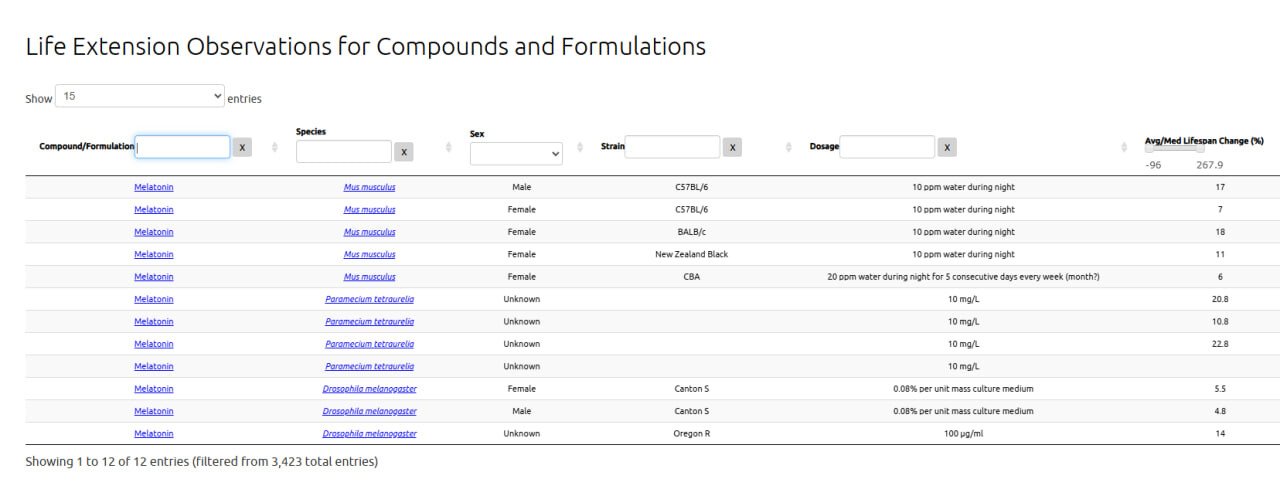
I took every melatonin study in this thread and fed it into ChatGPT and got it to spit out a summary of all of them:
 Core Biological Roles of Melatonin
Core Biological Roles of Melatonin
1. Circadian Regulation
- Melatonin is primarily secreted by the pineal gland and plays a key role in synchronizing circadian rhythms.
- It follows a light-dependent cycle, peaking at night and signaling darkness to the body, thereby promoting sleep and regulating hormonal cycles (including cortisol and reproductive hormones).
2. Mitochondrial Health & Energy Metabolism
- Melatonin is synthesized not only in the pineal gland but also in mitochondria.
- Studies show it enhances mitochondrial function by:
- Promoting ATP production.
- Reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress.
- Improving mitochondrial calcium homeostasis.
- It can stimulate muscle fiber conversion (from glycolytic to oxidative) in diabetic models—mimicking some effects of endurance exercise.
3. Antioxidant & Free Radical Scavenging
- Melatonin directly scavenges reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
- It also upregulates endogenous antioxidant enzymes (e.g., SOD, glutathione peroxidase).
- Unique among antioxidants, it crosses the blood-brain barrier and concentrates in mitochondria and nuclei.
 Neuroprotection & Brain Health
Neuroprotection & Brain Health
4. Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s Disease
- Melatonin reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and Aβ accumulation in animal models.
- Enhances glymphatic clearance of metabolic waste, possibly reducing risk of neurodegeneration.
- Supports mitochondrial integrity in neurons and may help counter age-related metabolic shifts in brain cells.
5. Cognitive Function & Memory
- Improves long-term memory formation in rodents via modulation of protein phosphorylation.
- Enhances glymphatic function post-intracerebral hemorrhage, resulting in improved cognitive recovery.
 Sleep and Chronobiology
Sleep and Chronobiology
6. Sleep Quality
- Meta-analyses show optimal efficacy for:
- 3–4 mg taken ~3 hours before bedtime.
- Helps reduce sleep onset latency and increase total sleep time.
- Especially effective in older adults and those with insomnia or circadian rhythm disorders.
7. Jet Lag, Shift Work, and Chronotherapy
- Well-suited for shifting circadian phase in cases of jet lag and shift work.
- Has been studied as a tool in chronotherapy to align medication administration with biological rhythms.
 Cardiovascular & Metabolic Health
Cardiovascular & Metabolic Health
8. Blood Pressure Regulation
- Reduces nocturnal blood pressure (more in “non-dippers”), possibly via improved endothelial function and oxidative stress reduction.
9. Glucose Metabolism and Diabesity
- In diabetic models:
- Enhances insulin sensitivity.
- Supports healthy skeletal muscle function.
- Promotes metabolic reprogramming of muscle and liver.
 Retinal and Ocular Health
Retinal and Ocular Health
10. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- Protects retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells by:
- Inhibiting necroptosis.
- Suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome via the SIRT1/Nrf2 pathway.
- Preserves retinal structure in AMD models.
 Immune Modulation
Immune Modulation
11. Dual Immunoregulation
- Acts as an immune buffer:
- Stimulates immunity in immunosuppressed states.
- Suppresses excessive inflammation during cytokine storms.
- Reduces IL-6 and TNF-α while promoting IL-10 and T-reg activity.
- Shown to modulate macrophage activity via NF-κB and AA-NAT upregulation.
12. Applications in Autoimmune and Infectious Disease
- May help in autoimmune diseases and as an adjunct in viral infections (e.g., COVID-19) by dampening hyperinflammation while preserving immune competence.
 Anti-Aging and Lifespan Extension
Anti-Aging and Lifespan Extension
13. Lifespan Studies
- Melatonin extended lifespan in several animal models (e.g., flies, mice, aquatic invertebrates), possibly due to its mitochondrial and antioxidant actions.
- Highlighted in DrugAge as a candidate longevity agent.
14. Aging Phenotypes
- Maintains mitochondrial and glymphatic function with age.
- Prevents pathological metabolic reprogramming in aged neurons.
 Cancer and Cell Growth
Cancer and Cell Growth
15. Anticancer Activity
- Shown to inhibit proliferation in some cancer cell lines.
- May sensitize tumors to chemotherapy while protecting normal cells from side effects (radioprotective and antioxidant roles).
 Safety, Risks, and Considerations
Safety, Risks, and Considerations
16. Generally Safe — But Not Always Benign
- Very high doses (up to 200 mg/day) used in research with minimal side effects reported.
- Most common mild side effects: vivid dreams, morning grogginess, headaches.
17. Rare Case Reports
- One case report linked melatonin to ventricular arrhythmias (PVCs), which resolved after stopping supplementation — indicates rare individual susceptibility.
18. Hormonal & Developmental Considerations
- Low melatonin levels in children with hypothalamic hamartomas were linked to precocious puberty, suggesting a role in reproductive timing.
Summary: The Case for Melatonin
Melatonin is a pleiotropic molecule:
- Antioxidant, immunomodulator, chronobiotic, and neuroprotective agent.
- It impacts systems far beyond sleep, including metabolism, immunity, cognition, mitochondrial health, and aging.
- Therapeutically, it is among the most underrated low-toxicity compounds with broad potential — though rare risks exist and personalization is warranted.