Her Company:
AI Summary:
Introduction to Neuroage Therapeutics
- Dr. Kristen Glorioso, a physician and neuroscientist, is the co-founder and CEO of Neuroage Therapeutics, an early-stage biotech company focused on reprogramming brain aging to treat dementia.
- The foundation of Neuroage is built upon two decades of Dr. Glorioso’s research at MIT and Carnegie Mellon, emphasizing the potential to address neurodegenerative diseases through therapeutic and lifestyle interventions.
- Neuroage offers a consumer-facing product called the Neuroage test, which assesses brain age and predicts future risks of neurodegenerative diseases over 30 years in advance.
- The test utilizes a multiomic and multimodal approach, generating a unique longitudinal dataset essential for drug discovery related to Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment.
- Neuroage positions itself similarly to Tesla, utilizing consumer products to gather data that can inform future innovations in Alzheimer’s research.
Personal Motivation for Founding Neuroage
- Dr. Glorioso’s personal connection to Alzheimer’s disease stems from her grandmother’s seven-year battle with the condition, which significantly influenced her career path.
- The impact of her grandmother’s illness was compounded by the fact that her aunt is currently facing late-stage Alzheimer’s, further intensifying Dr. Glorioso’s commitment to finding solutions.
- Dr. Glorioso has a genetic risk factor, the ApoE4 allele, which is associated with a higher likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s, making the issue of dementia particularly personal and urgent for her.
- Globally, over 60 million people suffer from age-related neurodegenerative conditions, with aging being the most significant risk factor for dementia, particularly after age 70.
Understanding Dementia and Its Types
- Dementia is an umbrella term encompassing various types, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and frontotemporal dementia, all sharing common symptoms like memory loss and disorientation.
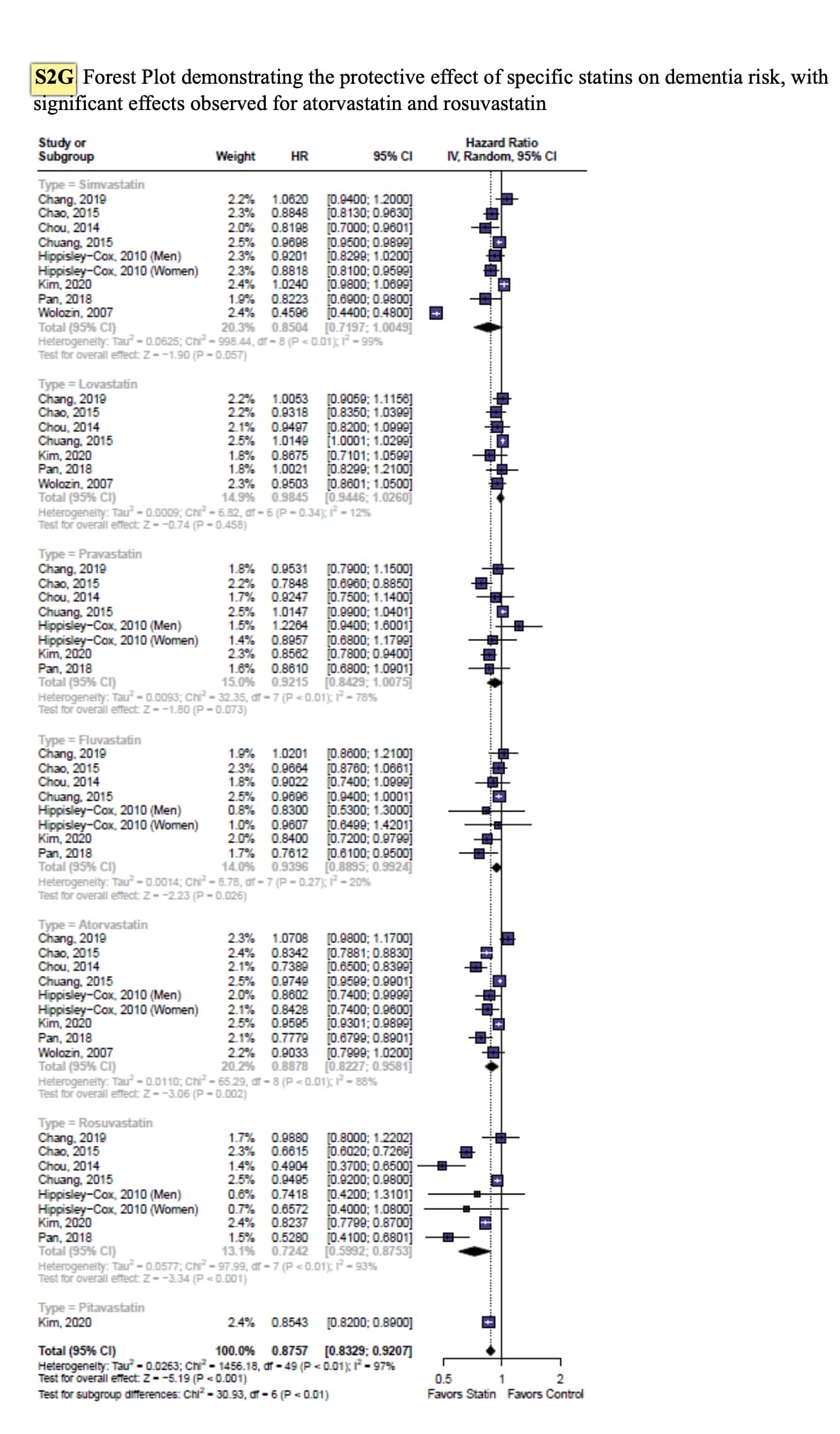
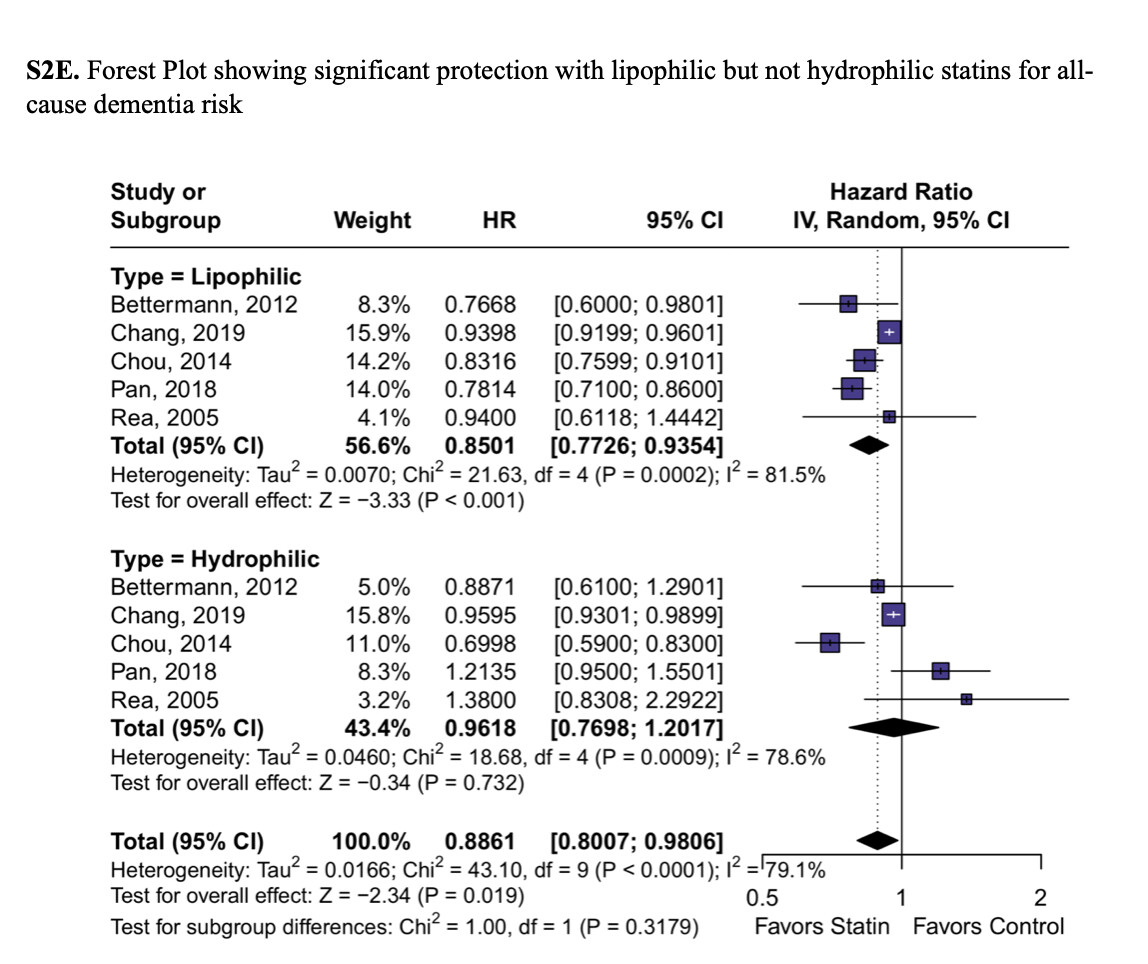
- Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent form of dementia, followed by vascular dementia and mixed dementia, each associated with the death of neurons in specific brain regions.
