, and separately rapamycin/acarbose.
Looks like we both sponsored LCA. Wasn’t marked as sponsored and still isn’t…guess I’ve got a mail to write
Lercanidipine: +24%! And many still alive.
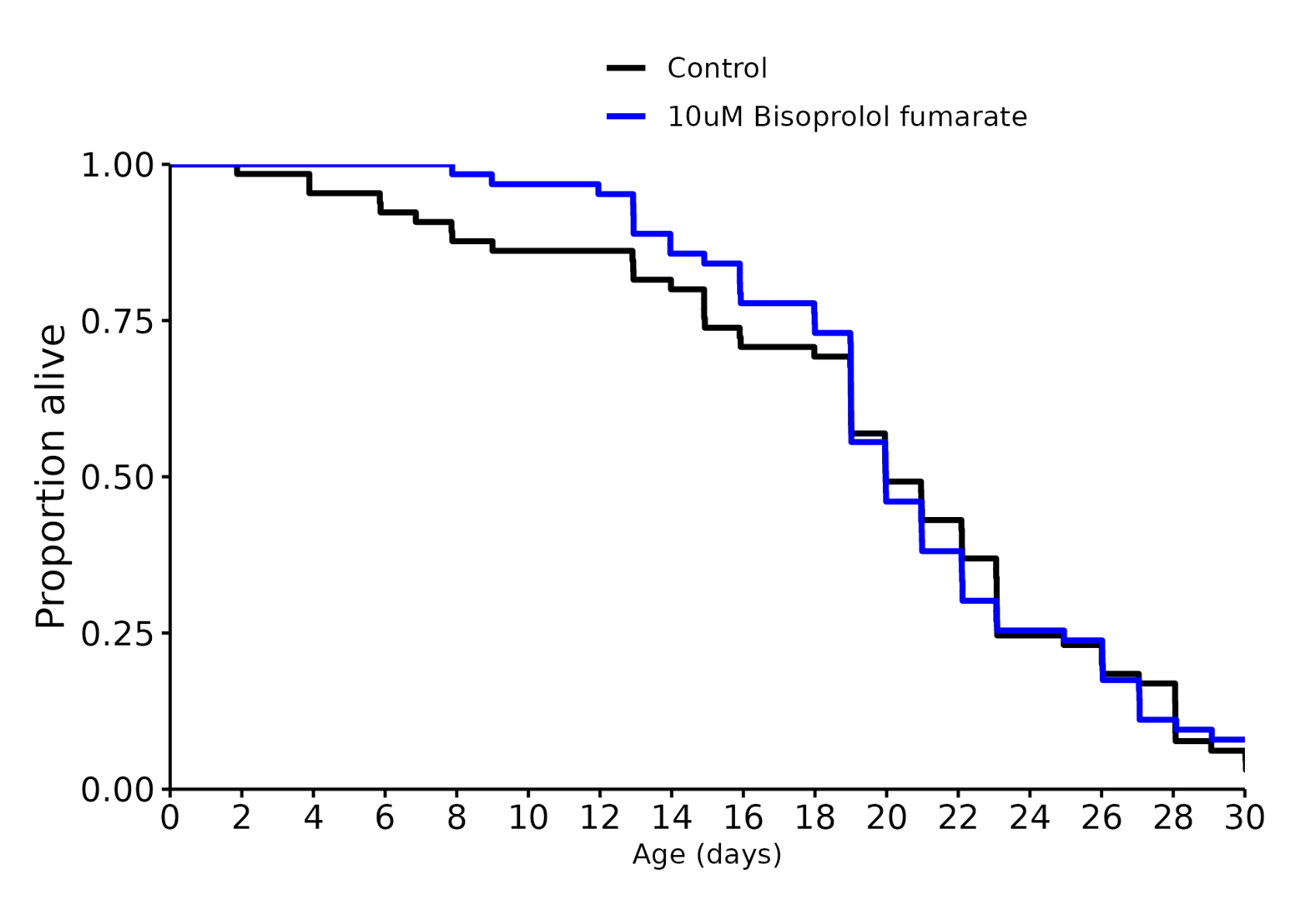
Bisoprolol: +0%
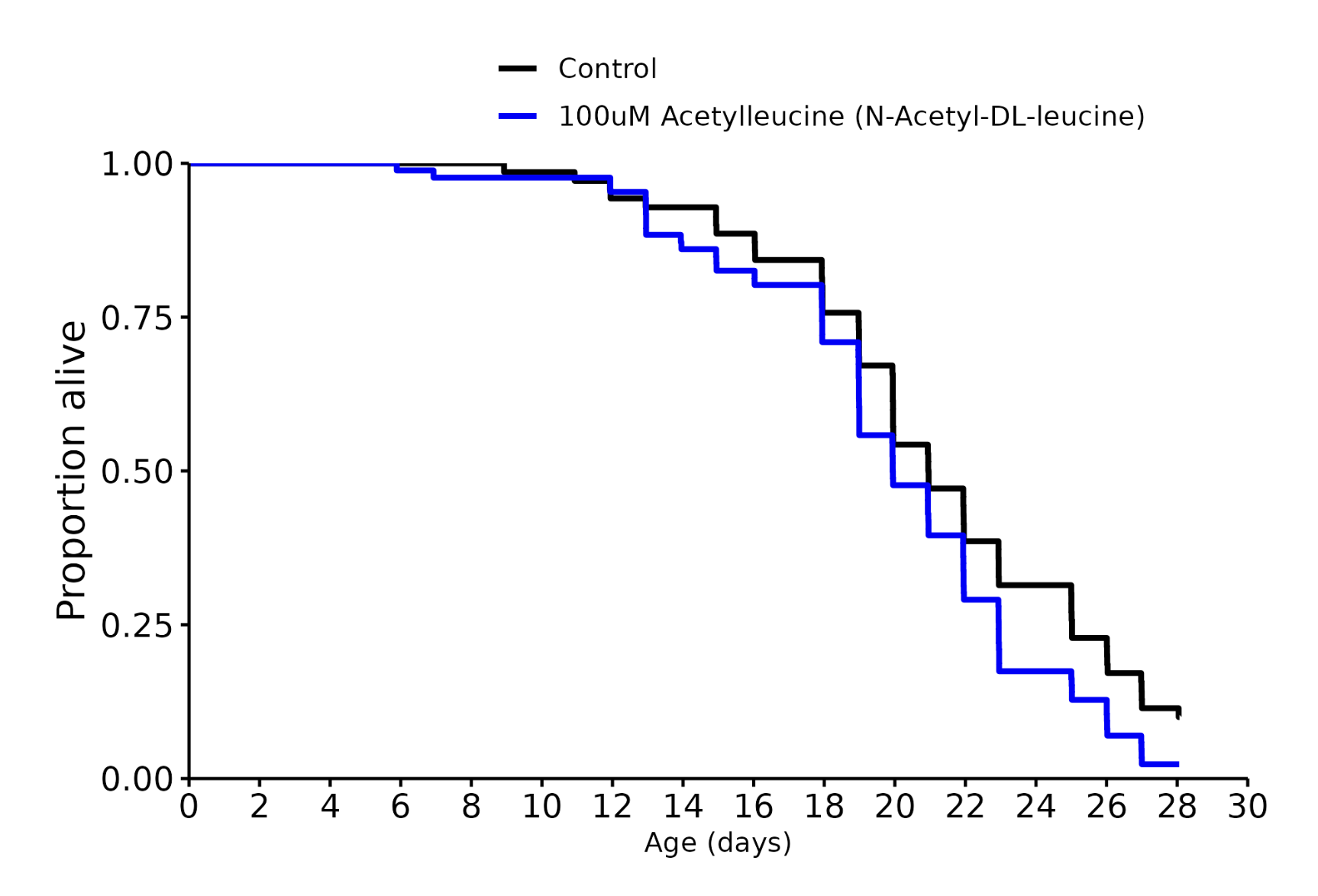
N-acetyl-DL-leucine (Tanganil): -5%
