I got rid of my weighted blanket. I felt like I was being slowly crushed every night. Not trying that again.
I’m surprised people can get away with such high doses of melatonin without feeling groggy. Even just 5mg makes me tired well into the next day. It’s a relaxing feeling at least.
I find it quite useful as a “stress buffer”, so for example if I exercise a lot of am cutting calories, I can get away with higher doses without as much sedation.
The research is certainly promising.
Timing is key, not only against the circadian cycle, but also against ultradian cycles.
Way way higher than 180
Tg2576 mice receiving ~66.66 mg/kg daily starting at age 4 months showed a significant reduction in Aβ levels in brain tissues, as well as lowered abnormal nitration of proteins [362]. Importantly, Tg2576 mice receiving ~266.66 mg/kg daily starting at age 4 months produced the most impressive results where the brains of mice terminated at 15.5 months not only exhibited a dramatic decline in oligomeric Aβ40, but also a significant increase in soluble monomeric Aβ40. A noticeable decreasing trend in Aβ42 was observed in treated compared to untreated mice at the same age [361]. When Tg2576 mice from two separate experiments were administered ~266.66 mg/kg melatonin in drinking water daily starting at age 4 months until termination at 15.5 months, survival was significantly increased in treated compared to untreated mice [361,362]. Melatonin treatment at ~266.66 mg/kg daily in drinking water was able to reduce mortality in Tg2576 mice to levels observed in wild-type mice [361] (Table 2). Consequently, the effective translation of melatonin doses between animals and humans becomes the primary consideration when designing the dosage for clinical trials.
Table 3. Calculations of three HEDs converted from animal doses using different adjustments that account for differences in (A) Metabolic rates by scaling to the ¾-power; (B) Bioavailability; (C) Bioavailability that is enhanced by solubility and/or formulation.
| Study Design/Total Daily Dose/Duration/Ref. | Results | (A) HED Daily Total (mg/kg) Scaled to Mb3/4 | (B) Dose (A) Adjusted by Bioavailability | (C) Dose (A) Adjusted by Enhanced Bioavailability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg/mL in drinking water, Tg2576 AD mice/266.66 mg/kg/11.5 mos starting at 4 mos old/[361,362] | Striking reductions in Aβ aggregates at all ages during treatment; dramatic extension of survival of AD mice to levels similar to wild types. | 2499 mg (35.7 mg/kg) | 4831 mg (69 mg/kg) | 10,621 mg (151.73 mg/kg) |
| 0.5 mg/mL in drinking water, Tg2576 AD mice/66.66 mg/kg/11.5 mos starting at 4 mos old/[362] | Striking reductions in Aβ levels in brain tissues of treated mice at 8, 9.5, 11, and 15.5 months. | 625 mg (8.928 mg/kg) | 1208 mg (17.26 mg/kg) | 2656 mg (37.94 mg/kg) |
| 0.016 mg/mL in drinking water, Tg2576 AD mice/2.13 mg/kg/10 wks starting at age 14 mos old/[363] | Failed to reduce brain Aβ levels, unable to reverse oxidative damage. | 19.96 mg (0.285 mg/kg) | 38.58 mg (0.55 mg/kg) | 84.83 mg (1.21 mg/kg) |
| 10 mg/kg in drinking water, healthy, normal C57BL/6J mice/14 days after tauopathy initiation/[366] | Reduced memory impairment, tau hyperphosphorylation, ROS, and neuroinflammation. | 96.23 mg (1.375 mg/kg) | 186.0 mg (2.66 mg/kg) | 408.98 mg (5.84 mg/kg) |
| 40 ppm in food pellets, healthy, normal B6C3F1 mice/7.2 mg/kg/11 weeks different age groups/[364] | Significant reduction in Aβ peptides in brain cortex tissues: 57% in Aβ40 and 73% in Aβ42; increased melatonin levels in cerebral cortex in all 3 treated age groups (12 > 6 > 27 mos) compared to untreated. | 69.29 mg (0.99 mg/kg) | 133.94 mg (1.91 mg/kg) | Not applicable |
| 10 mg/kg IP injection, C57BL/6J mice treated with Aβ1-42 peptide/daily IP injections for 3 wks/[365] | Reversed Aβ1-42-induced synaptic disorder, memory deficit; prevented Aβ1-42-induced apoptosis, neurodegeneration, and tau phosphorylation. | 98.55 mg (1.41 mg/kg) | 486.15 mg (6.95 mg/kg) | Not applicable |
Based on the info in this thread, I have increased my Melatonin dose to 20 mg extended release. I feel so much more rested in the AM. I was a skeptic.