- The loss of neurons can be visualized via MRI or postmortem examinations, revealing distinct patterns of brain shrinkage based on the type of dementia.
- Different types of dementia arise from various causes, such as cardiovascular issues leading to vascular dementia or alcohol-related conditions resulting in Wernicke’s encephalopathy due to vitamin B1 deficiency.
Diagnosis and Importance of Timely Intervention
- Diagnosing dementia involves ruling out vitamin deficiencies and thyroid issues, conducting brain MRIs, and performing physical exams to assess movement disorders like tremors.
- The commonly used mental status exam consists of 30 questions designed to evaluate orientation, memory, and cognitive function, with a typical score of 30 indicating normal cognitive health.
- Timely diagnosis is crucial, as some dementia causes can be reversible, such as thyroid conditions or vitamin deficiencies that can be treated effectively.
- Understanding the underlying causes of dementia is essential for treatment, as certain conditions can be managed similarly to cardiovascular diseases, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention.
The Amyloid Hypothesis and Its Controversies
- The amyloid hypothesis posits that amyloid plaques in the brain are a primary cause of Alzheimer’s disease, a theory that originated from early examinations of Alzheimer’s patients’ brains.
- Recent research has raised questions about the amyloid hypothesis, particularly since many cognitively normal individuals exhibit amyloid accumulation without showing symptoms of Alzheimer’s.
- New tools, such as PET scans and blood tests, have been developed to measure amyloid levels in living patients, enabling better tracking of disease progression and risk assessment.
- Despite advancements, the amyloid hypothesis remains contentious, with some studies revealing falsified data and challenges related to mouse models that do not accurately reflect human Alzheimer’s pathology.
Recent Developments in Alzheimer’s Drug Therapies
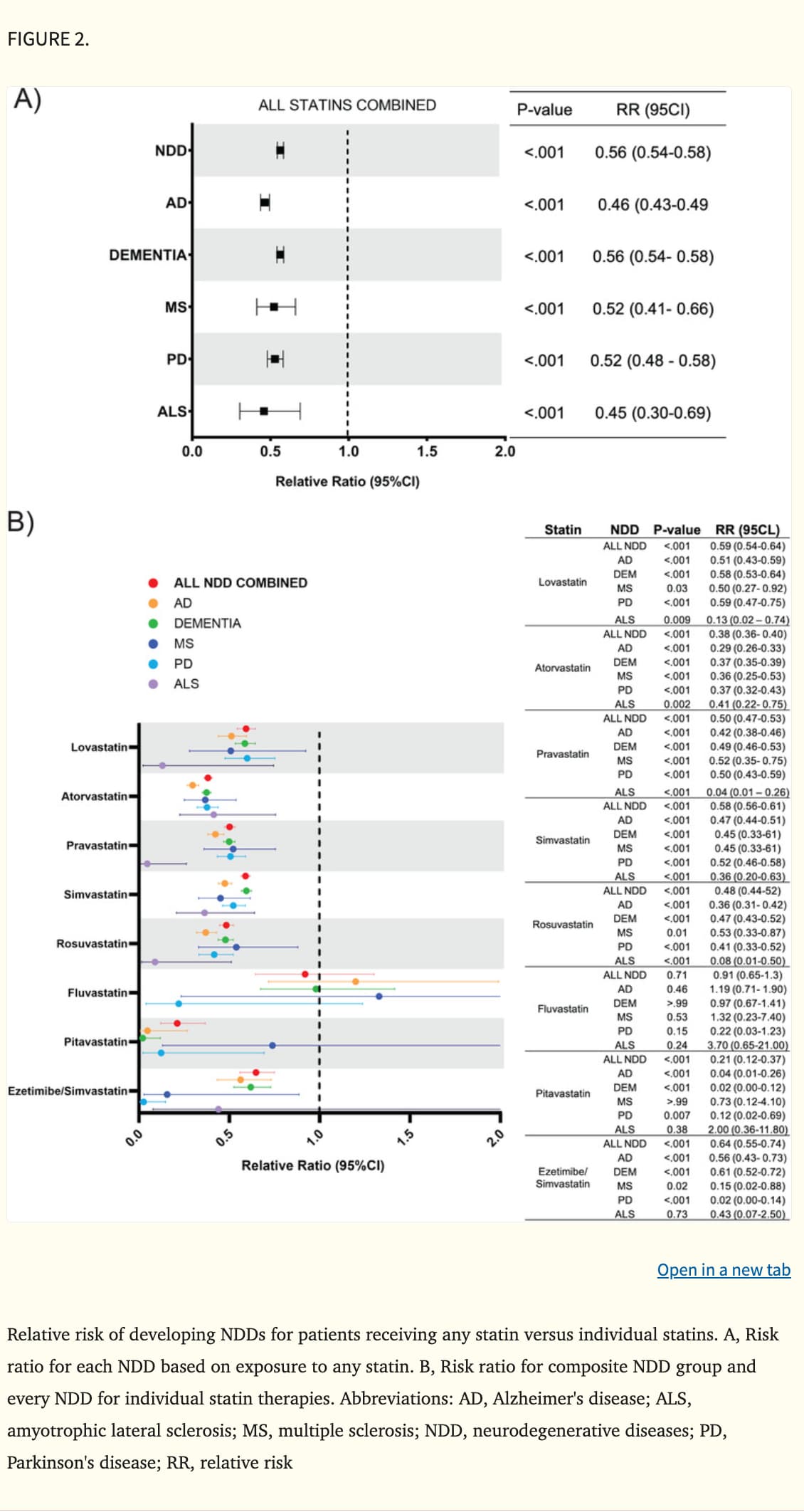
- Two recent drugs targeting amyloid, Donanemab by Eli Lilly and Lecanemab by Biogen, have been approved, showing a 30% reduction in disease progression but with significant side effects.
- Approximately 50% of patients treated with Donanemab exhibited no progression of Alzheimer’s or mild cognitive impairment after one year, indicating potential efficacy despite the risks involved.
- The approval and use of these drugs highlight the importance of understanding amyloid as a risk factor rather than a sole cause of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Future research aims to better segment patients for treatment, as earlier intervention is crucial for the effectiveness of these therapies, which may eventually evolve into preventative measures against dementia.