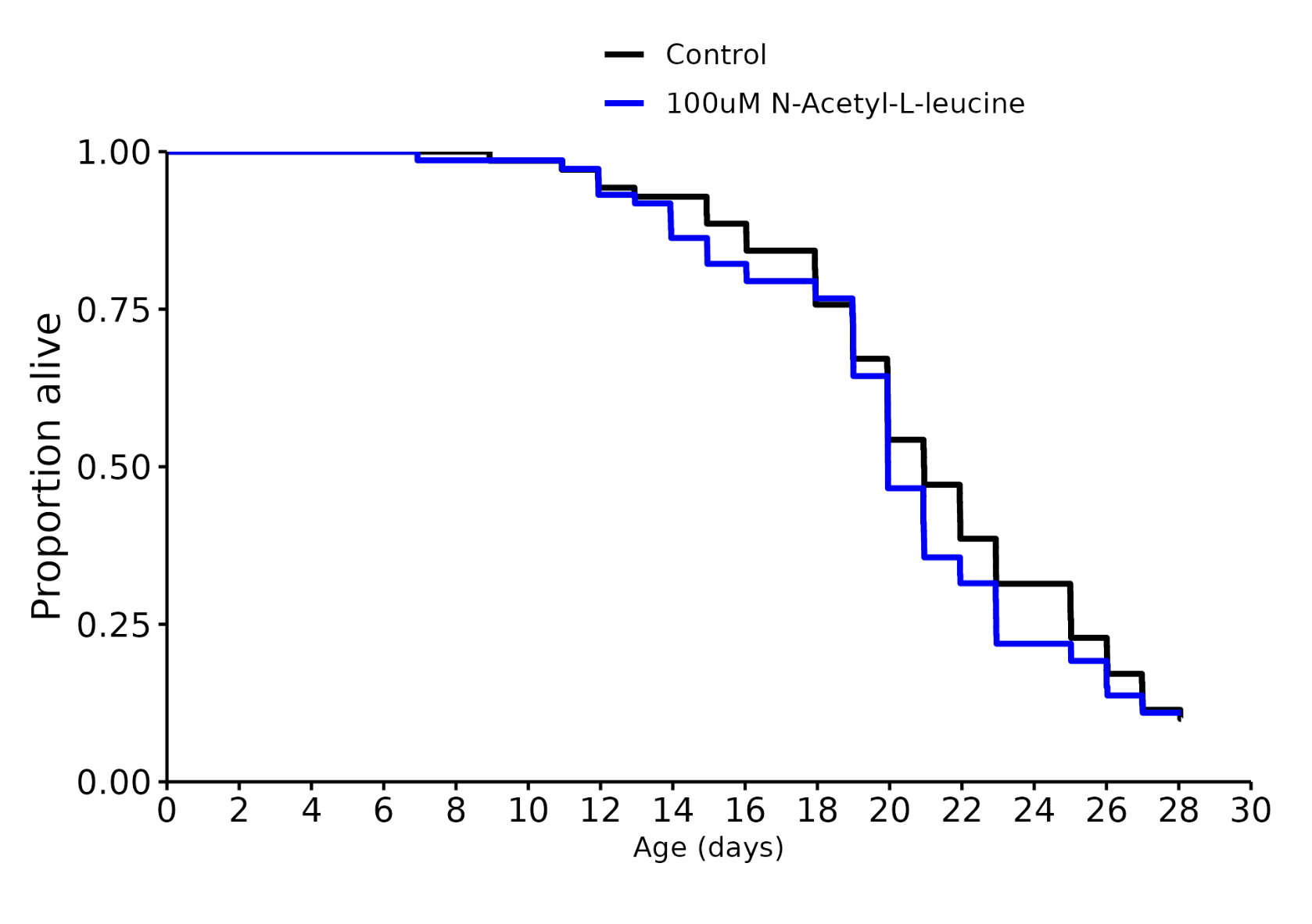
N-acetyl-L-leucine: -5%
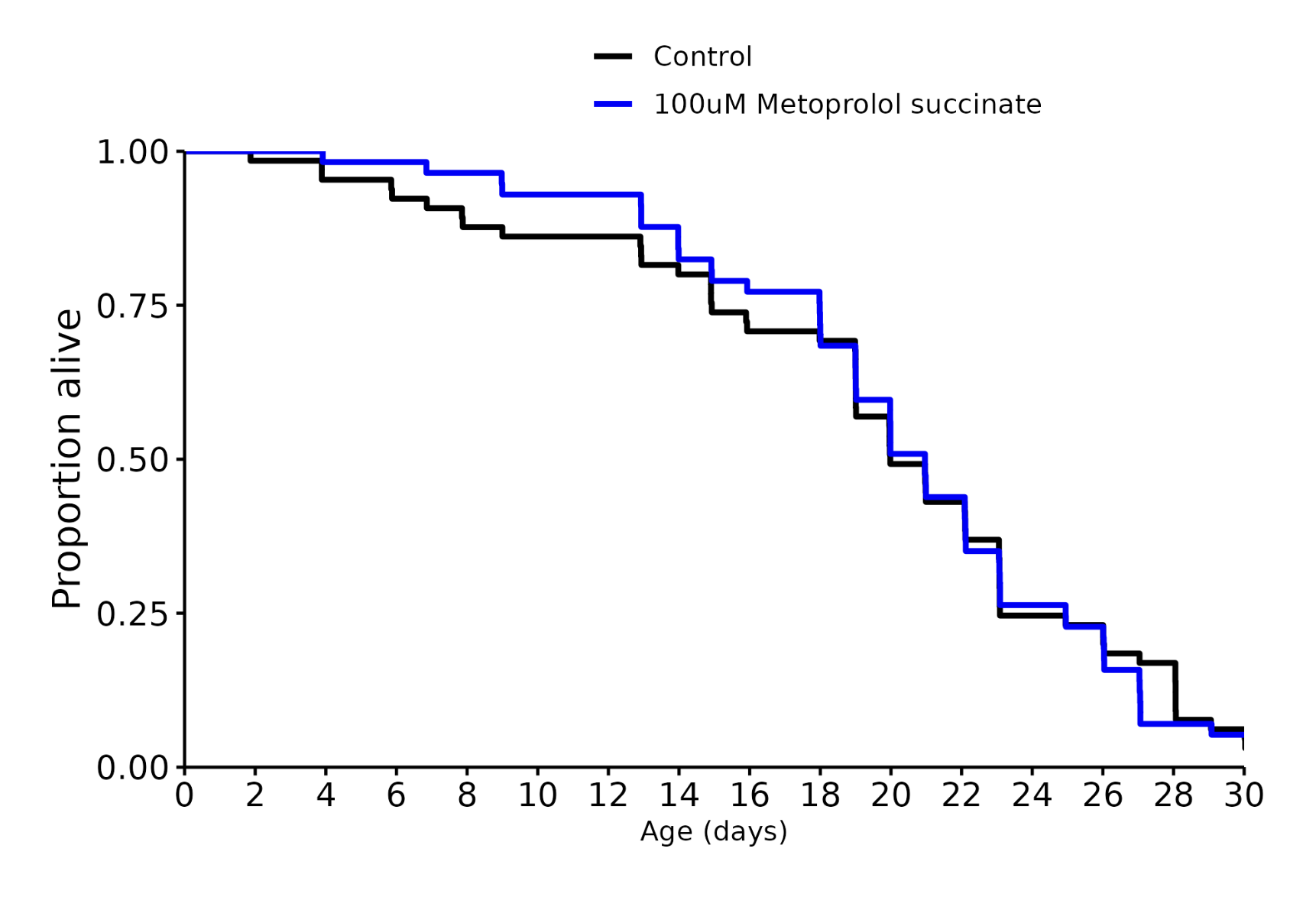
Metoprolol: +5%
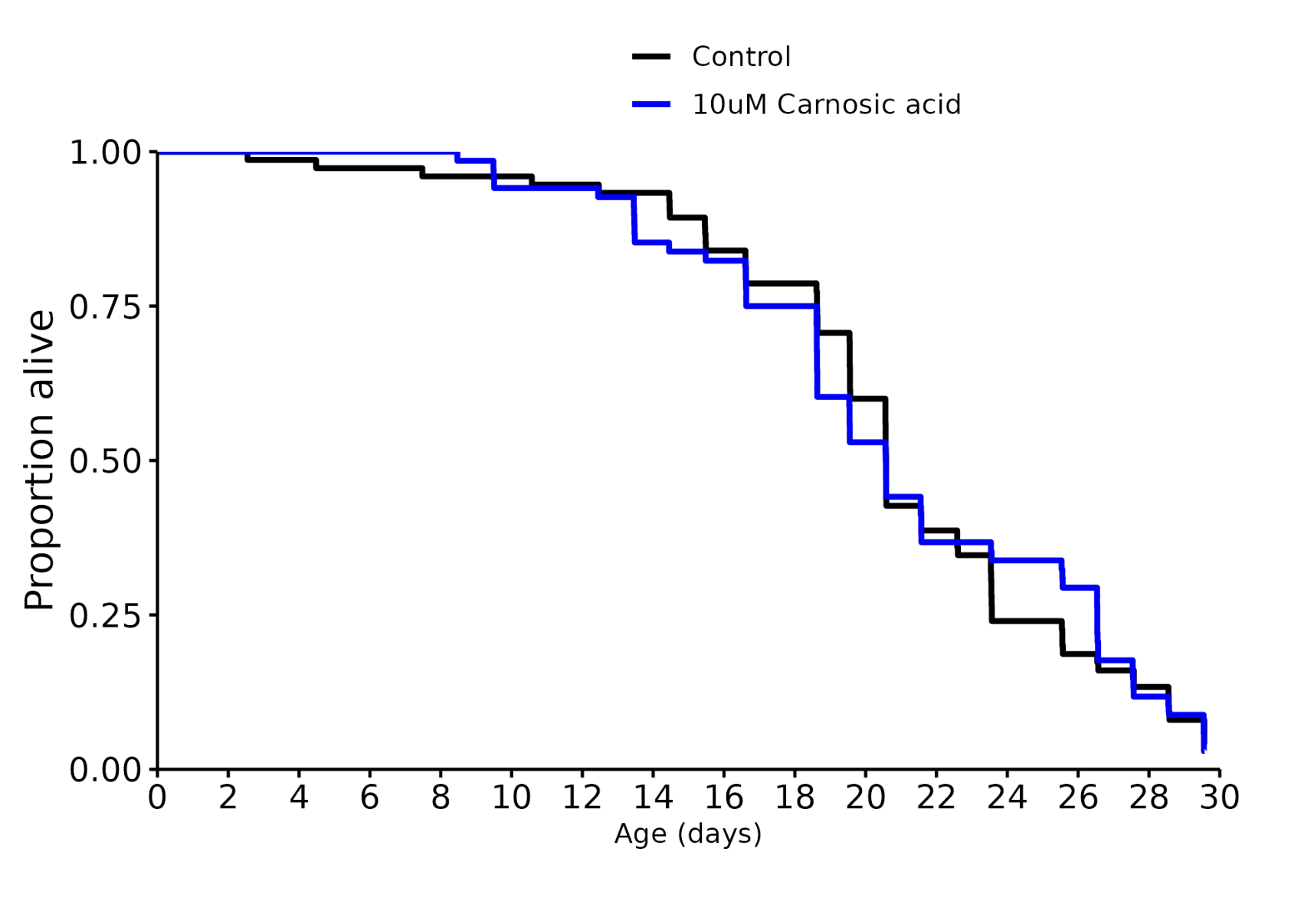
Carnosic acid: +0%