I was surprised also. John Hemming’s report of his personal usage inspired me to take a closer look at the literature. Because melatonin has many anti-cancer properties I was interested in increasing my dose. I just assumed that taking high doses would induce daytime sleepiness. That is not the case. I have experienced zero daytime sleepiness from taking doses of 60 to 100 mg at night. The number of adverse events associated with taking high-dose melatonin is very small.
“Beyond its sleep and chronobiotic properties, melatonin is a potent antioxidant9 and has the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier,10 with suggested anti-amyloid properties. Due to this, melatonin has been increasingly investigated in many varying conditions, including cancer, cardiometabolic conditions and neurodegenerative diseases at higher doses, where there is less documentation of its safety. Doses ranging from 30 to 100 mg are being suggested or tested for effectiveness in a range of conditions and ages, including ocular ischaemic syndrome”
“In supporting the anti-cancer effect of melatonin, its efficacy in reducing the incidence of cancer has been proven through animal studies and clinical trials”
“Safety of higher doses of melatonin in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis”
I’m back up to 40mg time released melatonin and on days off if I wake up too early or in the middle of the night I’ll take an additional 80mg bulk powder. I’m currently doing shift work from 06:30-19:00 so sleep can be a bit challenging. When I was taking high doses before I thought it was causing hair shedding but apparently it was a coincidence because I don’t have that problem this time around.
I was wondering if anyone has read that melatonin can help menopause by lowering FSH/LH? I had run across that info years ago but haven’t been able to confirm if it’s true. My menopausal symptoms seem greatly improved with a high enough dose of melatonin -although it could be placebo.
I dont know about any specific reasearch about menopause. However, the body generates melatonin in the mitochondria to handle oxidative stress. Exogenous melatonin will top up the mitochondrial melatonin.
Very cheap for 50grams
This makes taking 1g per day possible… That said kids overdose on it so maybe try 200 to 400 mg at first. I’ve definitely done 300mg at once before
More broadly this may be THE way to ameliorate Adderall neurotoxicity (socially important in a world of shrinking AGI timelines)
It’s also worth using it while taking an ION panel to see effects on 8 oxo g
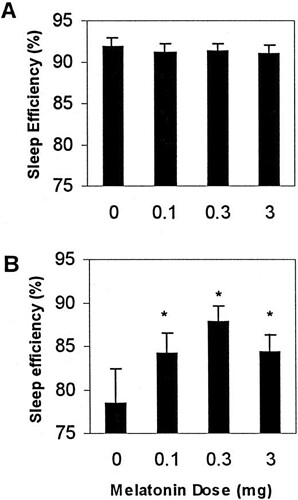
The physiologic melatonin dose (0.3 mg) restored sleep efficiency (P < 0.0001), acting principally in the midthird of the night; it also elevated plasma melatonin levels (P < 0.0008) to normal. The pharmacologic dose (3.0 mg), like the lowest dose (0.1 mg), also improved sleep; however, it induced hypothermia and caused plasma melatonin to remain elevated into the daylight hours.
3 mg do not return to same levels as placebo.
I don’t think high dose melatonin will improve sleep, except placebo of course, it will probably harm sleep. With constant circulating melatonin how is it going to function to signal night-time & day-time?