Neuroage’s Innovative Approach to Brain Aging
- Neuroage is exploring a novel theory of Alzheimer’s that focuses on brain aging itself, identifying specific pathological processes that occur even in young adults.
- Key factors in brain aging include calcium dysregulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA damage, and changes in neurotransmitter signaling, all of which contribute to the hallmarks of cognitive decline.
- The company has identified “boss proteins” that regulate gene expression changes leading to brain aging, which may be targetable by drugs for therapeutic interventions.
- Through machine learning algorithms, Neuroage can predict brain age based on various biological markers, allowing for the identification of individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
The Neuroage Test and Lifestyle Interventions
- The Neuroage test combines genetic data, brain MRI results, and cognitive assessments to produce a comprehensive brain aging score, which can inform lifestyle modifications to reduce dementia risk.
- Research indicates that approximately 40% of brain aging is influenced by lifestyle choices, including exercise, diet, sleep, stress management, and mental activity.
- The test provides personalized recommendations based on individual health data, encouraging users to adopt healthier habits to improve their cognitive health.
- Recent studies have shown that even small increases in physical activity can lead to measurable improvements in brain health, highlighting the importance of lifestyle interventions in dementia prevention.
Future Directions and Clinical Applications
- Neuroage aims to develop therapeutics targeting the biological mechanisms of brain aging, with a focus on small molecules and antibodies that could potentially reverse cognitive decline.
- The company is building a robust dataset from the Neuroage test, which will serve as a foundation for future drug development and clinical research.
- Neuroage’s approach emphasizes the use of multiomic data to identify genes and pathways responsible for variations in brain aging rates among individuals.
- The ultimate goal is to create a preventative framework for dementia, similar to how cholesterol levels are monitored for heart disease risk.
Conclusion and Call to Action
- Dr. Glorioso invites individuals to participate in the Neuroage test, emphasizing the importance of early detection and lifestyle management in the fight against dementia.
- The company is launching its consumer-facing product and aims to make brain health monitoring as routine as other health checks.
- Through ongoing research and collaboration, Neuroage seeks to transform the landscape of Alzheimer’s treatment and prevention, ultimately improving the quality of life for millions affected by neurodegenerative diseases.