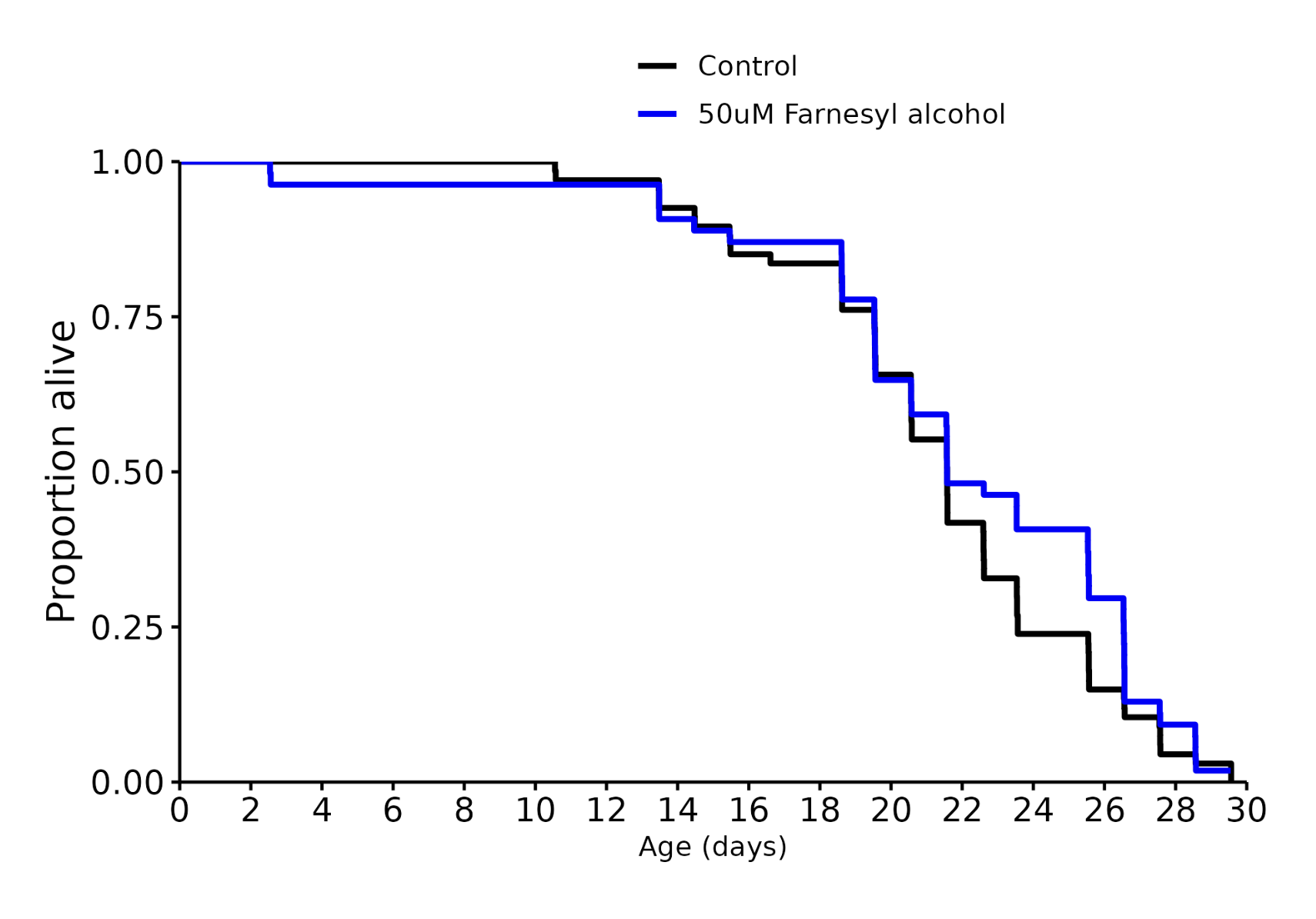
Farnesyl alcohol: +0%
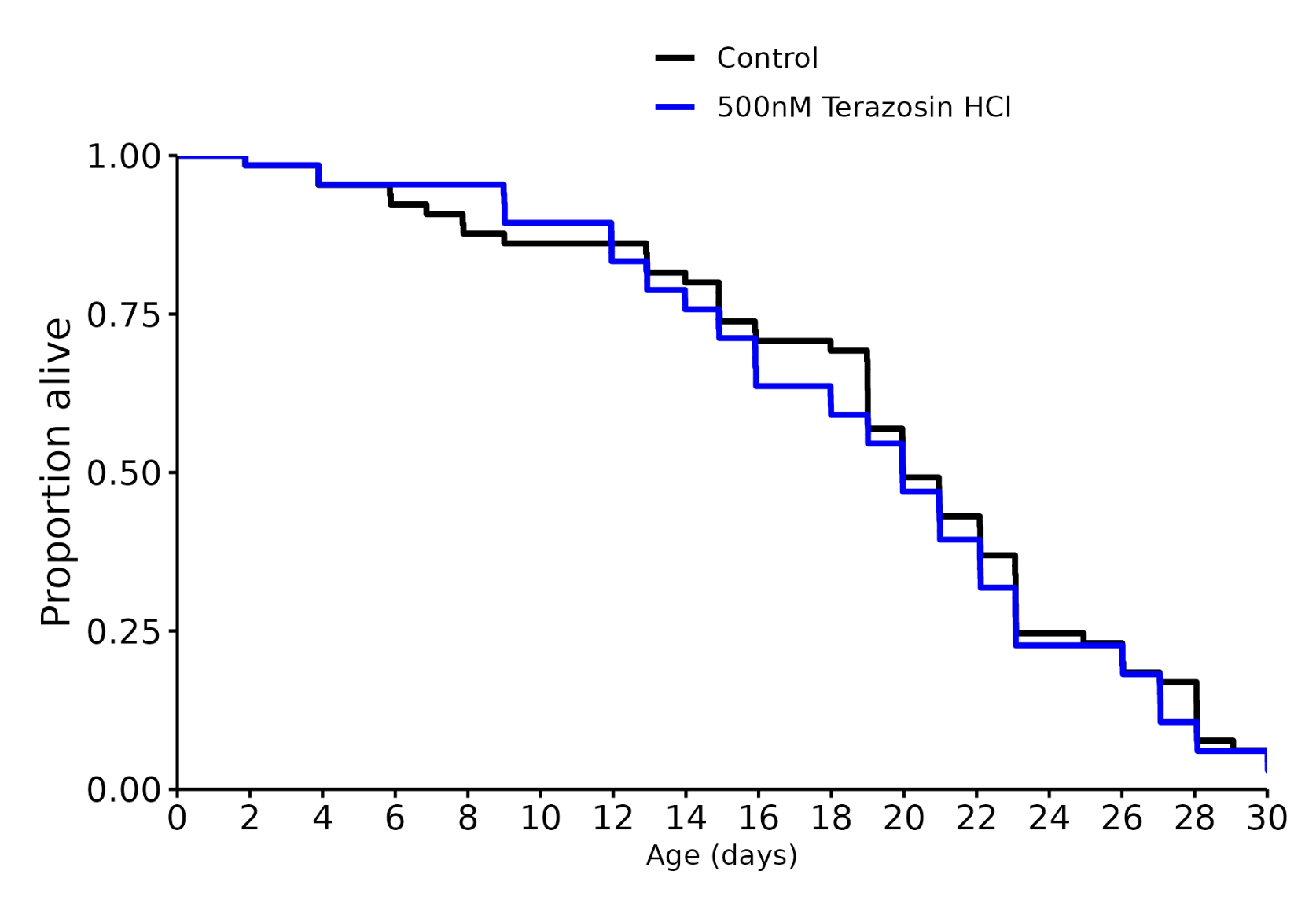
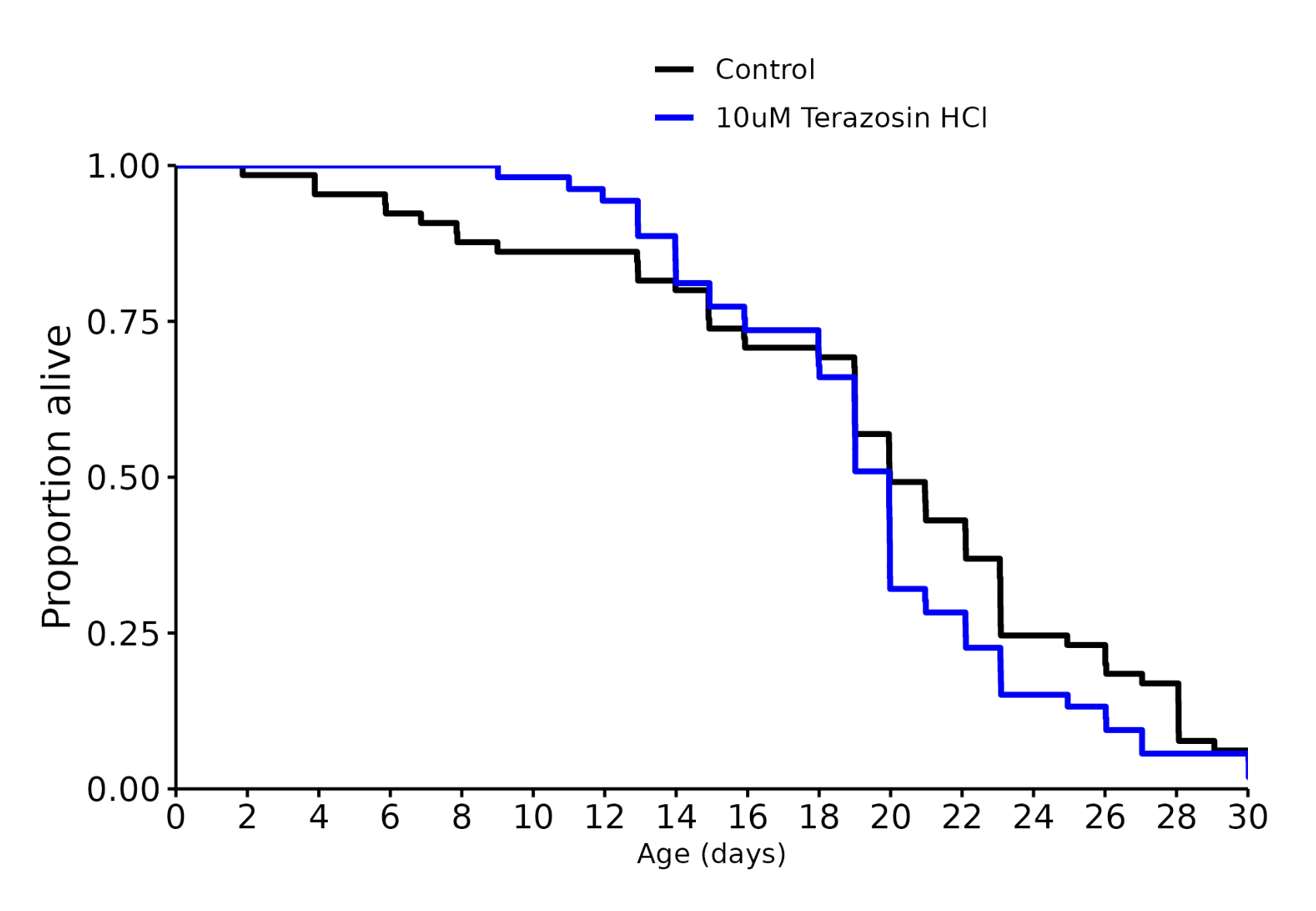
Terazosin 500 nM: +0%