Inhibition of insulin release:
Some mechanistic data suggests melatonin may inhibit insulin production, which would increase blood glucose, looking for studies rn…
First, several genome-wide associations studies (GWAS) have reported, that the frequent rs10830963 single-nucleotide polymorphism, located in the melatonin receptor 2 gene (MTNR1B), which may be a gain-of-function variant, is strongly associated with elevated fasting glucose and risk of type 2 diabetes.4-8 Second, acute daytime administration of melatonin results in 10%–25% decreased insulin sensitivity.9-11 On the other hand, carriers of rare loss-of-function variants in the MTNR1B and individuals with low nightly melatonin secretion have increased risk of type 2 diabetes.12, 13 As the use of melatonin is increasing as a sleep aid in both adults14 and children,15 it is advantageous to clarify the metabolic effects of long-term melatonin treatment on glucose metabolism. A number of placebo-controlled randomized studies have addressed this question, but the outcomes have been limited to glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, fasting plasma glucose and insulin levels, mostly with beneficial effects.16 We recently performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of the metabolic consequences of melatonin treatment in healthy individuals and patients with metabolic diseases and found no effects of treatment on fasting plasma glucose, but reduced fasting insulin levels and a tendency towards increased insulin sensitivity measured by homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR).16 However, none of the previous long-term placebo-controlled randomized studies stratified on rs10830963 genotype and none of the studies evaluated the metabolic effects of melatonin treatment beyond fasting glucose and insulin levels. Thus, a comprehensive assessment of the metabolic effects of melatonin treatment with direct measurements of insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes stratified on rs10830963 genotype is warranted.
In our study, the treatment of male patients with type 2 diabetes with 10 mg of melatonin for 3 months before bedtime reduces insulin sensitivity
Very small sample size: "Our current study is limited by the relatively small sample size that restricts conclusions drawn from the genotype-specific analyses, "
All of the subjects already had type II diabetes. All of the subjects were overweight.
Participants had a BMI (kg/m2) of 29 ± 3.5, putting them in the overweight to obese range.
If your BMI is 25.0 to 29.9, it falls within the overweight range. If your BMI is 30.0 or higher, it falls within the obese range.
The subjects were already type II diabetics.
Millions of people have been taking what is high-dose melatonin in the U.S, because that is what is on offer at places like Walmart. If there was a significant danger of developing lower insulin sensitivity or development of type II diabetes, it surely would have been noticed by now.
I have been taking high-dose melatonin for over 40 years and I am not even pre-diabetic.
I don’t know how long John Hemming has been taking high-dose melatonin but he is not diabetic either.
I don’t know why they don’t read the literature before doing these poorly thought-out studies.
Read this paper it is a much more thorough review of the safety of melatonin.
“Safety of higher doses of melatonin in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis”
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jpi.12782
I think taking melatonin that has an effect before initial sleep is a bad idea. Time release may be ok.
John, does melatonin ever make you drowsy in a consequential way? Excluding events where you use it to ameliorate alcohol consumption.
I tried taking 5mg in the middle of the night. Was notably sleepy the next day. N=1 of course. I’m having a hard time imagining taking hundreds of mg and not having an adverse effect on the following day.
I don’t think they reported blood glucose / insulin levels as adverse events, if they even measured it.
Any adverse event from slightly higher blood glucose levels will take a long time to occur if it happens.
I think high dose melatonin doesn’t work for me.
Also adverse events might not be reported:
Importantly, we found that ≥10 mg doses of melatonin increase the likelihood of AEs and that there was marked variability in the quality of safety data collection and reporting in the trials conducted to date. This may indeed reflect the general opinion of the overall safety of melatonin leading to less stringent collection and/or reporting of AEs.
Same, personally I get drowsy the next day, the few times I tested a higher dose, 0.3 mg I can barely feel except I think my sleep is just better. It probably differs between people. I use electronic devices (I block blue light though) near bedtime so I naturally don’t have much melatonin. It was a longer time ago I tried higher dose melatonin, so maybe it works differently now. I have an Oura ring so I could try a self-blinded experiment.
Same here when I tried Melatonin during the night. On a side note what helps me getting back to sleep is 1g Taurine
It is very rare that i am drowsy from melatonin and not in a consequential way, but i start with bad insomnia. We cannot assume everyone has precisely the same metabolism. I took some time getting my dosing level up.
Hey Alex! Any information on Melatonin and Adderall Neurotoxicity? Im on Vyvanse for ADHD and I’d like to counteract the dangers of long term use of that medication as well.