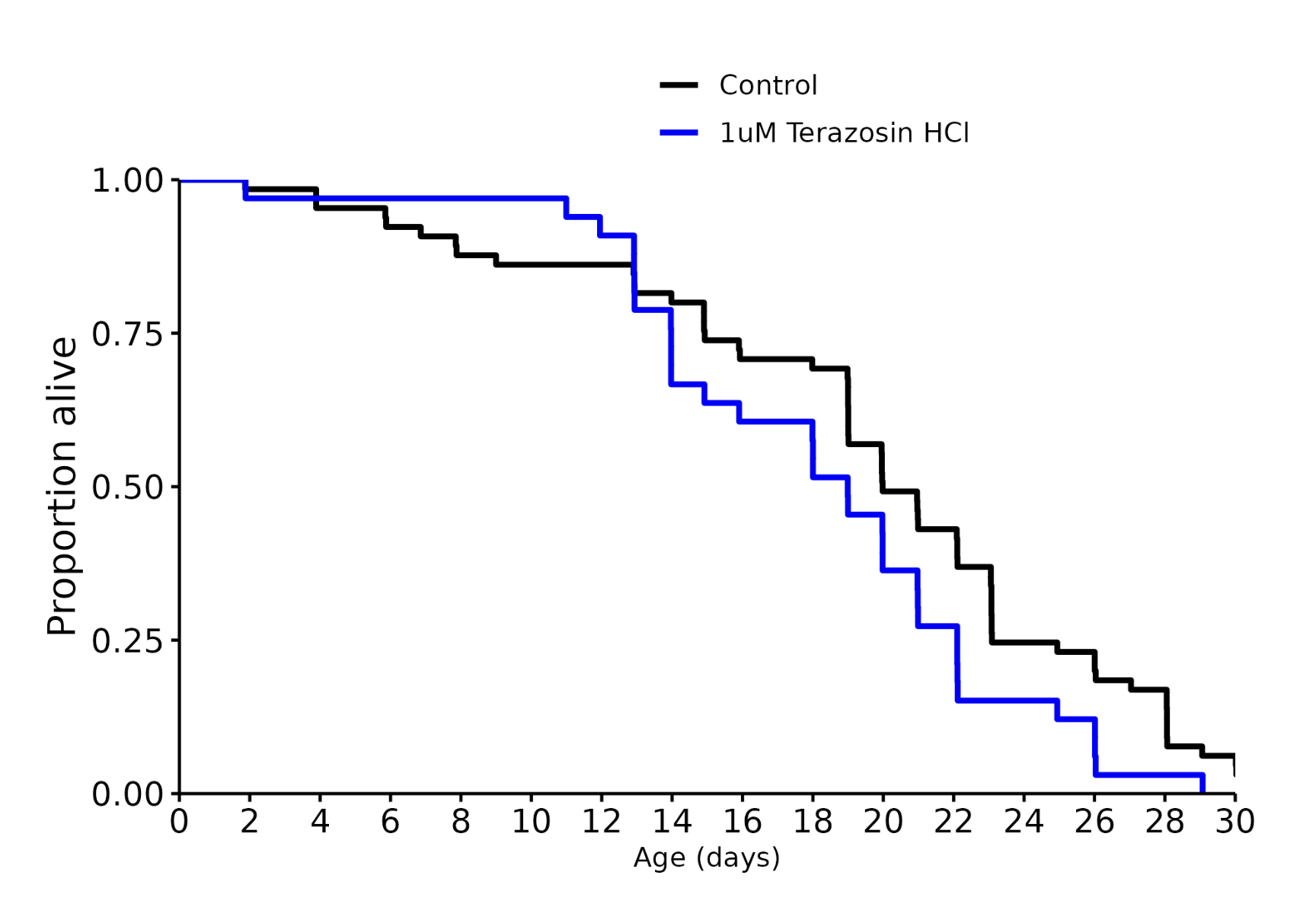
Terazosin 1 uM: -5%
Terazosin 10 uM: +0%
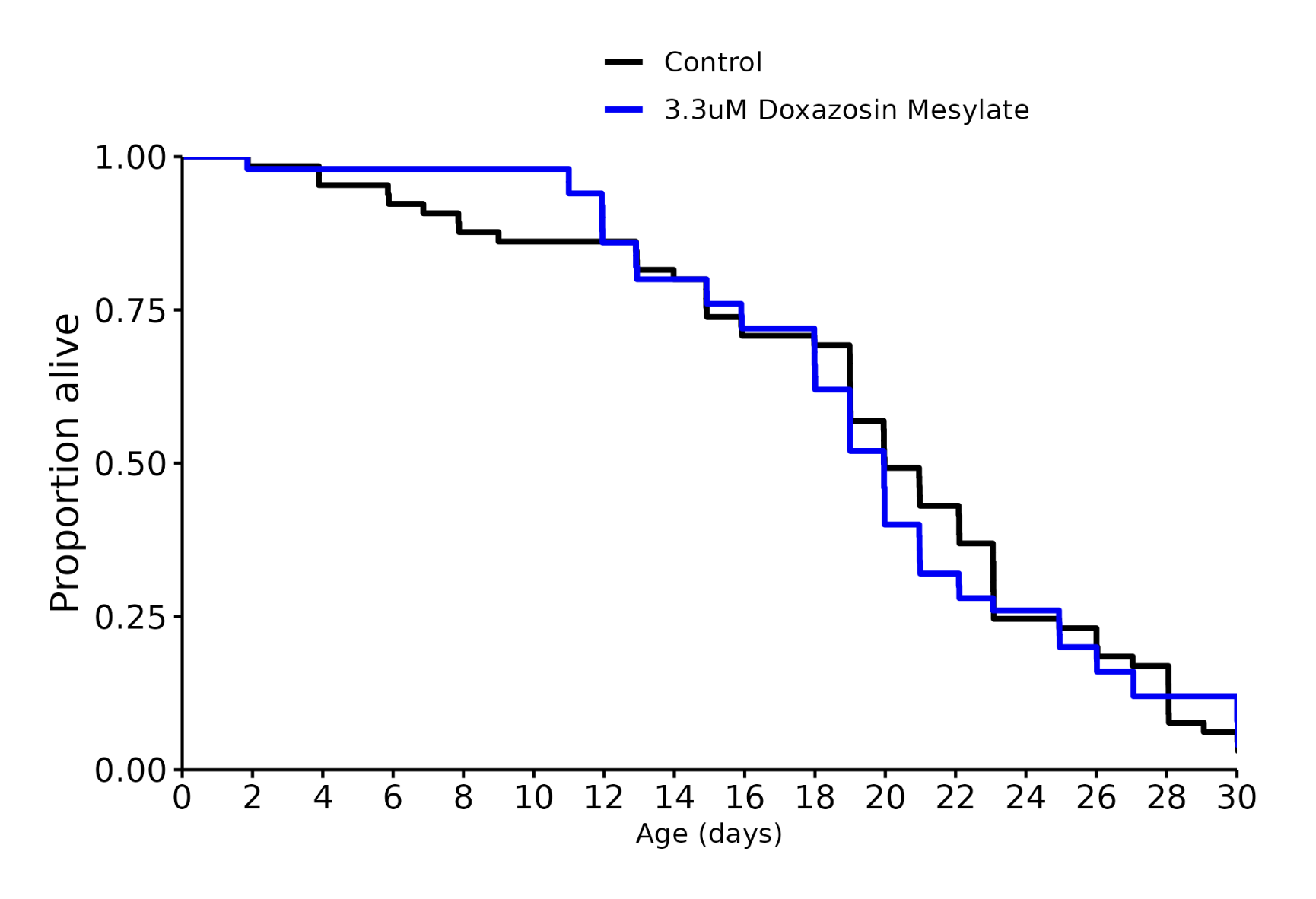
Doxazosin 3.3 uM: +0% (disappointing after a previous good result: Ora Biomedical Million Molecule Challenge Results - #229 by adssx )
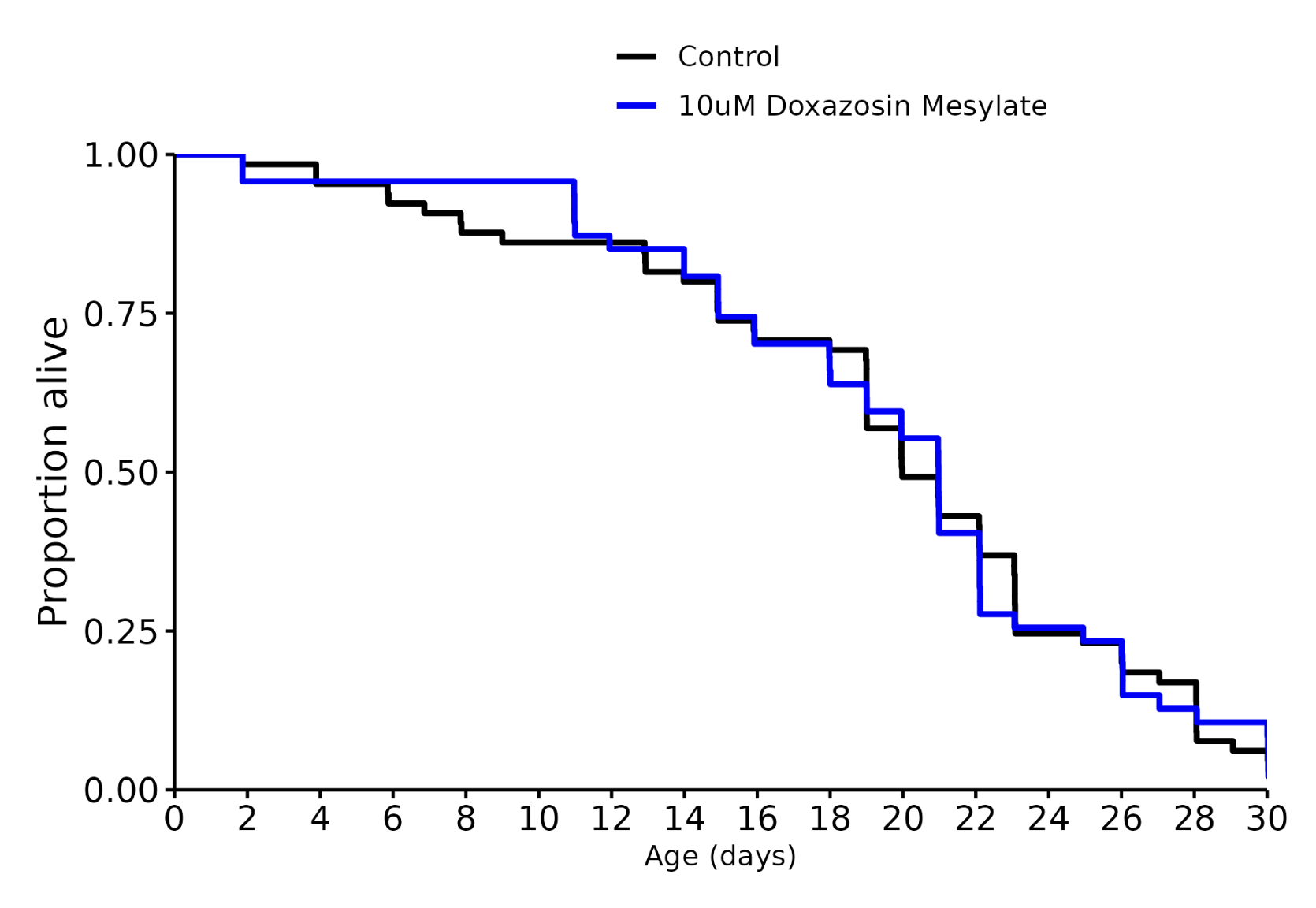
Doxazosin 10 uM: +5%
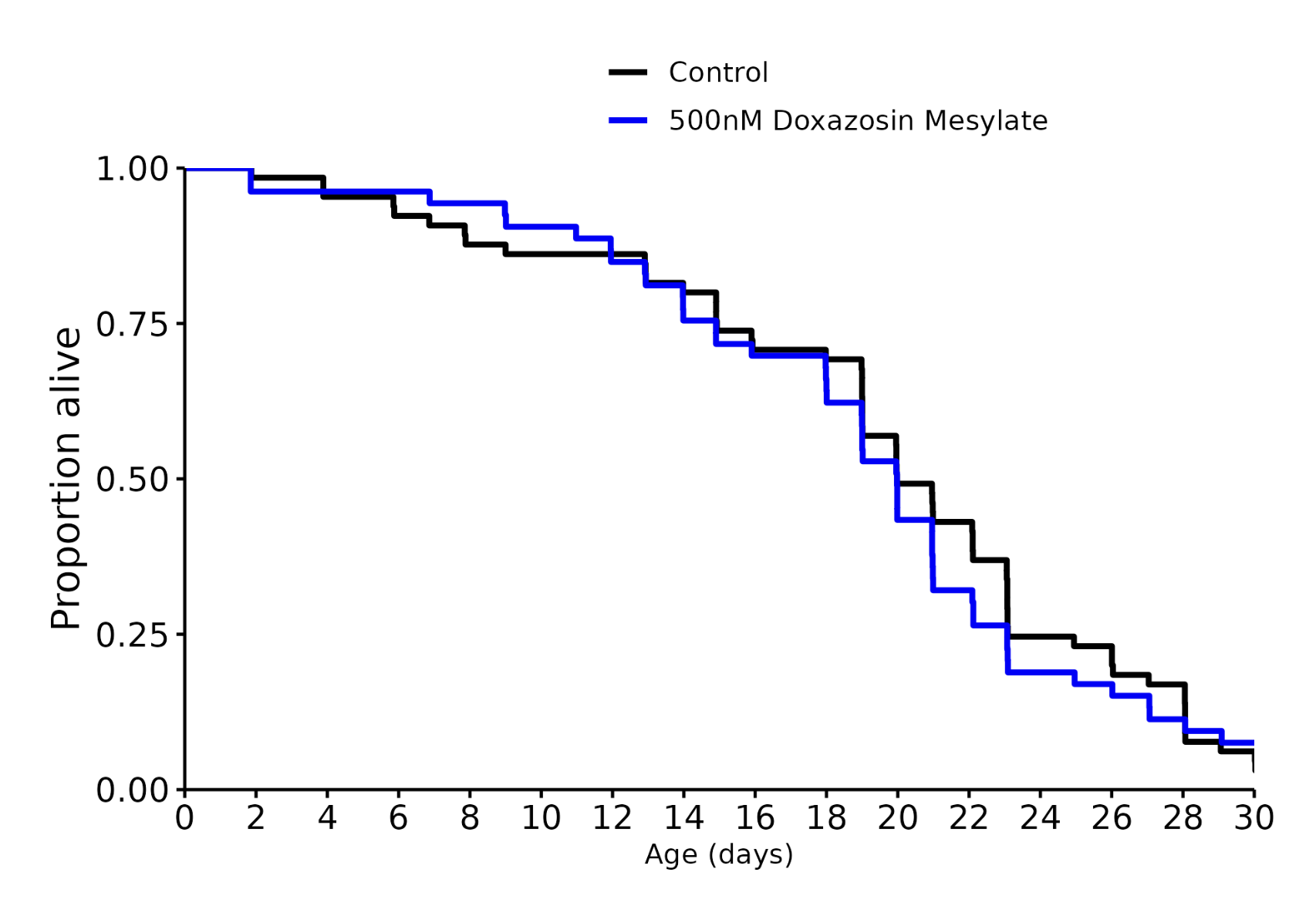
Doxazosin 500 nM: +0%
Gemfibrozil 10 uM: -5%
Gemfibrozil 50 uM: -5% (disappointing after a previous good result: Ora Biomedical Million Molecule Challenge Results - #229 by adssx )
Gemfibrozil 100 uM: +0%
Semaglutide 1 uM: +6%
Semaglutide 10 nM: +11%
Semaglutide 100 nm: +6%
TUDCA 2 mM: +6%
TUDCA 4 mM: +6%